(Press-News.org) Can physical activity extend the lifespans of older adults? A review article published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231336 summarizes the considerable evidence supporting the important role physical activity plays in preventing or reducing the effects of diseases and discusses how to prescribe effective exercise for older adults.
Canada’s population is aging, with at least 1 in 5 people aged 65 years or older in 2025, and the number of people older than age 85 years is expected to triple in the next 20 years. However, for many people, these added years do not mean healthy years. More than 80% of adults do not meet the recommendations for physical activity from the Canadian Physical Activity Guidelines.
“Physical activity is one of the most important ways to preserve or improve functional independence, including among older adults who are frail or deemed to be at increased risk of falling,” writes Dr. Jane Thornton, associate professor at Schulich School of Medicine & Dentistry, Western University, London, Ontario, and director of health, medicine and science at the International Olympic Committee. “Higher levels of physical activity in older age are associated with improvements in cognition, mental health, and quality of life.”
A 2023 meta-analysis of several large studies found that 150 minutes of moderate physical activity every week reduced risk of death from all causes by 31%. Physical activity is essential for aging well and can help prevent or reduce disease in more than 30 chronic conditions, such as coronary artery disease, heart failure, type 2 diabetes mellitus, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, osteoporosis, depression, dementia, and cancer.
Benefits of activity include the following:
Protection against risk of death from any cause
Falls prevention through increased muscle strength and better balance
Bone and joint health, including improved bone density and alleviation of some osteoarthritis symptoms
Improved cognitive function, and better mood and mental health
Ability to engage in daily activities and improved quality of life
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends 150–300 minutes weekly of moderate-to-intense physical activity for adults, including older adults.
How can clinicians prescribe physical activity?
“As many older adults live with chronic health conditions or reduced mobility, clinicians should tailor and encourage them to take a gradual approach to increasing their physical activity, which should include resistance training (muscle strengthening) as an essential component,” said Dr. Samir Sinha, professor of medicine at the University of Toronto and director of health policy research, National Institute on Ageing.
The WHO 5-step framework — called the “5As” — can provide clinicians with a roadmap to promote activity in their patients. The authors also suggest inputting physical activity in patient records as a vital sign to follow over time.
“Physical activity is underused as a health intervention both in the community and in the delivery of health care for older adults. Age, frailty, or existing functional impairments should not be viewed as absolute contraindications to physical activity but rather key reasons to prescribe it, considering the benefits of physical activity interventions for older adults. Older adults who become more physically active can potentially add years to their lives as well as higher quality of life to those years,” the authors conclude.
END
Move more, age well: Prescribing physical activity for older adults as a recipe for healthy aging
2025-01-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Botanic Gardens must team up to save wild plants from extinction
2025-01-27
A major study of botanic gardens around the world has revealed their struggles with one fundamental aim: to safeguard the world’s most threatened plants from extinction.
Researchers analysed a century’s worth of records - from 1921 to 2021 - from fifty botanic gardens and arboreta currently growing half a million plants, to see how the world’s living plant collections have changed over time.
The results suggest that the world’s living collections have collectively reached peak capacity, and that restrictions ...
Approaching the red planet from the kitchen
2025-01-27
Niigata, Japan - Rootless cones are small volcanic landforms ranging from several to several hundred meters in diameter, formed by continuous explosions resulting from the interaction between surface lava and water bodies like lakes and rivers (Figure 1). Unlike regular volcanoes originating from magma rising from deep underground, rootless cones form when lava covers a water-containing layer, triggering explosive reactions. Due to this process, they are also called pseudocraters. While Iceland hosts many rootless cones, they ...
How Camellias evolved with the formation of the Japanese archipelago?
2025-01-27
Niigata, Japan – The distribution of plants has been shaped by geological and climatic changes over time through repeated migration, extinction, and adaptation to new environments. The genus Camellia, comprising over 100 species mainly in East Asia, is a representative warm-temperate tree of the Sino-Japanese Floristic Region.
In Japan, four species of Camellia are found, with Camellia japonica and Camellia rusticana being the most well known. C. japonica has a broad distribution from Aomori Prefecture in the cool-temperate ...
Study succeeds in the early diagnosis of leptomeningeal disease in diffuse midline gliomas by liquid biopsy
2025-01-27
Niigata, Japan – A group led by the Department of Neurosurgery, Brain Research Institute, Niigata University succeeded in the diagnosis of leptomeningeal disease in diffuse midline gliomas by detecting H3K27M-mutant droplets from circulating tumor DNA of cerebrospinal fluid taken from these patients. In two patients, leptomeningeal disease was diagnosed earlier than with traditional methods such as MRI and cerebrospinal fluid cytology. In one patient, long term survival after the diagnosis of leptomeningeal disease by early ...
Understanding the science of meaty flavors could be key to sustainable diets, says academic
2025-01-27
Understanding the science behind meaty tastes and textures could be the key for more people switch to a planet-friendly plant diet, researchers suggest.
Ole G. Mouritsen, a professor of gastrophysics, addresses the urgent need to make changes to culinary cultures where animal-based proteins play a central role.
Replicating a little-known meaty flavour and a sensation of richness could encourage more plant-based eating, he explains.
“To ensure that there is enough food for a growing world population, to lessen the burden on the environment, and to promote healthier, sustainable eating patterns, it ...
Patients who received Ross procedure demonstrate excellent survival rates after 20 years
2025-01-26
LOS ANGELES —January 26, 2024 — Young patients who have undergone the Ross procedure for aortic valve disease have shown excellent long-term survival, the majority without the need for additional surgery two decades later.
These findings, presented today at the 61st annual meeting of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS), were the result of a 22-year study at the Narayana Institute of Cardiac Sciences in Bengaluru, India.
“The Ross operation can be performed safely with results comparable to mechanical valve replacement,” said the study’s lead author, cardiac surgeon ...
Lung volume reduction surgery for emphysema may have better outcomes than previously reported
2025-01-26
LOS ANGELES—January 26, 2025—As contemporary surgical practice continues to evolve, patients who undergo surgical lung volume reduction (LVRS) for advanced emphysema may survive longer and with fewer complications than they did in the past—and they may even fare better than those who opt for endobronchial valve (EBV) placement.
At the 2025 Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) Annual Meeting, researchers presented risk-adjusted findings that shed new light on treatments for severe emphysema. Despite having shorter hospital stays, lower hospital ...
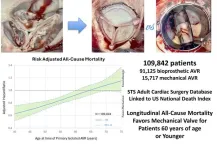
New study finds mechanical valves offer superior long-term survival for aortic valve replacement patients aged 60 and younger
2025-01-25
LOS ANGELES—January 25, 2025—A late-breaking study presented today at the 2025 Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) Annual Meeting reveals that mechanical aortic valve replacements (AVRs) provide significant long-term survival benefits for patients aged 60 and younger compared to bioprosthetic valves. The study, leveraging data from the STS Adult Cardiac Surgery Database (ACSD), offers the most comprehensive analysis to date of prosthetic valve outcomes, encompassing over 100,000 patients.
The study addressed a critical question ...
Anatomic lung resection linked to improved survival for early-stage lung cancer
2025-01-25
LOS ANGELES—January 25, 2025 New research presented at the 2025 Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) Annual Meeting reveals that anatomic lung resections, such as lobectomy and segmentectomy, are associated with improved long-term survival compared to wedge resection for patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
The study analyzed outcomes for more than 32,000 stage 1A NSCLC patients using data from the STS General Thoracic Surgery Database (STS GTSD) with long-term follow-up linked to the National Death Index and Centers ...
Combination of dual-targeted therapies and chemotherapy shows high response rates in BRAF-mutated metastatic colorectal cancer
2025-01-25
SAN FRANCISCO – Patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) harboring BRAF V600E mutations benefitted from first-line treatment with the targeted therapies encorafenib and cetuximab plus a mFOLFOX6 chemotherapy regimen, according to results from the Phase III BREAKWATER trial led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The findings, presented today at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Gastrointestinal Cancers (ASCO GI) Annual Symposium and published in Nature Medicine, demonstrated a 60.9% overall response rate (ORR) with the three-drug combination ...