Study succeeds in the early diagnosis of leptomeningeal disease in diffuse midline gliomas by liquid biopsy
Detection of circulating tumor DNA in the cerebrospinal fluid of H3K27M-mutant diffuse midline glioma patients-
2025-01-27
(Press-News.org)
Niigata, Japan – A group led by the Department of Neurosurgery, Brain Research Institute, Niigata University succeeded in the diagnosis of leptomeningeal disease in diffuse midline gliomas by detecting H3K27M-mutant droplets from circulating tumor DNA of cerebrospinal fluid taken from these patients. In two patients, leptomeningeal disease was diagnosed earlier than with traditional methods such as MRI and cerebrospinal fluid cytology. In one patient, long term survival after the diagnosis of leptomeningeal disease by early and aggressive intervention including surgery, radiation, and intrathecal delivery of chemotherapeutic agents led to long term survival.
A team led by Dr. Manabu Natsumeda used droplet digital PCR, a highly sensitive PCR system, to detect trace amounts of circulating tumor DNA from the cerebrospinal fluid of these patients. “We found that detecting circulating tumor DNA in the cerebrospinal fluid of diffuse midline glioma patients was more difficult than other brain tumor patients such primary central nervous system lymphoma and glioblastoma. However, when we were able to detect mutant tumor DNA, often the tumor had already spread to the cerebrospinal fluid, causing leptomeningeal disease. We think that early diagnosis and treatment of leptomeningeal disease in diffuse midline gliomas can improve survival.” explains Dr. Natsumeda. The results of the study were published online in journal Pediatric Blood and Cancer on January 9, 2025.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-01-27
Understanding the science behind meaty tastes and textures could be the key for more people switch to a planet-friendly plant diet, researchers suggest.
Ole G. Mouritsen, a professor of gastrophysics, addresses the urgent need to make changes to culinary cultures where animal-based proteins play a central role.
Replicating a little-known meaty flavour and a sensation of richness could encourage more plant-based eating, he explains.
“To ensure that there is enough food for a growing world population, to lessen the burden on the environment, and to promote healthier, sustainable eating patterns, it ...
2025-01-26
LOS ANGELES —January 26, 2024 — Young patients who have undergone the Ross procedure for aortic valve disease have shown excellent long-term survival, the majority without the need for additional surgery two decades later.
These findings, presented today at the 61st annual meeting of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS), were the result of a 22-year study at the Narayana Institute of Cardiac Sciences in Bengaluru, India.
“The Ross operation can be performed safely with results comparable to mechanical valve replacement,” said the study’s lead author, cardiac surgeon ...
2025-01-26
LOS ANGELES—January 26, 2025—As contemporary surgical practice continues to evolve, patients who undergo surgical lung volume reduction (LVRS) for advanced emphysema may survive longer and with fewer complications than they did in the past—and they may even fare better than those who opt for endobronchial valve (EBV) placement.
At the 2025 Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) Annual Meeting, researchers presented risk-adjusted findings that shed new light on treatments for severe emphysema. Despite having shorter hospital stays, lower hospital ...
2025-01-25
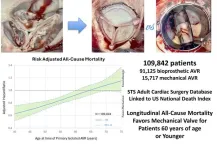
LOS ANGELES—January 25, 2025—A late-breaking study presented today at the 2025 Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) Annual Meeting reveals that mechanical aortic valve replacements (AVRs) provide significant long-term survival benefits for patients aged 60 and younger compared to bioprosthetic valves. The study, leveraging data from the STS Adult Cardiac Surgery Database (ACSD), offers the most comprehensive analysis to date of prosthetic valve outcomes, encompassing over 100,000 patients.
The study addressed a critical question ...
2025-01-25
LOS ANGELES—January 25, 2025 New research presented at the 2025 Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) Annual Meeting reveals that anatomic lung resections, such as lobectomy and segmentectomy, are associated with improved long-term survival compared to wedge resection for patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
The study analyzed outcomes for more than 32,000 stage 1A NSCLC patients using data from the STS General Thoracic Surgery Database (STS GTSD) with long-term follow-up linked to the National Death Index and Centers ...
2025-01-25
SAN FRANCISCO – Patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC) harboring BRAF V600E mutations benefitted from first-line treatment with the targeted therapies encorafenib and cetuximab plus a mFOLFOX6 chemotherapy regimen, according to results from the Phase III BREAKWATER trial led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The findings, presented today at the American Society of Clinical Oncology Gastrointestinal Cancers (ASCO GI) Annual Symposium and published in Nature Medicine, demonstrated a 60.9% overall response rate (ORR) with the three-drug combination ...
2025-01-25
Boston – A data analysis from a randomized clinical trial for stage 3 colon cancer patients by investigators at Dana-Farber Brigham Cancer Center found that patients with evidence of residual cancer in their blood after surgery to remove the cancer, may benefit from adding of celecoxib, to post surgery treatment. The analysis showed that patients with positive blood tests for circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) had worse outcomes in general, but those who were treated with celecoxib, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, experienced significantly improved disease-free survival.
“This is one of the first studies to show that ctDNA status has predictive utility in terms of selecting ...
2025-01-25
The Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology today announced the results of a data analysis from a randomized phase III clinical trial involving patients with stage III colon cancer, which found that adding the drug celecoxib to treatment after surgery might help those who still have traces of cancer in their blood. The analysis showed that patients with signs of cancer in their blood measured by Signatera™, a circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) test, tended to have worse outcomes. However, those who took celecoxib after surgery had a much better chance of staying cancer-free. These results are being presented in a late-breaking ...
2025-01-25
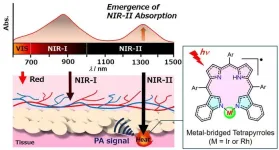
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a new dye that can strongly absorb second near-IR radiation and transform it to heat. Starting with a dye from the bile pigment family, they designed a unique ring structure which can bind rhodium and iridium. Measurements and modeling revealed strong second near-IR absorptions and exceptional photostability. Second near-IR waves easily penetrate human tissue; the new dye may be applied in deep tissue therapies and imaging.
The second near-IR region of the electromagnetic spectrum (1000-1700 nanometers) ...
2025-01-25
Researchers at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus have found a promising drug candidate that could help restore vision in individuals with multiple sclerosis (MS) and other neurological conditions that damage neurons.
The study was published this week in the journal Nature Communications.
The drug, LL-341070, enhances the brain's ability to repair damaged myelin— the protective sheath around nerve fibers. Damage to myelin is a hallmark of diseases like MS, as well as a natural consequence of aging, often resulting in vision loss, loss of motor skills, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study succeeds in the early diagnosis of leptomeningeal disease in diffuse midline gliomas by liquid biopsy
Detection of circulating tumor DNA in the cerebrospinal fluid of H3K27M-mutant diffuse midline glioma patients-