(Press-News.org)
New York, NY [January 27, 2025]—The Mount Sinai Hospital has performed New York City’s first procedure using the HYDROS™ Robotic System, a cutting-edge technology designed to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), or an enlarged prostate. The minimally invasive procedure offers new hope for patients experiencing the symptoms of BPH, including frequent urination, incomplete bladder emptying, and nighttime urgency.
Urologists at the hospital recently performed the health system’s first three procedures, with all patients responding well to the treatment and being discharged the following day.
“This technology provides a much-needed option for men dealing with the burdens of BPH,” says Steven A. Kaplan, MD, Director of the Men's Wellness Program, Mount Sinai Health System, and Professor of Urology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. “What makes HYDROS™ stand out is how it combines advanced imaging, robotic precision, and a heat-free approach to tissue removal, all while preserving crucial functions like continence and sexual health.”
BPH affects more than 50 percent of men over 60 and 80 to 90 percent of men over 70 years of age, making it one of the most prevalent conditions impacting older adults. While noncancerous, the condition can significantly impact quality of life, leading to discomfort, frustration, and lifestyle adjustments for millions of men.
The HYDROS™ system builds on traditional surgical methods for treating BPH, such as transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) and laser treatments, by introducing several notable innovations. It features artificial intelligence (AI)-powered treatment planning through FirstAssist AI™, a sophisticated image recognition software that identifies critical anatomical structures using ultrasound. This technology aids in creating personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient's prostate anatomy.
Additionally, the system combines advanced ultrasound imaging with digital cystoscopy, providing surgeons with a detailed, multidimensional view of the prostate. This improved visualization supports greater precision during procedures and enhances surgical planning.
HYDROS™ also employs a robotic-assisted heat-free waterjet for tissue resection, allowing for effective removal of obstructive tissue while preserving key anatomical structures. This approach reduces the risk of complications, such as incontinence or erectile dysfunction.
Finally, the system is designed to streamline the surgical workflow with features like an integrated tower for setup, an adjustable touchscreen for better ergonomics, and user-friendly software to guide surgeons through each step of the procedure.
These advancements provide a more precise and patient-friendly treatment option compared to traditional methods, addressing common challenges such as tissue damage and unwanted side effects.
To expand access to this innovative technology, The Mount Sinai Hospital has prioritized training for its urology team. Dr. Kaplan, who has performed well over 400 aquablation procedures with the earlier model, recently completed advanced HYDROS training. He will be joined by Mount Sinai surgeons who will begin performing the procedure in the coming months.
“This new technology is part of our commitment to delivering the most advanced and patient-centered care,” says Dr. Kaplan. “The positive outcomes we’ve seen so far are a testament to the potential of HYDROS to redefine how we approach BPH treatment.”
With this milestone, Mount Sinai continues to establish itself as a leader in robotic surgical care. The team plans to track patient outcomes closely to contribute to a growing body of evidence supporting the benefits of HYDROS therapy for men with BPH.
The HYDROS™ Robotic System, developed by PROCEPT BioRobotics® Corporation, received FDA 510(k) clearance on August 21, 2024.
-####-
About the Mount Sinai Health System
Mount Sinai Health System is one of the largest academic medical systems in the New York metro area, with 48,000 employees working across eight hospitals, more than 400 outpatient practices, more than 600 research and clinical labs, a school of nursing, and a leading school of medicine and graduate education. Mount Sinai advances health for all people, everywhere, by taking on the most complex health care challenges of our time—discovering and applying new scientific learning and knowledge; developing safer, more effective treatments; educating the next generation of medical leaders and innovators; and supporting local communities by delivering high-quality care to all who need it.
Through the integration of its hospitals, labs, and schools, Mount Sinai offers comprehensive health care solutions from birth through geriatrics, leveraging innovative approaches such as artificial intelligence and informatics while keeping patients’ medical and emotional needs at the center of all treatment. The Health System includes approximately 9,000 primary and specialty care physicians and 11 free-standing joint-venture centers throughout the five boroughs of New York City, Westchester, Long Island, and Florida. Hospitals within the System are consistently ranked by Newsweek’s® “The World’s Best Smart Hospitals, Best in State Hospitals, World Best Hospitals and Best Specialty Hospitals” and by U.S. News & World Report's® “Best Hospitals” and “Best Children’s Hospitals.” The Mount Sinai Hospital is on the U.S. News & World Report® “Best Hospitals” Honor Roll for 2024-2025.
For more information, visit https://www.mountsinai.org or find Mount Sinai on Facebook, Twitter and YouTube.
END
As harmful algal blooms (HABs) continue to spread across the globe, urgent research is needed to address this growing threat. Studies in Italy, China, and the Atlantic basin have shown that many water bodies have high nitrogen-to-phosphorus ratios, making phosphorus a key factor that drives these blooms. This highlights the critical need for more effective phosphorus management strategies to curb the rise of HABs and protect our ecosystems.
Recently, there’s been a growing interest in finding useful ways to repurpose troublesome algal biomass, which could be turned into valuable products like bioplastics, biofertilizers, and biofuels. Researchers have ...
DALLAS, January 27, 2025 — About 6.7 million American adults are living with heart failure (HF), and prevalence is expected to reach more than 8 million by 2030.[1]
While there is no cure for HF, many people with this condition can live full, enjoyable lives and disease progression can be slowed. While people with early-stage HF often can manage their condition with lifestyle modifications and medications, more advanced therapies may be needed as the disease progresses. Yet, a significant number of patients who may benefit from advanced HF specialty care don’t receive it — a gap that particularly affects populations ...
An international team of scientists has discovered a way to store and release volatile hydrogen using lignin-based jet fuel that could open new pathways for sustainable energy production.
In a new study in the International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Washington State University Professor Bin Yang and colleagues demonstrated that a type of lignin-based jet fuel they developed can chemically bind hydrogen in a stable liquid form. The research has many potential applications in fuels and transportation and could ultimately make it easier to harness ...
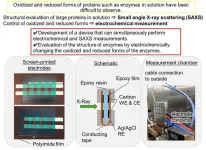
Redox enzymes are proteins that catalyze oxidation-reduction reactions, which involve the transfer of electrons between molecules. Redox enzymes are crucial in bioelectrochemical devices, such as biosensors or biofuel cells. For instance, biosensors catalyze reactions that convert biochemical signals into measurable electrical signals, enabling the detection of substances like glucose. In biofuel cells, redox enzymes convert biological energy into electricity, powering small devices like medical implants. Their ability to facilitate the efficient transfer of electrons between molecules makes them indispensable ...
The Earth’s surface is constantly reshaped by the movement of tectonic plates, which make up the continental crust on which we are living. These tectonic plates are in continuous motion, and when one plate is pushed under another, it is called “subduction.” These processes play a crucial role in shaping the Earth’s landmasses, including the islands of Japan, over several hundred million years. Studying ancient mineral deposits offers a valuable way to uncover the timing of these events. However, determining the precise timing of these tectonic events has ...
Clouds, composed of tiny water droplets or ice crystals, play a vital role in regulating Earth’s climate by influencing the amount of solar radiation that reaches the surface. The cloud phase significantly impacts the surface energy balance as liquid water clouds reflect more radiation than ice clouds. Ice clouds typically form at temperatures below −38°C, but recent observations indicate their formation at higher temperatures in the Arctic. This phenomenon is facilitated by ice-nucleating particles (INPs), including mineral dust, organic aerosols and bioaerosols, which promote ice cloud formation above the usual freezing ...
Scientists have recently shown that both the quality and the amount of sleep we get may influence our risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
Now, a study suggests that people who take significantly longer to start the dream phase of sleep, known as rapid eye movement (REM), may be experiencing an early symptom of the disease.
REM follows three phases of non-REM sleep, each deeper than the last. The four phases take 90 minutes or more to complete, depending on age, and a person may cycle through them four or five times in a typical night. Older people take longer to reach REM.
During REM sleep the brain processes memories, ...
Weight-Loss Surgery Lowers Risk of Developing Complications of Liver Disease in Patients with Cirrhosis and Obesity
SPECCIAL study suggests bariatric surgery favorably influences progression of cirrhosis
UNDER EMBARGO Monday, January 27, 2025, at 05:00 AM (US Eastern Time) CLEVELAND: A Cleveland Clinic study shows that patients with obesity and fatty liver-related cirrhosis who had bariatric (weight-loss) surgery significantly lowered their future risk of developing serious ...
Highlights:
According to the American Heart Association’s 2025 Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics Update, heart disease remains the leading cause of death in the U.S.
While medical advances have helped more people live longer with cardiovascular diseases, many of the risk factors which lead to these diseases, including high blood pressure and obesity, continue to grow at alarming rates.
Cardiovascular diseases, including heart disease and stroke, claim more lives in the U.S. than all forms of cancer and accidental deaths – the #2 and #3 causes of death – combined.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT / 5 a.m. ET Monday, Jan. 27, 2025
DALLAS, Jan. 27, 2025 — Heart ...
A large proportion of babies born very early need intensive care, which can be painful. But the healthcare system fails to provide pain relief to the full extent. This is shown by the largest survey to date of pain in neonatal care, now published in the journal Pain.
Every day for 4.5 years, neonatal care staff have recorded the occurrence of pain, the causes of pain, and how pain is assessed and treated in premature babies in Sweden. The study covers 3,686 babies born between 22 and 31 weeks of gestation from 2020 to 2024. The total observation time was just over 185,000 days of care. Data were collected in the Swedish ...