(Press-News.org) New research indicates that regularly seeing the same GP could reduce workload in practices and hospitals, potentially freeing up appointments for patients.
The study was conducted by Cambridge Judge Business School, University of Cambridge, the University of Exeter Medical School and St Leonard’s Practice in Exeter. The research focuses on continuity of care – whether there’s any benefit from patients seeing the same GP at most of their appointments. This continuity has been steadily decreasing in patient care since 2012, and increasingly patients see multiple GPs within a practice, or temporarily placed GPs, known as locums.
Now, the new research, published in the British Journal of General Practice, suggests seeing the same GP results in fewer follow-up appointments, both in practices and in A&E departments of hospitals.
The research analysed the Clinical Practice Research Datalink, which contains anonymised data from 222 practices across England spanning 2015 to 2017. In the study, researchers looked at patients who were initially seen for appointments that did not relate to long-term conditions. The researchers looked at how they were followed up over time. They split GPs into three categories: the patients’ regular GPs with whom the patient had continuity, all other practice GPs without continuity with the patient, and GP locums. Between these three categories, they compared the time to the next consultation, plus hospital usage after the appointment. Locums often see more on-the-day patients so for a fair comparison, this study only looked at consultations in which the GP prescribed antibiotics.
The research team made adjustments to account for factors including the patients’ age and number of overlapping conditions. They found that patients who saw the same GP regularly had a longer time before their next consultation – an average of 61 days, compared with 56 for any other GP, meaning fewer consultations were needed in the practice.
The team also found that patients seeing their regular GP were less likely (22 percent for non-regular GPs and 30 percent for locums) to attend emergency departments in the same week and were also significantly more likely to be referred to a specialist.
Professor Stefan Scholtes from Cambridge Judge Business School said: “We know that patients are having difficulties in getting GP appointments, and we’re seeing long waiting times at A&E departments. It’s encouraging that this research shows that if general practices help patients to see their regular GP more often, fewer consultations and attendances at emergency departments are needed overall. Making efforts for patients to see the same GP regularly could help patients by reducing pressure in both general practices and emergency departments.”
Professor Philip Evans from the University of Exeter and the St Leonard’s Research Practice, Exeter, said: “Our previous research has indicated that seeing the same GP regularly is linked to numerous patient benefits, including fewer hospitalisations and risk of death, and better care for people with dementia. At a time when workload is probably the biggest problem facing general practices, it’s promising to find a research-based way of working which can reduce overall practice workload.”
The study is entitled ‘Continuity and locum use for acute consultations: observational study of subsequent workload’ and is published in the British Journal of General Practice.
ENDS
END
Regularly seeing the same GP could free up NHS appointments, research shows
New research indicates that regularly seeing the same GP could reduce workload in practices and hospitals, potentially freeing up appointments for patients
2025-01-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Australian innovation ‘sifts’ space for mysteries
2025-01-28
The first trial of an Australian-developed technology has detected mysterious objects by sifting through signals from space like sand on a beach.
Astronomers and engineers at CSIRO, Australia’s national science agency, developed the specialised system, CRACO, for their ASKAP radio telescope to rapidly detect mysterious fast radio bursts and other space phenomena.
The new technology has now been put to the test by researchers led by the Curtin University node of the International Centre for Radio Astronomy ...
Senior Bowl players learn CPR, join the Nation of Lifesavers movement
2025-01-28
MOBILE, Ala., Jan. 27, 2025 — The American Heart Association and the Reese’s Senior Bowl™ teamed up to ensure more people are confident and capable when faced with a cardiac emergency. On Senior Bowl Community Service Day, Jan. 27, the potential NFL Draft prospects who have completed their college eligibility and coaches learned Hands-Only CPR and how to use an automatic external defibrillators (AED) to respond in a cardiac emergency. According to American Heart Association data, 9 out of every 10 of people who experience cardiac arrest outside of a hospital die, in part because ...
Young adults more active after starting work, but sleep less – unless working from home
2025-01-28
When young adults start working, the amount of daily physical activity they do increases sharply, only to fall away again over the new few years, while the amount of sleep they get falls slightly, according to new research led by scientists at the University of Cambridge.
The increase in physical activity was mainly seen in those doing semi-routine occupations such as bus driving or hairdressing, and routine occupations such as cleaning or waiting, or technical jobs. There was little change seen among people entering managerial or professional occupations.
The largest drop in levels of physical activity was seen ...
Archaeologists find ‘lost’ site depicted in the Bayeux Tapestry
2025-01-28
Archaeologists have uncovered evidence that a house in England is the site of a lost residence of Harold, the last Anglo-Saxon King of England, and shown in the Bayeux Tapestry.
By reinterpreting previous excavations and conducting new surveys, the team from Newcastle University, UK, together with colleagues from the University of Exeter, believe they have located a power centre belonging to Harold Godwinson, who was killed in the Battle of Hastings in 1066.
Bosham, on the coast of West Sussex, is depicted ...
Recommendations for mitochondria transfer and transplantation research
2025-01-27
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Most animal, plant and fungal cells contain organelles called mitochondria. These descendants of a primordial bacterial endosymbiont still preserve distinct genes and are known for their ability to create ATP as chemical energy. They also have other important functions, including cell signaling, viral and bacterial sensing, cell division, cell death, and innate and adaptive immune responses. Consequently, impairment in mitochondrial function can result in aging and age-related diseases.
An emerging area of research is the evolutionarily conserved transfer of mitochondria between cells. Yet researchers ...
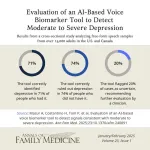
AI-based tool uses speech patterns to detect moderate to severe depression
2025-01-27
Background and Goal: Depression impacts an estimated 18 million Americans each year, yet depression screening rarely occurs in the outpatient setting. This study evaluated an AI-based machine learning biomarker tool that uses speech patterns to detect moderate to severe depression, aiming to improve access to screening in primary care settings.
Study Approach: The study analyzed over 14,000 voice samples from U.S. and Canadian adults. Participants answered the question, “How was your day?” with at least 25 seconds of free-form ...
Taking blood pressure in a public or noisy settings does not affect reading
2025-01-27
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 27 January 2025
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
Primary care physicians face significant gaps in caring for adopted adults with limited family medical history
2025-01-27
Background and Goal: Adopted individuals often have limited access to their family medical history, complicating their health care. This study explored the approaches of primary care physicians when caring for adult adopted patients with limited family medical history.
Study Approach: Researchers conducted in-depth interviews, including hypothetical clinical scenarios, with 23 primary care physicians from Rhode Island and Minnesota to understand their experiences, practices, knowledge, and training gaps when addressing limited family medical history and adoption-related issues.
Main Results:
Primary care physicians report ...
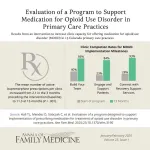
Support program for small, rural primary care clinics increases their ability to prescribe buprenorphine for opioid use disorder fivefold
2025-01-27
Background and Goal: Despite the removal of the X-waiver requirement, which once restricted clinicians from prescribing buprenorphine for opioid use disorder (OUD), only a small percentage of primary care clinicians currently prescribe medication for OUD (MOUD). This study evaluated a structured support program to help small, rural primary care clinics improve their capacity to provide this treatment.
Study Approach: Researchers worked with 15 primary care practices in Colorado over a 12-month period from January 2022 through January 2023. The program provided clinics with monthly educational sessions, direct access to an addiction medicine specialist, and support from practice facilitators ...
Peer health navigators improve health equity and patient well-being for transgender and gender-diverse patients
2025-01-27
Background and Goal: Transgender and gender-diverse individuals often experience additional difficulties navigating health care. This study examined the effectiveness of a peer health navigator pilot program in Saskatchewan, Canada that aimed to improve access to affirming health care for transgender and gender-diverse individuals.
Study Approach: Two peer health navigators were recruited to pilot the program. The navigators were required to be transgender or gender diverse and have experience in health care or community-based organizations. Navigators supported clients by providing information on gender transition and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Regularly seeing the same GP could free up NHS appointments, research showsNew research indicates that regularly seeing the same GP could reduce workload in practices and hospitals, potentially freeing up appointments for patients