(Press-News.org) Arecent study conducted by University of Florida geologists and geographers has shed new light on the effects of climate change on Antarctic ice shelves. It found that while there has been broad ice shelf loss due to warming temperatures, the frequency and size of major iceberg calving events has not changed significantly.
This study was led by Assistant Professor of Geological Sciences Emma MacKie, Ph.D., and Assistant Professor of Geography Katy Serafin, Ph.D., along with a collaborator at the Colorado School of Mines.
“Our results suggest that the primary threat to our ice shelves is ‘death by a thousand cuts’ via small calving events, rather than catastrophic extremes,” said MacKie.
Calving, when chunks of ice break off from ice shelves to form icebergs, is common and increasingly influenced by climate change. For extremely large icebergs, this process is typically slow, often starting with small rifts that spread across the ice shelf before fully breaking off.
These rifts can be detected as they form and grow using satellite data, but their random nature and the risks associated with sending scientists to observe them in-person make it extremely difficult to predict when future rifts or calving events may occur. Major calving events are particularly challenging to study. While smaller calving events occur frequently, large events — where over 100 square kilometers of ice break away — are exceptionally rare.
This study is the first of its kind to focus on these large calving events. Even with 47 years’ worth of satellite data from 1976 to 2023, the team was still faced with a small sample size. This challenge was addressed with extreme value theory, a type of statistical analysis used when studying rare natural disasters like major earthquakes, extreme floods, or volcanic eruptions. As an expert on extreme flooding, Serafin was no stranger to this type of data analysis.
“Statistical models relating event size and frequency are tools that have been used for estimating rare flood events, like a 100-year flood, for decades,” said Serafin. “Now that satellite imagery can more consistently track large calving events, we thought we’d test whether we could apply the same tools for understanding how likely these massive calving events are.”
Using this method, the team analyzed extreme calving events found in the satellite record and developed a model to predict the likelihood of these events over time. While creating their models, researchers also developed scenarios to predict how large calving events could be. By their estimates, a once in a decade iceberg could be as large as 6,100 square kilometers, only slightly larger than an extreme calving event in 2017, when an iceberg roughly the size of Delaware broke off the Antarctic ice sheet. A once in a century eventcould produce an iceberg about 45,000 square kilometers, slightly larger than the entire country of Denmark.
“A once in a century iceberg would be several times larger than any in the observational record and would have a significant impact on ice-sheet stability and ocean processes,” said MacKie.
The team found no evidence that large icebergs have increased in size over the last half century, with the peak iceberg surface areas occurring between 1986 and 2000. This indicates that extreme calving events do not correlate with climate change, although overall ice shelf loss has increased due to climate change. While extreme calving events continue to be rare and may be part of a larger natural cycle, more numerous small calving events have dominated Antarctic ice shelf loss over the last half century.
This study was published November 29, 2024 by the American Geophysical Union.
END
Antarctic ice sheet faces “death by a thousand cuts”
2025-01-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Massachusetts General Hospital, Matthew Perry Foundation announce Fellowship in Addiction Medicine
2025-01-28
BOSTON, MA— The Matthew Perry Foundation and Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system, today announced the establishment of the Matthew Perry Foundation Fellowship in Addiction Medicine for the 2025/2026 academic year. The fellow will join a highly competitive Addiction Medicine fellowship program, which is one of only 105 available in the United States and trains physicians who have completed an accredited residency program to become specialists and leaders in Addiction Medicine. The fellowship focuses on developing clinical expertise, leadership skills, and training ...
Study shows promise for treating core symptom of frontotemporal dementia
2025-01-28
A new study led by Western researchers found frequent treatment with intranasal oxytocin – a hormone in the brain associated with empathy – offers promise for addressing a key symptom among patients with frontotemporal dementia (FTD): Apathy.
It’s a common issue among those with FTD which affects the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain, impacting language, behaviour and decision making. Patients with FTD lose interest in hobbies and passions that previously brought them joy and, most devastatingly, become apathetic ...
Book will guide teachers and child care providers in using the Pyramid Model
2025-01-28
LAWRENCE — A new book co-edited by a researcher at the University of Kansas is a guide for early childhood education professionals to implement the Pyramid Model framework for promoting social-emotional competence in infants and young children.
According to publisher Brookes, “Unpacking the Infant–Toddler Pyramid Model: A Practical Guide for Teachers and Providers” is the first book to provide “a comprehensive, step-by-step overview of the widely used Pyramid Model Practices for infants and toddlers from birth to 3. With this accessible training guide, teachers and providers will use research-based practices to meet the unique needs of ...
Large magma bodies found beneath dormant volcanoes, surprising scientists
2025-01-28
ITHACA, N.Y. – New Cornell University led-research challenges the long-standing belief that active volcanoes have large magma bodies that are expelled during eruptions and then dissipate over time as the volcanoes become dormant.
Researchers used seismic waves to identify magma chambers beneath the surface of six volcanoes of various sizes and dormancy within the Cascade Range, which includes half of the U.S. volcanoes designated by the U.S. Geological Survey as “very high threat.” The team found that all of the volcanoes, including dormant ones, have persistent and large magma bodies.
The ...
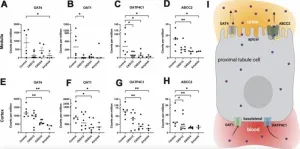
Renal transporter genes and uremic toxins in aging cats with chronic kidney disease
2025-01-28
“Cats and humans share 90.9%, 77.8%, and 82.5% identities in OAT1, OATP4C1, and ABCC2 proteins, respectively.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 28, 2025 – A new research paper was published in Volume 16, Issue 22 of Aging (Aging-US) on December 20, 2024, titled, “Impaired renal transporter gene expression and uremic toxin excretion as aging hallmarks in cats with naturally occurring chronic kidney disease.”
This study, led by researchers Qinghong Li, James A. Holzwarth, Bethany Smith, Sonia Karaz, Mathieu Membrez, ...
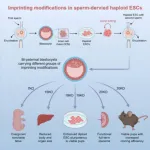
First mouse with two male parents to reach adulthood
2025-01-28
A team of stem cell scientists have successfully used embryonic stem cell engineering to create a bi-paternal mouse—a mouse with two male parents—that lived until adulthood. Their results, publishing on January 28, 2025, in the Cell Press journal Cell Stem Cell, describe how targeting a particular set of genes involved in reproduction allowed the researchers to overcome previously insurmountable challenges in unisexual reproduction in mammals.
Scientists have attempted to create bi-paternal mice before, but the embryos ...
Novel lab-on-chip platform promises to expedite cancer diagnoses
2025-01-28
WASHINGTON, Jan. 28, 2025 – Cancer accounted for nearly 10 million deaths in 2020 – almost one in every six deaths globally – according to the World Health Organization. Because the detection of abnormal diseased cellular growth often occurs too late, timely cancer diagnosis remains one of humanity’s most pressing and elusive medical objectives. Recent research has focused on the detection in peripheral blood of rare circulating tumor cells (CTCs), which serve as noninvasive markers that can help inform diagnoses.
It is inherently difficult to separate controllable target cells to examine. Traditional ...
Largest study ever done on cannabis and brain function finds impact on working memory
2025-01-28
A new study published today in JAMA Network Open explores the effects of both recent and lifetime cannabis use on brain function during cognitive tasks.
The study, the largest of its kind ever to be completed, examined the effects of cannabis use on over 1,000 young adults aged 22 to 36 using brain imaging technology. The researchers found that 63% of heavy lifetime cannabis users exhibited reduced brain activity during a working memory task, while 68% of recent users also demonstrated a similar impact.
This decline in brain activity was associated with worse performance on working memory - the ability to retain and use information to perform tasks. For example, working ...
Brain function outcomes of recent and lifetime cannabis use
2025-01-28
About The Study: Lifetime history of heavy cannabis use was associated with lower brain activation during a working memory task in this study of young adults. These findings identify negative outcomes associated with heavy lifetime cannabis use and working memory in healthy young adults that may be long lasting.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Joshua L. Gowin, PhD, email joshua.gowin@cuanschutz.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.57069)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
Nourishing T cells to fight cancer
2025-01-28
Researchers from the University of Pittsburgh have developed a new way to grow T cells in the lab that enables them to live longer and better destroy cancer cells in a mouse model of melanoma compared to those grown in traditional growth media.
The findings, published recently in Cell Metabolism, have the potential to greatly improve the effectiveness of cancer immunotherapies that involve taking T cells from a patient and growing them to enormous numbers in the lab before reinfusing them back into the body.
“The way we traditionally grow T cells ...