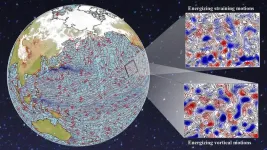
(Press-News.org) Much like the windy weather patterns that affect the Earth’s surface, our planet’s oceans experience their own distinct weather patterns. These weather patterns, known as eddies, are circular currents of water that are typically about 100 kilometers wide.
A new study of satellite imagery and high-resolution climate model data by scientists at the University of Rochester upends previous assumptions and provides insight about how those surface and ocean weather patterns interact. Scientists formerly believed atmospheric wind had a damping effect, slowing the eddies, but the study, published in Nature Communications, offers a new theory that better explains the complexities of how atmospheric wind affects eddies.
“It’s actually more interesting than what people had previously thought,” says Hussein Aluie, a professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering and the Department of Mathematics and senior scientist at the University’s Laboratory for Laser Energetics “There’s a marked asymmetry in how the wind affects these motions, and it depends on the direction they spin.”
Aluie says that prevailing winds that move longitudinally across the globe, such as the westerlies and trade winds, will slow the eddies when they move in the opposite direction but energize them if their spin is aligned.
In between the swirling eddies are intricate tangles of ocean weather patterns known as strain. While strain patterns aren’t as easily distinguished by the naked eye, Aluie says they account for about half of the ocean’s kinetic energy and are damped or energized by wind in similar ways as eddies.
“The new energy pathways between the atmosphere and the ocean that we discovered can help design better ocean observation systems and improve climate models,” says Shikhar Rai ’23 PhD (mechanical engineering), first author of the study and a postdoctoral investigator at Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution. In addition to improving climate modeling, being able to better predict the ocean’s weather patterns could have practical applications for fisheries and help better direct commercial ships where to go.
The study was supported by the National Science Foundation, NASA, the Department of Energy, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, focused largely on the mechanical interactions between the atmosphere and the ocean. In future studies, Aluie plans to investigate the role eddies play in transporting energy between the oceans and atmosphere.
END
How does the atmosphere affect ocean weather?
New research reveals the surprising ways atmospheric winds influence ocean eddies, shaping the ocean’s weather patterns in more complex ways than previously believed.
2025-01-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Robots get smarter to work in sewers
2025-01-31
The ambitious project PIPEON* will develop new robotic and AI-based technologies for mapping, monitoring, and maintaining Europe’s sewer networks using autonomous “thinking” robots and AI-based modelling and analysis tools.
The development and application of such new technologies would have major societal, environmental and economic impact. Instead of repairing in-sewer defects and removing blockages after streets and homes have been flooded with sewage, defects can be quickly identified and repaired and blockages removed when they are still small. Early, preventative repair and maintenance actions will limit the frequency and ...
Speech Accessibility Project data leads to recognition improvements on Microsoft Azure
2025-01-31
Microsoft's Azure AI Speech platform achieved “significant improvements” in recognizing non-standard English speech thanks to recordings and transcripts from University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Speech Accessibility Project participants. Its accuracy gains range from 18% to 60%, depending on the speaker’s disability.
The changes are currently rolling out on Microsoft's Cloud endpoint for third-party customers.
Until now, the majority of voice recognition technology trained using recordings and transcriptions from audiobooks. But an audiobook narrator and an individual with aphasia after a stroke sound different.
When the Speech ...
Tigers in the neighborhood: How India makes room for both tigers and people
2025-01-31
In India, tigers haven’t just survived − they’ve made a comeback. Despite a growing population and increasing pressure on their habitats, the number of wild tigers is rising. The reason? A combination of ecological restoration, economic initiatives, and political stability. And just as important: a deeply rooted reverence for tigers that has fostered a culture where humans and predators can coexist.
How do you protect an endangered species when that species is a tiger − a predator that also poses a threat to humans? India has found a way by combining protected reserves with areas where tigers and people share space. The result? A 30% increase in ...
Grove School’s Arthur Paul Pedersen publishes critical essay on scientific measurement literacy
2025-01-31
Arthur Paul Pedersen, faculty research scientist with the CUNY Remote Sensing Earth Systems (CREST) Institute and adjunct assistant professor of computer science at The City College of New York’s Grove School of Engineering, is lead author of a critical essay on measurement in scientific discourse. The essay, published in the journal of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, warns of the dangerous implications of measurement illiteracy in contemporary scientific discourse and urges broad, ...
Moffitt study finds key biomarker to predict KRASG12C inhibitor effectiveness in lung cancer
2025-01-31
TAMPA, Fla. (Jan. 31, 2025) — A new study from Moffitt Cancer Center could help doctors predict how well patients with a specific type of lung cancer will respond to new therapies. The research, published in Clinical Cancer Research, found that measuring the interaction between two proteins, RAS and RAF, could provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of treatments for patients with KRASG12C-mutant non-small cell lung cancer, a type of lung cancer known for being particularly difficult to treat.
The findings revealed that tumors with higher levels ...
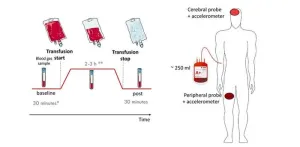
Improving blood transfusion monitoring in critical care patients: Insights from diffuse optics
2025-01-31
Red blood cell transfusions (RBCTs) are life-saving treatments for critically ill patients suffering from anemia, a condition where the body lacks enough healthy red blood cells to deliver oxygen effectively. While effective in increasing oxygen levels in the blood, transfusions can disrupt blood flow and oxygen distribution, potentially causing harm to vital organs like the brain. To address this, researchers are exploring new tools to monitor these effects more precisely.
A recent study reported in Biophotonics Discovery investigated a novel technology called hybrid diffuse optics (DO), which uses near-infrared light to continuously measure changes in blood flow and oxygen ...
Powerful legal and financial services enable kleptocracy, research shows
2025-01-31
Powerful legal and financial service industries are enabling kleptocracy and corrupt elites to operate with relative impunity, a new study shows.
The research details how “enablers” from these industries exploit deregulation and the under-enforcement of the law to game the system. They can offshore their clients' wealth, and enhance their reputations and influence via philanthropy, political donations, and the use of the UK's punitive libel regime.
Most of this “enabling” is likely ...
Carbon capture from constructed wetlands declines as they age
2025-01-31
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Constructed wetlands do a good job in their early years of capturing carbon in the environment that contributes to climate change – but that ability does diminish with time as the wetlands mature, a new study suggests.
Researchers examined soil core samples taken from two constructed freshwater wetlands and compared them to data from previous studies of the same wetlands over 29 years to determine how well human-made wetlands sequester — or capture and store — ...
UCLA-led study establishes link between early side effects from prostate cancer radiation and long-term side effects
2025-01-31
Men undergoing radiation therapy for prostate cancer who experience side effects early in treatment may face a higher risk of developing more serious long-term urinary and bowel health issues, according to a new study led by investigators from the UCLA Health Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center.
The study found that patients who experienced moderate acute urinary side effects in the first three months after radiation were nearly twice as likely to develop late urinary complications years later compared to those without early symptoms. Similarly, patients with early bowel side effects had nearly double the risk of chronic bowel issues.
The findings, ...
Life cycles of some insects adapt well to a changing climate. Others, not so much.
2025-01-31
As insect populations decrease worldwide in what some have called an "insect apocalypse," biologists are desperate to determine how the six-legged creatures are responding to a warming world and to predict the long-term winners and losers.
A new study of Colorado grasshoppers shows that, while the answers are complicated, biologists have much of the knowledge they need to make these predictions and prepare for the consequences.
The findings, published Jan. 30 in the journal PLOS Biology, come thanks to the serendipitous ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
[Press-News.org] How does the atmosphere affect ocean weather?New research reveals the surprising ways atmospheric winds influence ocean eddies, shaping the ocean’s weather patterns in more complex ways than previously believed.