(Press-News.org) Recycling lithium-ion batteries to recover their critical metals has significantly lower environmental impacts than mining virgin metals, according to a new Stanford University lifecycle analysis published in Nature Communications. On a large scale, recycling could also help relieve the long-term supply insecurity – physically and geopolitically – of critical battery minerals.
Lithium-ion battery recyclers source materials from two main streams: defective scrap material from battery manufacturers, and so-called “dead” batteries, mostly collected from workplaces. The recycling process extracts lithium, nickel, cobalt, copper, manganese, and aluminum from these sources.
The study quantified the environmental footprint of this recycling process, and found it emits less than half the greenhouse gases (GHGs) of conventional mining and refinement of these metals and uses about one-fourth of the water and energy of mining new metals. The environmental benefits are even greater for the scrap stream, which comprised about 90% of the recycled supply studied, coming in at: 19% of the GHG emissions of mining and processing, 12% of the water use, and 11% of the energy use. While it was not specifically measured, reduced energy use also correlates with less air pollutants like soot and sulfur.
“This study tells us that we can design the future of battery recycling to optimize the environmental benefits. We can write the script,” said William Tarpeh (BS ’12), assistant professor of chemical engineering in the School of Engineering and the study’s senior author.
Location, location
Battery recycling’s environmental impacts depend heavily on the processing facility’s location and electricity source.
“A battery recycling plant in regions that rely heavily on electricity generated by burning coal would see a diminished climate advantage,” said Samantha Bunke, a PhD student at Stanford and one of the study’s three lead investigators.
“On the other hand, fresh-water shortages in regions with cleaner electricity are a great concern,” added Bunke.
Most of the study’s data for battery recycling came from Redwood Materials in Nevada — North America’s largest industrial-scale lithium-ion battery recycling facility — which benefits from the western U.S.’s cleaner energy mix, which includes hydropower, geothermal, and solar.
Transportation is also a crucial factor. In the mining and processing of cobalt, for example, 80% of the global supply is mined in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Then, 75% of the cobalt supply for batteries travels by road, rail, and sea to China for refining. Meanwhile, most of the global supply of lithium is mined in Australia and Chile. Most of that supply also makes its way to China. The equivalent process for battery recycling is collecting used batteries and scrap, which must then be transported to the recycler.
“We determined that the total transport distance for conventional mining and refining of just the active metals in a battery averages about 35,000 miles (57,000 kilometers). That’s like going around the world one and a half times,” said Michael Machala, PhD ’17, also a lead author of the study.
“Our estimated total transport of used batteries from your cell phone or an EV to a hypothetical refinement facility in California was around 140 miles (225 kilometers),” added Machala, who was a postdoctoral scholar at Stanford’s Precourt Institute for Energy at the time of research and is now a staff scientist for the Toyota Research Institute. This distance was based on presumed optimal locations for future refining facilities amid ample U.S. recyclable batteries.
Patent advantage
Redwood’s environmental outcomes do not represent the nascent battery recycling industry’s overall environmental performance for recycling used batteries. Conventional pyrometallurgy, a key refining step, is very energy intensive, usually requiring temperatures of more than 2,550 degrees Fahrenheit (1,400 degrees Celsius).
Redwood, however, has patented a process called “reductive calcination,” which requires considerably lower temperatures, does not use fossil fuels, and yields more lithium than conventional methods.
“Other pyrometallurgical processes similar to Redwood’s are emerging in labs that also operate at moderate temperatures and don’t burn fossil fuels,” said the third lead author, Xi Chen, a postdoctoral scholar at Stanford during the time of research and now an assistant professor at City University of Hong Kong.
“Every time we spoke about our research, companies would ask us questions and incorporate what we were finding into more efficient practices,” added Chen. “This study can inform the scale-up of battery recycling companies, like the importance of picking good locations for new facilities. California doesn’t have a monopoly on aging lithium-ion batteries from cell phones and EVs.”
Looking ahead
Industrial-scale battery recycling is growing, but not quickly enough, according to senior author Tarpeh.
“We’re forecast to run out of new cobalt, nickel, and lithium in the next decade. We’ll probably just mine lower-grade minerals for a while, but 2050 and the goals we have for that year are not far away,” he said.
While the U.S. now recycles about 50% of available lithium-ion batteries, it has successfully recycled 99% of lead acid batteries for decades. Given that used lithium-ion batteries contain materials with up to 10 times higher economic value, the opportunity is significant, Tarpeh said.
“For a future with a greatly increased supply of used batteries, we need to design and prepare a recycling system today from collection to processing back into new batteries with minimal environmental impact,” he added. “Hopefully, battery manufacturers will consider recyclability more in their future designs, too.”
END
Recycling lithium-ion batteries cuts emissions and strengthens supply chain
2025-01-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study offers new hope for relieving chronic pain in dialysis patients
2025-01-31
People undergoing hemodialysis treatment for kidney failure often experience chronic pain related to their condition, but it can be difficult to manage with opioid medication and other conventional treatments.
A new study published in JAMA Internal Medicine finds that offering these patients pain coping skills training (PCST) significantly reduced their suffering and improved their quality of life.
“This is particularly important for these patients, since the therapeutic choices for pain management are limited and the use of opioids has been shown ...
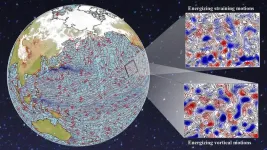
How does the atmosphere affect ocean weather?
2025-01-31
Much like the windy weather patterns that affect the Earth’s surface, our planet’s oceans experience their own distinct weather patterns. These weather patterns, known as eddies, are circular currents of water that are typically about 100 kilometers wide.
A new study of satellite imagery and high-resolution climate model data by scientists at the University of Rochester upends previous assumptions and provides insight about how those surface and ocean weather patterns interact. Scientists formerly believed atmospheric wind had a damping effect, ...
Robots get smarter to work in sewers
2025-01-31
The ambitious project PIPEON* will develop new robotic and AI-based technologies for mapping, monitoring, and maintaining Europe’s sewer networks using autonomous “thinking” robots and AI-based modelling and analysis tools.
The development and application of such new technologies would have major societal, environmental and economic impact. Instead of repairing in-sewer defects and removing blockages after streets and homes have been flooded with sewage, defects can be quickly identified and repaired and blockages removed when they are still small. Early, preventative repair and maintenance actions will limit the frequency and ...
Speech Accessibility Project data leads to recognition improvements on Microsoft Azure
2025-01-31
Microsoft's Azure AI Speech platform achieved “significant improvements” in recognizing non-standard English speech thanks to recordings and transcripts from University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign Speech Accessibility Project participants. Its accuracy gains range from 18% to 60%, depending on the speaker’s disability.
The changes are currently rolling out on Microsoft's Cloud endpoint for third-party customers.
Until now, the majority of voice recognition technology trained using recordings and transcriptions from audiobooks. But an audiobook narrator and an individual with aphasia after a stroke sound different.
When the Speech ...
Tigers in the neighborhood: How India makes room for both tigers and people
2025-01-31
In India, tigers haven’t just survived − they’ve made a comeback. Despite a growing population and increasing pressure on their habitats, the number of wild tigers is rising. The reason? A combination of ecological restoration, economic initiatives, and political stability. And just as important: a deeply rooted reverence for tigers that has fostered a culture where humans and predators can coexist.
How do you protect an endangered species when that species is a tiger − a predator that also poses a threat to humans? India has found a way by combining protected reserves with areas where tigers and people share space. The result? A 30% increase in ...
Grove School’s Arthur Paul Pedersen publishes critical essay on scientific measurement literacy
2025-01-31
Arthur Paul Pedersen, faculty research scientist with the CUNY Remote Sensing Earth Systems (CREST) Institute and adjunct assistant professor of computer science at The City College of New York’s Grove School of Engineering, is lead author of a critical essay on measurement in scientific discourse. The essay, published in the journal of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, warns of the dangerous implications of measurement illiteracy in contemporary scientific discourse and urges broad, ...
Moffitt study finds key biomarker to predict KRASG12C inhibitor effectiveness in lung cancer
2025-01-31
TAMPA, Fla. (Jan. 31, 2025) — A new study from Moffitt Cancer Center could help doctors predict how well patients with a specific type of lung cancer will respond to new therapies. The research, published in Clinical Cancer Research, found that measuring the interaction between two proteins, RAS and RAF, could provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of treatments for patients with KRASG12C-mutant non-small cell lung cancer, a type of lung cancer known for being particularly difficult to treat.
The findings revealed that tumors with higher levels ...
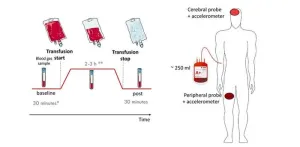
Improving blood transfusion monitoring in critical care patients: Insights from diffuse optics
2025-01-31
Red blood cell transfusions (RBCTs) are life-saving treatments for critically ill patients suffering from anemia, a condition where the body lacks enough healthy red blood cells to deliver oxygen effectively. While effective in increasing oxygen levels in the blood, transfusions can disrupt blood flow and oxygen distribution, potentially causing harm to vital organs like the brain. To address this, researchers are exploring new tools to monitor these effects more precisely.
A recent study reported in Biophotonics Discovery investigated a novel technology called hybrid diffuse optics (DO), which uses near-infrared light to continuously measure changes in blood flow and oxygen ...
Powerful legal and financial services enable kleptocracy, research shows
2025-01-31
Powerful legal and financial service industries are enabling kleptocracy and corrupt elites to operate with relative impunity, a new study shows.
The research details how “enablers” from these industries exploit deregulation and the under-enforcement of the law to game the system. They can offshore their clients' wealth, and enhance their reputations and influence via philanthropy, political donations, and the use of the UK's punitive libel regime.
Most of this “enabling” is likely ...
Carbon capture from constructed wetlands declines as they age
2025-01-31
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Constructed wetlands do a good job in their early years of capturing carbon in the environment that contributes to climate change – but that ability does diminish with time as the wetlands mature, a new study suggests.
Researchers examined soil core samples taken from two constructed freshwater wetlands and compared them to data from previous studies of the same wetlands over 29 years to determine how well human-made wetlands sequester — or capture and store — ...