(Press-News.org)
With demand for physical therapy services projected to increase 27 percent by 2030, Tufts University School of Medicine (TUSM) and ATI Physical Therapy (ATI), a leading provider of physical therapy services across the United States, are launching a joint initiative aimed at expanding the physical therapist workforce and making the Doctor of Physical Therapy (DPT) Programs at TUSM more accessible.
As part of the first-of-its-kind collaboration, TUSM and ATI will contribute scholarships each semester for up to 45 ATI employees in TUSM’s DPT programs each academic year. The accelerated programs, which combine rigorous online coursework with in-person clinical sessions in Boston, Phoenix, and Seattle, are known for their nationally recognized hybrid curriculum that focuses on both clinical skills and community service and feature faculty who are experts in their fields.
"This alliance reflects our commitment to expanding access to health care education," said Helen Boucher, MD, dean at Tufts University School of Medicine and chief academic officer for Tufts Medicine. "By combining our training programs with ATI's clinical experience, we're creating new opportunities for aspiring physical therapists who will be valuable partners for patients and health care practitioners."
ATI will further sponsor up to 20 employees to attend TUSM-DPT’s 12-week, online Accelerated Development of Excellence in Physical Therapy (ADEPT) program, which offers students personalized support to get the most out of their degree. All TUSM-DPT students will also have increased access to clinical rotations at ATI’s network of more than 850 outpatient clinics within the United States.
“This collaboration is a transformative step in supporting the profession and our ATI team members who aspire to become physical therapists,” said Sharon Vitti, chief executive officer of ATI Physical Therapy. “By expanding access to education, we’re fostering a reliable and sustainable pipeline of skilled, homegrown talent for years to come.”
"We want to create clear pathways from early career interest through residencies, fellowships, and specialization in physical therapy," said Eric Hegedus, DPT, PhD, professor and chair of the Department of Rehabilitation Sciences at Tufts University School of Medicine. "By reducing financial barriers and providing early preparation through ADEPT, we're working to ensure that motivated students can access the education they need to meet the growing demand for care.”
The initiative is the first of its kind in the physical therapy profession and for TUSM-DPT—bringing together academic and industry expertise with the goal of making physical therapy education more financially accessible to students from diverse backgrounds. This support is considered mission critical for the long-term success of the field as not enough first-generation college students and students from lower-income households pursue a doctorate in physical therapy to meet demand among underserved populations, according to Hegedus.
TUSM and ATI are also collaborating to advance residency and fellowship training through admission pathways from TUSM-DPT to ATI’s multi-site sports and orthopedic residencies and co-developing a primary care physical therapy fellowship. These efforts will create additional opportunities for professional advancement in the field and prepare practitioners for the specialized skills as leaders in musculoskeletal care.
“This joint initiative is distinguished by Tufts University's exceptional quality of instruction, robust program offerings, and innovative program formats,” said Chuck Thigpen, PhD, senior vice president for clinical excellence at ATI Physical Therapy. “This multi-faceted collaboration will also open joint research initiatives and opportunities for ATI clinicians to contribute to Tufts’ programs and signifies the commitment to bridge the gap between academic excellence and high quality clinical practice.”
###
About Tufts University School of Medicine
Tufts University School of Medicine is a premier medical school, revolutionizing health education for a diverse body of students and advancing medical knowledge in a dynamic and collaborative environment, including with a comprehensive network of affiliated teaching hospitals and health care facilities. The school prepares students to become skilled, passionate health care providers and researchers that make a difference in every type of community, with graduates continuing on to top-tier residencies or taking leadership roles at prestigious organizations around the country.
About ATI Physical Therapy, Inc.
At ATI Physical Therapy, we are committed to making every life an active life. We provide convenient access to high-quality care to prevent and treat musculoskeletal (MSK) pain. Our 850+ locations in 24 states and virtual practice operate under one of the largest single-branded platforms built to support standardized clinical guidelines and operating processes. With outcomes from more than 3 million unique patient cases, ATI strives to utilize quality standards designed to deliver proven, predictable, and impactful patient outcomes. From preventative services in the workplace and athletic training support to outpatient clinical services and online physical therapy via our online platform, CONNECT™, a complete list of our service offerings can be found at ATIpt.com. ATI is based in Downers Grove, Illinois.
END
Emerging evidence suggests that lycopene—a natural plant extract—may have antidepressant properties. New research in Food Science & Nutrition reveals the mechanisms behind its antidepressant effects.
In mice with depressive-like behaviors, brain analyses revealed impairments in the hippocampus. Lycopene treatment lessened these impairments and reversed the animals’ depressive-like traits.
Lycopene treatment boosted the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein with roles in many aspects of brain function. Experiments indicated that a signaling pathway involving BDNF (called the BDNF-TrkB pathway, ...
Researchers at Vanderbilt and the University of Michigan have shown that a simple at-home urine test for prostate cancer screening is highly accurate. The exciting new results, published in The Journal of Urology, build upon a prior Vanderbilt study of prostate cancer screening that required a digital rectal exam.
The results are important because this could enable at-home testing and increased access to testing for patients undergoing telehealth care or living in remote areas.
Traditional prostate cancer screening with PSA testing and biopsy has been shown to lead to unnecessary procedures and overdiagnosis of low-grade cancers, according to ...
The world of display technology is on the cusp of a transformative breakthrough, with electrochemical stimuli-responsive materials gaining more attraction. Based on external stimuli, such as low voltage, these materials can instantaneously undergo electrochemical reactions. These electrochemical reactions can result in the production of different colors, revolutionizing the age of display solutions. An electrochemical system consists of electrodes and electrolytes. Combining the luminescent and coloration molecules on the electrodes instead of the electrolyte can offer higher efficiencies and stability for display devices.
To this end, a research team ...
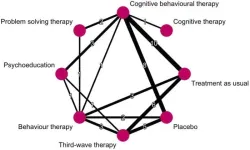
Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a well-known neurodevelopmental disorder that affects the brain's ability to regulate attention and control impulses. It poses many challenges to those affected, typically making it difficult for them to sustain focus, follow through with instructions, and maintain a calm and restful state. As one of the most common neurodevelopmental disorders, ADHD impacts individuals throughout their lives, creating a breadth of social, emotional, academic, and workplace challenges.
Despite its high ...
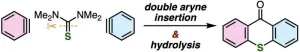
Thioxanthones are fascinating organic compounds that have found their way into many industrial and everyday applications. In the printing industry, for example, they help inks dry faster when exposed to light thanks to their light-absorption properties, making the printing process quicker and more efficient. Some thioxanthones have been developed into FDA-approved drugs used to treat parasitic infections and cancer. Additionally, their effectiveness as photocatalysts has led some researchers to explore their potential as stabilizers against electrical breakdown. Thioxanthones have also been ...
A national study seeking more effective treatment for deadly metaplastic breast cancer has identified two inhibitor drugs with the potential to interrupt disease progression.
Houston Methodist and a team of researchers from across the country examined the biology of metaplastic breast cancer, comparing it to non-metaplastic triple negative breast cancer. They discovered metaplastic breast cancers typically exhibit two unique signaling pathways in their cell interaction. Researchers were able to disrupt these pathways using a class of inhibitors typically used to treat advanced ...
PHOENIX — Mayo Clinic researchers have identified a targeted therapy that could bring relief to people living with lichen planus, a chronic inflammatory skin condition of the skin, hair, nails, mouth and genitals. They described their findings in a study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation that described their first-in-human, phase 2 clinical trial.
The researchers identified unique molecular and cellular changes in the skin with lichen planus, particularly an overactive immune response involving specific types of T cells, a crucial immune system component.
The ...
Tiny copper ‘nano-flowers’ have been attached to an artificial leaf to produce clean fuels and chemicals that are the backbone of modern energy and manufacturing.
The researchers, from the University of Cambridge and the University of California, Berkeley, developed a practical way to make hydrocarbons – molecules made of carbon and hydrogen – powered solely by the sun.
The device they developed combines a light absorbing ‘leaf’ made from a high-efficiency solar cell material called perovskite, with a copper nanoflower catalyst, to convert carbon dioxide into useful molecules. Unlike most metal catalysts, which can only convert CO₂ into single-carbon ...
Embargoed until 10am GMT UK time (5am US Eastern Time) on Monday 03 February 2025 (Nature Geoscience embargo)
-With pictures-
The Greenland Ice Sheet is cracking open more rapidly as it responds to climate change.
The warning comes in a new large-scale study of crevasses on the world’s second largest body of ice.
Using 3-D surface maps, scientists led by Durham University, UK, found crevasses had significantly increased in size and depth at the fast-flowing edges of the ice sheet over the ...
*EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL MONDAY, FEB. 3, AT 5 A.M. ET*
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center and Bloomberg~Kimmel Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy have developed a computer model to help scientists identify tumor-fighting immune cells in patients with lung cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
In their study published Feb. 3 in Nature Communications, the team, including first author Zhen Zeng, Ph.D., a bioinformatics research associate at the Kimmel Cancer Center, demonstrated that their three-gene “MANAscore” computer model can identify ...