(Press-News.org) Sustainability certificates such as Fairtrade, Rainforest Alliance and Cocoa Life promise to improve the livelihoods of small-scale cocoa producers while preserving the biodiversity on their plantations. Together with the European Commission's Joint Research Centre, researchers from the University of Göttingen have investigated whether sustainability certificates actually achieve both these goals. To find out, they carried out an analysis within the Ghanaian cocoa production sector. Their results show that although certification improves both cocoa yield and cocoa income for small-scale producers, they were unable to find any effects on biodiversity in the cocoa plantations. The results were published in the journal Ecological Economics.
Ghana is the second largest cocoa producer in the world; however, its cocoa sector is associated with many socio-economic and environmental problems. The current study is one of the most comprehensive to date on the effects of sustainability certification: the fieldwork included interviews with 814 cocoa-producers and biodiversity surveys on 119 cocoa plantations, covering 46 villages in five major cocoa-growing regions of the country. The researchers conclude that the implementation of sustainability certification in Ghana is achieving its goal in promoting the economic situation for small-scale producers, but they were unable to find any improvements or negative effect on biodiversity.
“The higher yields and associated income from cocoa are a result of the certification requirements, as they motivate small-scale producers to participate in training,” explains first author Marlene Wätzold at Göttingen University’s Research Training Group on Sustainable Food Systems. “Although certified small-scale producers are also encouraged to promote the biodiversity in their plantations, we found no significant environmental effects.”
“In our study, we found no evidence of a trade-off between yield and biodiversity,” adds Dr Carolina Ocampo-Ariza at Göttingen University’s Functional Agrobiodiversity and Agroecology Group. “However, it should be borne in mind that biodiversity changes over longer periods of time, meaning that identifying a change can take longer.”
The findings of the study suggest that to achieve tangible benefits to nature, the requirements for sustainability certification probably need to be complemented by further biodiversity conservation measures.
The research was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) as part of the Research Training Group “Sustainable Food Systems”.
Original publication: Marlene Yu Lilin Wätzold et al. “Do voluntary sustainability standards improve socioeconomic and ecological outcomes? Evidence from Ghana's cocoa sector”. Ecological Economics (2025). DOI: 10.1016/j.ecolecon.2024.108474
Contact:
Marlene Yu Lilin Wätzold
University of Göttingen
Research Training Group ‘Sustainable Food Systems’
Platz der Göttinger Sieben 5
37073 Göttingen, Germany
Tel: +49 (0)551 39-20210
Email: marlene.waetzold@uni-goettingen.de
www.uni-goettingen.de/de/647180.html
Dr Carolina Ocampo-Ariza
University of Göttingen
Faculty of Agricultural Sciences - Department of Functional Agrobiodiversity and Agroecology
Grisebachstraße 6
37077 Göttingen, Germany
Tel: +49 (0)551 39-22057
Email: carolinamaria.ocampoariza@uni-goettingen.de
www.uni-goettingen.de/en/600886.html
END
Protection for small-scale producers and the environment?
Researchers investigate certificates promising sustainability for cocoa cultivation in Ghana
2025-02-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers solve a fluid mechanics mystery
2025-02-03
What began as a demonstration of the complexity of fluid systems became an art piece in the American Physical Society’s Gallery of Fluid Motion, and ultimately its own puzzle that the researchers just solved. Their new study is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
“We came up with this experiment because we were having a hard time convincing people of certain effects happening for the problem of drag reduction,” said assistant
professor Paolo Luzzatto-Fegiz, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering, whose research specialties include modeling flow and investigating drag — as ...
New grant funds first-of-its-kind gene therapy to treat aggressive brain cancer
2025-02-03
The California Institute for Regenerative Medicine has awarded a $6 million grant to USC investigators pioneering a new first-of-its-kind genetic therapy for glioblastoma, a severe form of brain cancer. The treatment would be the first gene therapy for glioblastoma to use a novel, more precise delivery system that is less likely to harm non-cancerous cells.
Glioblastoma is an aggressive and fast-growing cancer originating in the brain that occurs primarily in adults and has no known cure. Patients diagnosed with this type of tumor have a five-year survival rate of just 5 percent. The cancer’s location—in the sensitive brain—combined ...
HHS external communications pause prevents critical updates on current public health threats
2025-02-03
The Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) is concerned that two weeks have passed since the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) announced a pause on mass communications and public appearances that are not directly related to emergencies or critical to preserving health. With the order remaining in effect until a new HHS secretary is confirmed, this unpredictable timeline prolongs uncertainty for both healthcare professionals and the public, and endangers the nation by hindering our ability to detect and respond to public health threats, such as avian influenza (H5N1). Public ...
New ACP guideline on migraine prevention shows no clinically important advantages for newer, expensive medications
2025-02-03
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 3 February 2025
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
New ...
Revolutionary lubricant prevents friction at high temperatures
2025-02-03
Through a multi-university collaboration, researchers at Virginia Tech have discovered a new, solid lubricating mechanism that can reduce friction in machinery at extremely high temperatures. It works well beyond the breakdown temperature of traditional solid lubricants such as graphite, and the findings were published in Nature Communications.
“This breakthrough solid-state lubricant could change how we design materials for high-tech engines, making them last longer and work better under extreme conditions,” said Rebecca Cai, associate professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and one of the ...
Do women talk more than men? It might depend on their age
2025-02-03
The stereotype that women are much more talkative than men is pervasive across many cultures, but a widely reported study by University of Arizona researchers in 2007 refuted the claim, finding that men and women speak roughly the same number of words per day – around 16,000.
A new, larger follow-up to that study paints a more nuanced picture, suggesting that women may be the chattier gender, but only during a certain period of life.
"There is a strong cross-cultural assumption that women talk a lot more than men," said ...
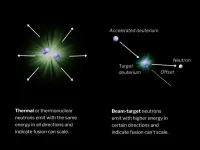
The right kind of fusion neutrons
2025-02-03
In physics, the term “isotropy” means a system where the properties are the same in all directions. For fusion, neutron energy isotropy is an important measurement that analyzes the streams of neutrons coming from the device and how uniform they are. This is critical because so-called isotropic fusion plasmas suggest a stable, thermal plasma that can be scaled to higher fusion energy gains, whereas anisotropic plasmas, those emitting irregular neutron energies, can lead to a dead end.
A new Zap research paper, published last week ...
The cost of preventing extinction of Australia’s priority species
2025-02-03
A new study has estimated it would cost $15.6 billion per year for 30 years to prevent extinction for 99 of Australia’s priority species.
The research, led by Griffith University’s Centre for Planetary Health and Food Security with WWF-Australia and the University of Queensland, highlights the urgent need for increased funding to combat threats such as habitat destruction, invasive species and climate change.
Australia has already lost more than 100 endemic species in the past three centuries, placing it at the forefront of the global extinction crisis.
The ...
JMIR Publications announces new CEO
2025-02-03
(Toronto, February 3, 2025) JMIR Publications, the leading open access publisher in digital health and open science, announced today that Sean Jeong has been appointed as its new chief executive officer (CEO), effective January 23, 2025. Dr Gunther Eysenbach, founder of JMIR Publications, will be stepping down as CEO after over two decades of transformative leadership to focus on new opportunities for innovation in academic publishing, including artificial intelligence (AI)–driven solutions and the advancement of Plan P. He will continue to serve as the editor in chief of the Journal of Medical ...
NCSA awards 17 students Fiddler Innovation Fellowships
2025-02-03
The National Center for Supercomputing Applications awarded Fiddler Innovation Fellowships to 17 University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and NCSA graduate students in a ceremony January 28 honoring the outstanding achievements and interdisciplinary contributions to NCSA programs Students Pushing Innovation (SPIN) and Design for America during the 2023-24 academic year.
The awards are part of a $2 million endowment from Jerry Fiddler and Melissa Alden to Illinois in support of student ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
[Press-News.org] Protection for small-scale producers and the environment?Researchers investigate certificates promising sustainability for cocoa cultivation in Ghana