(Press-News.org) A 3D model accurately mimicking the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) in a laboratory environment has been successfully developed by research teams led by Professor Jinah Jang from the Departments of Mechanical Engineering, Life Sciences, IT Convergence Engineering, and the Graduate School of Convergence at POSTECH, and Professor Sun Ha Paek from the Department of Neurosurgery at Seoul National University Hospital. This study was recently published in Biomaterials Research, an international academic journal on materials science.
Neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), result from the progressive decline of brain and nervous system functions, primarily due to aging. Chronic neuroinflammation, a key driver of these disorders, arises from the intricate interactions between cerebral blood vessels and neural cells, where the BBB plays a pivotal regulatory role. However, existing BBB models have been unable to replicate the complex three-dimensional 3D structure of cerebral blood vessels, posing significant challenges for research and drug development.
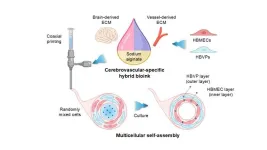
To address these limitations, the research team developed a cerebrovascular-specific bioink using "decellularized extracellular matrix" (CBVdECM), derived from porcine brain and blood vessels. Additionally, the team applied 3D bioprinting technology to construct a tubular vascular model that precisely replicates the anatomical structure and function of the human BBB.
A key feature of this model is the spontaneous formation of a dual-layered structure without external stimuli. When "HBMEC (human brain microvascular endothelial cells)" and "HBVP (human brain vascular pericytes)" were incorporated into the CBVdECM bioink and printed, the endothelial cells self-assembled into the inner vascular wall, while pericytes formed a surrounding layer. This resulted in the creation of a dual-layered structure that closely resembles the architecture of actual blood vessels.
Further, the research team successfully replicated the arrangement and organization process of "tight junction proteins," a component typically absent in conventional 2D models. Additionally, BBB permeability and inflammatory responses were observed following exposure to inflammation-inducing substances (TNF-α and IL-1β). This approach enabled the precise modeling of neuroinflammatory mechanisms, yielding critical insights into the role of BBB dysfunction and inflammation in the pathophysiology of neurodegenerative diseases.
Professor Sun Ha Paek of Seoul National University Hospital commented, "This study provides a crucial platform for investigating the pathological mechanisms of neuroinflammation and developing novel therapeutic strategies.” Professor Jinah Jang of POSTECH added, "We aim to integrate additional cell types, such as glial cells, neurons, and immune cells, to refine methods for quantifying inflammatory responses and permeability, while also expanding to patient-specific disease models."
This research was supported by Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy and the Korea Planning & Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology’s Industrial Technology Alchemist Project, as well as the National Research Foundation of Korea’s University-Focused Research Institute Support Program.
END
Self-assembling cerebral blood vessels: A breakthrough in Alzheimer’s treatment
2025-02-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Adverse childhood experiences in firstborns associated with poor mental health of siblings
2025-02-04
Children are nearly three-quarters (71%) more likely to develop mental health problems between the ages of five and 18, if the firstborn child in their family experienced adversity during their first 1,000 days, finds a new study led by UCL researchers.
The first-of-its-kind study, published in The Lancet Public Health and funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research Policy Research Programme, found that mothers whose firstborns had experienced adverse childhood experiences had a 71% increased risk of having children (aged five -18) with mental health problems, compared to mothers whose firstborn did not experience adversity.
This ...
Montana State scientists publish new research on ancient life found in Yellowstone hot springs
2025-02-04
BOZEMAN – In a new publication in the journal Nature Communications, Montana State University scientists in College of Agriculture highlight fresh knowledge of how ancient microorganisms adapted from a low-oxygen prehistoric environment to the one that exists today. The work builds on more than two decades of scientific research in Yellowstone National Park by MSU professor Bill Inskeep.
The article, titled “Respiratory Processes of Early-evolved Hyperthermophiles in Sulfidic and Low-oxygen Geothermal Microbial Communities” was published Jan. 2. Authors Inskeep, a professor in the Department of Land Resources and Environmental Sciences, and Mensur ...
Generative AI bias poses risk to democratic values
2025-02-04
Generative AI, a technology that is developing at breakneck speed, may carry hidden risks that could erode public trust and democratic values, according to a study led by the University of East Anglia (UEA).
In collaboration with researchers from the Getulio Vargas Foundation (FGV) and Insper, both in Brazil, the research showed that ChatGPT exhibits biases in both text and image outputs — leaning toward left-wing political values — raising questions about fairness and accountability in its design.
The study revealed ...
Study examines how African farmers are adapting to mountain climate change
2025-02-03
A new international study highlights the severity of climate change impacts across African mountains, how farmers are adapting, and the barriers they face – findings relevant to people living in mountain regions around the world.
"Mountains are the sentinels of climate change,” said Julia Klein, a Colorado State University professor of ecosystem science and sustainability and co-author of the study. “Like the Arctic, some of the first extreme changes we're seeing are happening in mountains, from glaciers melting to extreme events. There's greater warming at higher elevations, so what's happening in mountains is foreshadowing what's going ...
Exposure to air pollution associated with more hospital admissions for lower respiratory infections
2025-02-03
Air pollution is a well-known risk factor for respiratory diseases such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). However, its contribution to lower respiratory infections —those that affect the lower respiratory tract, including the lungs, bronchi and alveoli— is less well documented, especially in adults. To fill this gap in knowledge, a team from the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the ”la Caixa” Foundation, assessed the effect of air pollution ...
Microscopy approach offers new way to study cancer therapeutics at single-cell level
2025-02-03
Understanding how tumors change their metabolism to resist treatments is a growing focus in cancer research. As cancer cells adapt to therapies, their metabolism often shifts, which can help them survive and thrive despite medical interventions. This process, known as metabolic reprogramming, is a key factor in the development of treatment resistance. However, current methods to study these changes can be costly, complex, and often destructive to the cells being studied. Researchers at the University of Kentucky have developed a new, simpler approach to observe these metabolic shifts in cancer cells, offering a more accessible and effective tool for cancer research.
As ...
How flooding soybeans in early reproductive stages impacts yield, seed composition
2025-02-03
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. — With an increasing frequency and intensity of flooding events and an eye to capitalize on a common rice production technique, soybean breeders are on a quest to develop varieties with flood tolerance at any stage in the plant’s development.
Farmers who use zero-grade fields for rice as their main production system are also interested in flood-tolerant soybean varieties for crop rotation, said Caio Vieira, assistant professor of soybean breeding and a researcher for the Arkansas Agricultural Experiment Station, the University of Arkansas ...
Gene therapy may be “one shot stop” for rare bone disease
2025-02-03
For the last 10 years, the only effective treatment for hypophosphatasia (HPP) has been an enzyme replacement therapy that must be delivered by injection three-to-six times each week.
“It's been a tremendous success and has proven to be a lifesaving treatment,” said José Luis Millán, PhD, professor in the Human Genetics Program at Sanford Burnham Prebys. “Many children who have been treated otherwise would have died shortly after birth, and they are now able to look forward to long lives.
“It is, however, a very invasive treatment. Some patients have reactions from frequent injections and discontinue ...
Protection for small-scale producers and the environment?
2025-02-03
Sustainability certificates such as Fairtrade, Rainforest Alliance and Cocoa Life promise to improve the livelihoods of small-scale cocoa producers while preserving the biodiversity on their plantations. Together with the European Commission's Joint Research Centre, researchers from the University of Göttingen have investigated whether sustainability certificates actually achieve both these goals. To find out, they carried out an analysis within the Ghanaian cocoa production sector. Their results show that although certification improves both cocoa yield and cocoa income for small-scale producers, they were unable to ...
Researchers solve a fluid mechanics mystery
2025-02-03
What began as a demonstration of the complexity of fluid systems became an art piece in the American Physical Society’s Gallery of Fluid Motion, and ultimately its own puzzle that the researchers just solved. Their new study is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
“We came up with this experiment because we were having a hard time convincing people of certain effects happening for the problem of drag reduction,” said assistant
professor Paolo Luzzatto-Fegiz, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering, whose research specialties include modeling flow and investigating drag — as ...