(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this cohort study of all residents of Ontario, Canada, individuals with incident hospital-based cannabis use disorder care were at markedly increased risk of death compared with the general population. These findings suggest important clinical and policy implications, given global trends toward cannabis legalization and market commercialization accompanied by increasing cannabis use and cannabis use disorders.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Daniel T. Myran, MD, MPH, email dmyran@ohri.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.57852)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.57852?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=020625
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Cannabis use disorder emergency department visits and hospitalizations and 5-year mortality
JAMA Network Open
2025-02-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
COVID-19 pandemic and rates of common ophthalmic procedures among Medicare beneficiaries
2025-02-06
About The Study: The results of this study show that the COVID-19 pandemic caused a notable drop in the number of common ophthalmic procedures among Medicare beneficiaries, especially in laser peripheral iridotomy, while eye drug injections saw minimal changes. The Northeast experienced the largest reductions, highlighting the pandemic’s association with changes in eye care and indicating a need for focused recovery efforts in the hardest hit areas.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jessica D. Randolph, MD, email jessica.randolph@vcuhealth.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.6065)
Editor’s ...
Updated drug information handout outdoes FDA’s version
2025-02-06
A clinical trial comparing a one-page medication handout proposed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) with an updated version developed by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh that quantifies a drug’s risk and benefits showed that the latter was more informative and helped patients feel better equipped to make decisions.
Published today in JAMA Network Open, the study, which used the drug mifepristone as an example, highlights the importance of communicating risks and benefits of prescription medications – ...
Gemini North teams up with LOFAR to reveal largest radio jet ever seen in the early universe
2025-02-06
From decades of astronomical observations scientists know that most galaxies contain massive black holes at their centers. The gas and dust falling into these black holes liberates an enormous amount of energy as a result of friction, forming luminous galactic cores, called quasars, that expel jets of energetic matter. These jets can be detected with radio telescopes up to large distances. In our local Universe these radio jets are not uncommon, with a small fraction being found in nearby galaxies, but they have remained elusive in the distant, early Universe until now.
Using a combination of telescopes, astronomers have discovered a distant, two-lobed radio ...
Researchers discover a major driver of inflammatory pathology in autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases
2025-02-06
Our immune system is armed with an array of defenses designed to detect and eliminate harmful threats. One of its most powerful defense mechanisms is the complement system—a group of proteins that patrols our body, ever vigilant for signs of infection or injury. Now, over 100 years after the complement system was first described, researchers at Mass General Brigham have discovered that a protein known as granzyme K (GZMK) drives tissue damage and inflammation by activating the complement system against our own tissues. Their findings not only reshape the century-old understanding of the complement system but also open new avenues for therapies that could specifically ...
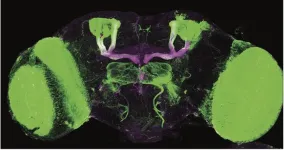
Research in fruit flies pinpoints brain pathways involved in alcohol-induced insomnia
2025-02-06
Alcohol use disorder, which affects over 10% of Americans, can lead to persistent and serious insomnia. Difficulties falling asleep and staying asleep can last even after months of sobriety, increasing the risk of relapse. But treating withdrawal-related insomnia is difficult, partly because what’s going on in the brain in this condition remains largely mysterious.
Now, research in fruit flies has identified specific brain signals and groups of brain cells that are involved in alcohol-induced insomnia. This work could ultimately lead ...
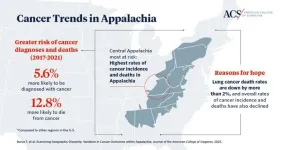
Cancer diagnoses and deaths are declining in Appalachia but remain significantly higher compared to other US regions
2025-02-06
Key Takeaways:
Appalachia is not uniform: There are important distinctions in cancer diagnoses and deaths among different regions of Appalachia, with certain areas of Central Appalachia experiencing the highest rates of cancer incidence and deaths among the greater Appalachian region.
Higher death rates from cancers that can be caught early with screening: Although the region has improved in screening rates, people in Appalachia still die more frequently from cancers that can be caught early with routine screening than elsewhere in the United States.
Reason for hope: Research can pave the way for targeted interventions that can reduce these ...
Why some heavy drinkers develop advanced liver disease, while others do not
2025-02-06
LOS ANGELES — Why do some people who consume a few glasses of alcohol a day develop advanced liver disease while others who drink the same amount don’t?
The answer may lie in three common underlying medical conditions, according to a new study published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology from Keck Medicine of USC. The research found that heavy drinkers with either diabetes, high blood pressure or a high waist circumference are as much as 2.4 times more likely to develop advanced liver disease.
“The results ...
OmicsFootPrint: Mayo Clinic’s AI tool offers a new way to visualize disease
2025-02-06
ROCHESTER, Minnesota — Mayo Clinic researchers have pioneered an artificial intelligence (AI) tool, called OmicsFootPrint, that helps convert vast amounts of complex biological data into two-dimensional circular images. The details of the tool are published in a study in Nucleic Acids Research.
Omics is the study of genes, proteins and other molecular data to help uncover how the body functions and how diseases develop. By mapping this data, the OmicsFootPrint may provide clinicians and researchers with a new way to visualize ...
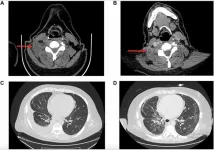
New genetic mutation linked to drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer patient
2025-02-06
“Here we present a case of a patient with stage IV CD-74-ROS1 fusion NSCLC discovered initially with RNA next generation sequencing (NGS) who acquired resistance to lorlatinib after 6 months on therapy through a novel RUFY1-RET fusion, detected only through RNA NGS.”
BUFFALO, NY - February 6, 2025 – A new case report was published in Volume 16 of Oncotarget on February 5, 2025, titled “Acquired RUFY1-RET rearrangement as a mechanism of resistance to lorlatinib in a patient with CD74-ROS1 rearranged non-small cell lung cancer: A case report."
In this case report, Jenny L. ...
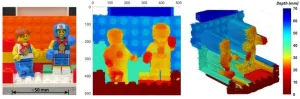
Single-photon LiDAR delivers detailed 3D images at distances up to 1 kilometer
2025-02-06
WASHINGTON — Researchers have designed a single-photon time-of-flight LiDAR system that can acquire a high-resolution 3D image of an object or scene up to 1 kilometer away. The new system could help enhance security, monitoring, and remote sensing by enabling detailed imaging even in challenging environmental conditions or when objects are obscured by foliage or camouflage netting.
“Our system uses a single-photon detector approximately twice as efficient as detectors deployed in similar LiDAR systems ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
[Press-News.org] Cannabis use disorder emergency department visits and hospitalizations and 5-year mortalityJAMA Network Open