(Press-News.org) A new method pioneered to optimally cook both the yolk and white (or albumen) of a boiled chicken egg has been published in Communications Engineering. The approach, which the authors call periodic cooking, yields an evenly-cooked egg with a higher nutritional content than shell-on eggs cooked by conventional boiling or sous vide methods.
The yolk and white in chicken eggs cook at two different temperatures: the albumen cooks at 85 degrees Celsius, while the yolk cooks at 65 degrees Celsius. Conventional methods for cooking eggs by hard-boiling at 100 degrees Celsius result in the yolk being fully set, while cooking them at temperatures between 60 and 70 degrees Celsius in a water bath for one hour (a method known as sous vide) leaves the white undercooked.
Pellegrino Musto and colleagues developed a method for consistently cooking eggs by first simulating the process in computational fluid dynamics software. The simulations suggested a method that consists of alternating an egg between a pan of boiling water kept at 100 degrees Celsius and a bowl kept at 30 degrees Celsius, transferring the egg from one to the other every two minutes for a total duration of 32 minutes. The authors then trialled this process in real life to produce food samples to analyse, calling it ‘periodic cooking’. Hard-boiled, soft-boiled, and sous vide eggs were also included in the analysis — the final cooked eggs were tested for their texture and sensory qualities, with their chemical properties evaluated using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance and High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry.
Periodically-cooked eggs had a soft yolk similar to that of a sous vide egg, while the consistency of the white was somewhere between that of sous vide and soft-boiled. Temperatures in the periodically-cooked egg white ranged between 35 and 100 degrees Celsius during cooking, while the yolk remained at a consistent temperature of 67 degrees Celsius. Chemical analysis suggested that the periodically-cooked egg yolks also contained more polyphenols — micronutrients which have been explored for their health benefits.
The authors believe their approach could also have applications in the curing and crystallisation of other materials.
END
Food: Cracking the method for the ‘perfect’ boiled egg
2025-02-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cannabis use disorder emergency department visits and hospitalizations and 5-year mortality
2025-02-06
About The Study: In this cohort study of all residents of Ontario, Canada, individuals with incident hospital-based cannabis use disorder care were at markedly increased risk of death compared with the general population. These findings suggest important clinical and policy implications, given global trends toward cannabis legalization and market commercialization accompanied by increasing cannabis use and cannabis use disorders.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Daniel ...
COVID-19 pandemic and rates of common ophthalmic procedures among Medicare beneficiaries
2025-02-06
About The Study: The results of this study show that the COVID-19 pandemic caused a notable drop in the number of common ophthalmic procedures among Medicare beneficiaries, especially in laser peripheral iridotomy, while eye drug injections saw minimal changes. The Northeast experienced the largest reductions, highlighting the pandemic’s association with changes in eye care and indicating a need for focused recovery efforts in the hardest hit areas.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jessica D. Randolph, MD, email jessica.randolph@vcuhealth.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2024.6065)
Editor’s ...
Updated drug information handout outdoes FDA’s version
2025-02-06
A clinical trial comparing a one-page medication handout proposed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) with an updated version developed by researchers at the University of Pittsburgh that quantifies a drug’s risk and benefits showed that the latter was more informative and helped patients feel better equipped to make decisions.
Published today in JAMA Network Open, the study, which used the drug mifepristone as an example, highlights the importance of communicating risks and benefits of prescription medications – ...
Gemini North teams up with LOFAR to reveal largest radio jet ever seen in the early universe
2025-02-06
From decades of astronomical observations scientists know that most galaxies contain massive black holes at their centers. The gas and dust falling into these black holes liberates an enormous amount of energy as a result of friction, forming luminous galactic cores, called quasars, that expel jets of energetic matter. These jets can be detected with radio telescopes up to large distances. In our local Universe these radio jets are not uncommon, with a small fraction being found in nearby galaxies, but they have remained elusive in the distant, early Universe until now.
Using a combination of telescopes, astronomers have discovered a distant, two-lobed radio ...
Researchers discover a major driver of inflammatory pathology in autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases
2025-02-06
Our immune system is armed with an array of defenses designed to detect and eliminate harmful threats. One of its most powerful defense mechanisms is the complement system—a group of proteins that patrols our body, ever vigilant for signs of infection or injury. Now, over 100 years after the complement system was first described, researchers at Mass General Brigham have discovered that a protein known as granzyme K (GZMK) drives tissue damage and inflammation by activating the complement system against our own tissues. Their findings not only reshape the century-old understanding of the complement system but also open new avenues for therapies that could specifically ...
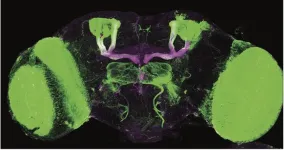
Research in fruit flies pinpoints brain pathways involved in alcohol-induced insomnia
2025-02-06
Alcohol use disorder, which affects over 10% of Americans, can lead to persistent and serious insomnia. Difficulties falling asleep and staying asleep can last even after months of sobriety, increasing the risk of relapse. But treating withdrawal-related insomnia is difficult, partly because what’s going on in the brain in this condition remains largely mysterious.
Now, research in fruit flies has identified specific brain signals and groups of brain cells that are involved in alcohol-induced insomnia. This work could ultimately lead ...
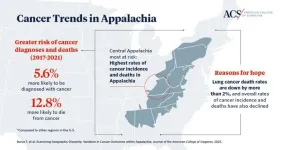
Cancer diagnoses and deaths are declining in Appalachia but remain significantly higher compared to other US regions
2025-02-06
Key Takeaways:
Appalachia is not uniform: There are important distinctions in cancer diagnoses and deaths among different regions of Appalachia, with certain areas of Central Appalachia experiencing the highest rates of cancer incidence and deaths among the greater Appalachian region.
Higher death rates from cancers that can be caught early with screening: Although the region has improved in screening rates, people in Appalachia still die more frequently from cancers that can be caught early with routine screening than elsewhere in the United States.
Reason for hope: Research can pave the way for targeted interventions that can reduce these ...
Why some heavy drinkers develop advanced liver disease, while others do not
2025-02-06
LOS ANGELES — Why do some people who consume a few glasses of alcohol a day develop advanced liver disease while others who drink the same amount don’t?
The answer may lie in three common underlying medical conditions, according to a new study published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology from Keck Medicine of USC. The research found that heavy drinkers with either diabetes, high blood pressure or a high waist circumference are as much as 2.4 times more likely to develop advanced liver disease.
“The results ...
OmicsFootPrint: Mayo Clinic’s AI tool offers a new way to visualize disease
2025-02-06
ROCHESTER, Minnesota — Mayo Clinic researchers have pioneered an artificial intelligence (AI) tool, called OmicsFootPrint, that helps convert vast amounts of complex biological data into two-dimensional circular images. The details of the tool are published in a study in Nucleic Acids Research.
Omics is the study of genes, proteins and other molecular data to help uncover how the body functions and how diseases develop. By mapping this data, the OmicsFootPrint may provide clinicians and researchers with a new way to visualize ...
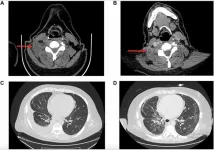
New genetic mutation linked to drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer patient
2025-02-06
“Here we present a case of a patient with stage IV CD-74-ROS1 fusion NSCLC discovered initially with RNA next generation sequencing (NGS) who acquired resistance to lorlatinib after 6 months on therapy through a novel RUFY1-RET fusion, detected only through RNA NGS.”
BUFFALO, NY - February 6, 2025 – A new case report was published in Volume 16 of Oncotarget on February 5, 2025, titled “Acquired RUFY1-RET rearrangement as a mechanism of resistance to lorlatinib in a patient with CD74-ROS1 rearranged non-small cell lung cancer: A case report."
In this case report, Jenny L. ...