(Press-News.org)
Humpback whale song is a striking example of a complex, culturally transmitted behavior, but up to now, there was little evidence it has language-like structure. Human language, which is also culturally transmitted, has recurring parts whose frequency of use follows a particular pattern. In humans, these properties help learning and may come about because they help language be passed from one generation to the next. This work innovatively applies methods inspired by how babies discover words in speech to humpback whale recordings, uncovering the same statistical structures found in all human languages. It reveals previously undetected structure in whale song, illustrating a deep commonality between two unrelated species united by the fact that their communication systems are culturally transmitted.
Whale song has language-like structure
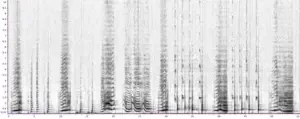
Language has long been considered a uniquely human trait, with features that mark it out as distinct from the communication of all other species. However, research published today in Science has uncovered the same statistical structure that is a hallmark of human language in humpback whale song.
Humpback whale song is a striking example of a complex, culturally transmitted behavior, but up to now, there was little evidence it has language-like structure. Human language, which is also culturally transmitted, has recurring parts whose frequency of use follows a particular pattern. In humans, these properties help learning and may come about because they help language be passed from one generation to the next. This work innovatively applies methods inspired by how babies discover words in speech to humpback whale recordings, uncovering the same statistical structures found in all human languages. This work reveals previously undetected structure in whale song, illustrating a deep commonality between two unrelated species united by the fact that their communication systems are culturally transmitted.
Led by Professor Inbal Arnon of the Hebrew University, Dr Ellen Garland of the University of St Andrews, and Professor Simon Kirby of the University of Edinburgh, in collaboration with Dr Claire Garrigue (IRD New Caledonia), Dr Jenny Allen (Griffith University), and Dr Emma Carroll (University of Auckland), this work represents a unique collaboration between linguists, developmental scientists, marine biologists and behavioural ecologists.
Humpback whale song is one of the most striking examples of a socially learned, culturally transmitted behaviour in a nonhuman animal. Whale song exhibits systematic structure, however, until now, there was little evidence that this structure was like that of human language. One of the big challenges in studying non-human communication is finding out what the relevant parts of the system are. The authors’ breakthrough was to use insights from how babies discover words in speech, and apply them to eight years of humpback whale song data collected in New Caledonia. The authors found that whale song showed the same key statistical properties present in all known human languages. They detected recurring parts whose frequency closely followed a particular skewed distribution, not previously found in any other non-human animal. This work reveals a deeply unexpected commonality between two unrelated species - humans and humpback whales - united by the fact that their communication system is culturally transmitted. This points to the crucial role of learning and transmission in the emergence of structure within such systems. Once thought of as the hallmark of human uniqueness, foundational aspects of human language may be shared across evolutionary distant species.
Dr Ellen Garland from the University of St Andrews said: “Revealing this hidden language-like structure in whale song was unexpected, but it strongly suggests this cultural behaviour holds crucial insight into the evolution of complex communication across the animal kingdom.”
“Whale song is not a language; it lacks semantic meaning. It may be more reminiscent of human music, which also has this statistical structure, but lacks the expressive meaning found in language.”
“Whether the units we detected using the infant-inspired method are salient to the whales themselves remains an open question.”
Prof Inbal Arnon from the Hebrew University said:
“Using insights and methods from how babies learn language allowed us to discover previously undetected structure in whale song”
“This work shows how learning and cultural transmission can shape the structure of communication systems: we may find similar statistical structure wherever complex sequential behaviour is transmitted culturally.”
“It raises the intriguing possibility that humpback whales, like human babies, may learn their song by tracking transitional probabilities between sound elements, and using dips in those probabilities as a cue to segment the song”
Prof Simon Kirby from the University of Edinburgh said:
“It suggests that our understanding of the evolution of language can benefit not only from looking at our closest primate relatives, but also at cases of convergent evolution elsewhere in nature.”
“Looking beyond the way language is used to express meaning, we should consider how language is learned and transmitted culturally over multiple generations.”
“These findings challenge long held assumptions about the uniqueness of human language, uncovering deep commonalities between evolutionarily distant species.”
END
In a groundbreaking study, University of Florida scientists statistically analyzed large amounts of data collected by Burmese python contractors, revealing critical insights about how to most efficiently remove the reptiles.
Researchers correlated survey outcomes, including python removals, with survey conditions, using statistical modeling. For example, the researchers examined if factors like time or temperature impacted the chance of removing a python. They also analyzed whether the most surveyed areas aligned with the highest python removals. This allowed the researchers to ...
During the Super Bowl, every decision matters. With millions of fans watching, the game often comes down to a single play call. And no call is more scrutinized than what a coach decides to do on fourth down. Punt? Attempt a field goal? Or go for it?
A new BYU study explains why NFL coaches, including Super Bowl contenders Andy Reid (Kansas City Chiefs) and Nick Sirianni (Philadelphia Eagles), may behave too conservatively on fourth down. Despite growing acceptance of analytics-driven decision-making, most coaches, ...
Researchers at Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M) have developed a new soft joint model for robots with an asymmetrical triangular structure and an extremely thin central column. This breakthrough, recently patented, allows for versatility of movement, adaptability and safety, and will have a major impact in the field of robotics.
“The main feature of this new design is that it allows greater bending angles to be achieved with less force, providing the robots with great versatility and adaptability of movement,” explains Concha Monje, professor in the UC3M Department ...
Some food labels designed to nudge Americans toward healthier food choices can have the opposite effect, new University of Florida research shows.
The study is particularly compelling because it comes as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration weighs whether to require front-of-package food labels. Through a newly proposed rule, the agency introduced labels highlighting saturated fat, sodium and added sugar. Each value on the labels, a percent of the recommended daily value, corresponds to one of three levels: low, medium and high.
The UF/IFAS study, published in the journal Food Policy, examined front-of-package labels professing the contents inside as “healthy.” ...
CLEVELAND—Nearly every disease has an inflammatory component, but blood tests can’t pinpoint inflammation in specific organs or tissues in the human body.
Now researchers at Case Western Reserve University have developed a method to detect inflammation using antibodies, potentially leading to blood tests for disease-specific biomarkers such as for heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease and various cancers. Their breakthrough also holds promise for drug discovery.
“This research opens up an amazing number of pathways ...
San Francisco, CA (Feb. 5, 2025) – The Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) are excited to host the annual Crohn’s & Colitis Congress®, taking place Feb. 6-8, in San Francisco, CA. This premier event will showcase cutting-edge research, innovative technologies, and advanced patient care strategies set to transform the lives of one in 100 Americans living with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Below ...
Vanilla is vital to the livelihoods of farmers in Madagascar, where the globally popular dessert ingredient is the country’s No. 1 export. A fun, thought-provoking game designed by a team of scientists and played by Malagasy vanilla farmers reveals the challenges of payment programs that incentivize forest conservation in the region, according to a study led by the University of California, Davis.
The study, published in the February issue of the journal Biological Conservation, found that even amid volatile markets and climate uncertainties, farmers highly value their vanilla crops, which are tied ...
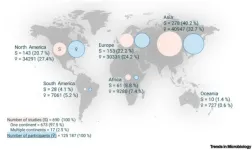
Vaginas host a complex microcosm of bacteria and yeasts that can fluctuate over time. However, little is known about these microbial communities and their roles in a person’s health, and 9 out of 10 studies only include participants from one continent, resulting in major geographical gaps in data. In a paper publishing February 6 in the Cell Press journal Trends in Microbiology, scientists share insights gleaned from a “sisterhood” of thousands of citizen scientists and demonstrate how international collaboration can help illuminate the gaps in our knowledge about the vaginal microbiome, including which bacteria are helpful ...
Four early-career scientists share how they’ve harnessed features of their lives—from music to AI technology—to inspire their career and uplift communities. Each winner receives $10,000 for their science with essays published in the journal Cell
Cell Press, Cell Signaling Technology (CST), and the Elsevier Foundation are proud to announce the winners of the 5th annual Rising Black Scientists Awards: Jheannelle Johnson of Stanford University; Victor Ekuta, MD, of the Morehouse School of Medicine; Kenna Gloria Agbugba of Philander Smith ...
A new method pioneered to optimally cook both the yolk and white (or albumen) of a boiled chicken egg has been published in Communications Engineering. The approach, which the authors call periodic cooking, yields an evenly-cooked egg with a higher nutritional content than shell-on eggs cooked by conventional boiling or sous vide methods.
The yolk and white in chicken eggs cook at two different temperatures: the albumen cooks at 85 degrees Celsius, while the yolk cooks at 65 degrees Celsius. Conventional methods for cooking ...