(Press-News.org)
Known for their powerful punch, mantis shrimp can smash a shell with the force of a .22 caliber bullet. Yet, amazingly, these tough critters remain intact despite the intense shockwaves created by their own strikes.
Northwestern University researchers have discovered how mantis shrimp remain impervious to their own punches. Their fists, or dactyl clubs, are covered in layered patterns, which selectively filter out sound. By blocking specific vibrations, the patterns act like a shield against self-generated shockwaves.
The study will be published on Friday (Feb. 7) in the journal Science.
The findings someday could be applied to developing synthetic, sound-filtering materials for protective gear as well as inspire new approaches to reducing blast-related injuries in military and sports.
“The mantis shrimp is known for its incredibly powerful strike, which can break mollusk shells and even crack aquarium glass,” said Northwestern’s Horacio D. Espinosa, the study’s co-corresponding author. “However, to repeatedly execute these high-impact strikes, the mantis shrimp’s dactyl club must have a robust protection mechanism to prevent self-damage. Most prior work has focused on the club’s toughness and crack resistance, treating the structure as a toughened impact shield. We found it uses phononic mechanisms — structures that selectively filter stress waves. This enables the shrimp to preserve its striking ability over multiple impacts and prevent soft tissue damage.”
An expert on bio-inspired materials, Espinosa is the James N. and Nancy J. Farley Professor in Manufacturing and Entrepreneurship and a professor of mechanical engineering at Northwestern’s McCormick School of Engineering, where he directs the Institute for Cellular Engineering Technologies. Espinosa led the study in partnership with M. Abi Ghanem of the Institute of Light and Matter, a joint research unit between Claude-Bernard-Lyon-I University and the Center for National Scientific Research in France.
A devastating blow
Living in shallow, tropical waters, mantis shrimp are armed with one hammer-like dactyl club on each side of its body. These clubs store energy in elastic, spring-like structures, which are held in place by latch-like tendons. When the latch is released, the stored energy, too, is released — propelling the club forward with explosive force.
With a single blow, mantis shrimp can slaughter prey or defend their territory from interloping competitors. As the punch rips through surrounding water, it creates a low-pressure zone behind it, causing a bubble to form.
“When the mantis shrimp strikes, the impact generates pressure waves onto its target,” Espinosa said. “It also creates bubbles, which rapidly collapse to produce shockwaves in the megahertz range. The collapse of these bubbles releases intense bursts of energy, which travel through the shrimp’s club. This secondary shockwave effect, along with the initial impact force, makes the mantis shrimp’s strike even more devastating.”
Protective patterns
Surprisingly, this force does not damage the shrimp’s delicate nerves and tissues, which are encased within its armor.
To investigate this phenomenon, Espinosa and colleagues used two advanced techniques to examine the mantis shrimp’s armor in fine detail. First, they applied transient grating spectroscopy, a laser-based method that analyzes how stress waves propagate through materials. Second, they employed picosecond laser ultrasonics, which provide further insights into the armor’s microstructure.
Their experiments revealed two distinct regions — each engineered for a specific function — within the mantis shrimp’s club. The impact region, responsible for delivering crushing blows, consists of mineralized fibers arranged in a herringbone pattern, giving it resistance to failure. Beneath this layer, the periodic region features twisted, corkscrew-like fiber bundles. These bundles form a Bouligand structure, a layered arrangement, in which each layer is progressively rotated relative to its neighbors.
While the herringbone pattern reinforces the club against fractures, the corkscrew arrangement governs how stress waves travel through the structure. This intricate design acts as a phononic shield, selectively filtering high-frequency stress waves to prevent damaging vibrations from propagating back into the shrimp’s arm and body.
“The periodic region plays a crucial role in selectively filtering out high-frequency shear waves, which are particularly damaging to biological tissues” Espinosa said. “This effectively shields the shrimp from damaging stress waves caused by the direct impact and bubble collapse.”
In this study, the researchers analyzed 2D simulations of wave behavior. Espinosa said 3D simulations are needed to fully understand the club’s complex structure.
“Future research should focus on more complex 3D simulations to fully capture how the club’s structure interacts with shockwaves,” Espinosa said. “Additionally, designing aquatic experiments with state-of-the-art instrumentation would allow us to investigate how phononic properties function in submerged conditions.”
The study, “Does the mantis shrimp pack a phononic shield?” was supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, the Office of Naval Research and the National Science Foundation.
END
A corn plant knows how to find water in soil with the very tips of its roots, but some varieties, including many used for breeding high-yielding corn in the U.S., appear to have lost a portion of that ability, according to a Stanford-led study. With climate change increasing droughts, the findings hold potential for developing more resilient varieties of corn.
The study, published in the journal Science, uncovers genetic mechanisms behind root “hydropatterning,” or how plant roots branch toward water and avoid dry spaces in soil. In particular, the researchers ...
Humpback whale song is a striking example of a complex, culturally transmitted behavior, but up to now, there was little evidence it has language-like structure. Human language, which is also culturally transmitted, has recurring parts whose frequency of use follows a particular pattern. In humans, these properties help learning and may come about because they help language be passed from one generation to the next. This work innovatively applies methods inspired by how babies discover words in speech to humpback whale recordings, uncovering the same statistical structures found in all human languages. It reveals previously undetected structure in ...
In a groundbreaking study, University of Florida scientists statistically analyzed large amounts of data collected by Burmese python contractors, revealing critical insights about how to most efficiently remove the reptiles.
Researchers correlated survey outcomes, including python removals, with survey conditions, using statistical modeling. For example, the researchers examined if factors like time or temperature impacted the chance of removing a python. They also analyzed whether the most surveyed areas aligned with the highest python removals. This allowed the researchers to ...
During the Super Bowl, every decision matters. With millions of fans watching, the game often comes down to a single play call. And no call is more scrutinized than what a coach decides to do on fourth down. Punt? Attempt a field goal? Or go for it?
A new BYU study explains why NFL coaches, including Super Bowl contenders Andy Reid (Kansas City Chiefs) and Nick Sirianni (Philadelphia Eagles), may behave too conservatively on fourth down. Despite growing acceptance of analytics-driven decision-making, most coaches, ...
Researchers at Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (UC3M) have developed a new soft joint model for robots with an asymmetrical triangular structure and an extremely thin central column. This breakthrough, recently patented, allows for versatility of movement, adaptability and safety, and will have a major impact in the field of robotics.
“The main feature of this new design is that it allows greater bending angles to be achieved with less force, providing the robots with great versatility and adaptability of movement,” explains Concha Monje, professor in the UC3M Department ...
Some food labels designed to nudge Americans toward healthier food choices can have the opposite effect, new University of Florida research shows.
The study is particularly compelling because it comes as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration weighs whether to require front-of-package food labels. Through a newly proposed rule, the agency introduced labels highlighting saturated fat, sodium and added sugar. Each value on the labels, a percent of the recommended daily value, corresponds to one of three levels: low, medium and high.
The UF/IFAS study, published in the journal Food Policy, examined front-of-package labels professing the contents inside as “healthy.” ...
CLEVELAND—Nearly every disease has an inflammatory component, but blood tests can’t pinpoint inflammation in specific organs or tissues in the human body.
Now researchers at Case Western Reserve University have developed a method to detect inflammation using antibodies, potentially leading to blood tests for disease-specific biomarkers such as for heart disease, Alzheimer’s disease and various cancers. Their breakthrough also holds promise for drug discovery.
“This research opens up an amazing number of pathways ...
San Francisco, CA (Feb. 5, 2025) – The Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation and the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) are excited to host the annual Crohn’s & Colitis Congress®, taking place Feb. 6-8, in San Francisco, CA. This premier event will showcase cutting-edge research, innovative technologies, and advanced patient care strategies set to transform the lives of one in 100 Americans living with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
Below ...
Vanilla is vital to the livelihoods of farmers in Madagascar, where the globally popular dessert ingredient is the country’s No. 1 export. A fun, thought-provoking game designed by a team of scientists and played by Malagasy vanilla farmers reveals the challenges of payment programs that incentivize forest conservation in the region, according to a study led by the University of California, Davis.
The study, published in the February issue of the journal Biological Conservation, found that even amid volatile markets and climate uncertainties, farmers highly value their vanilla crops, which are tied ...
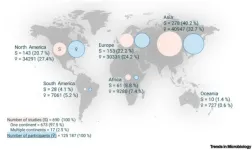
Vaginas host a complex microcosm of bacteria and yeasts that can fluctuate over time. However, little is known about these microbial communities and their roles in a person’s health, and 9 out of 10 studies only include participants from one continent, resulting in major geographical gaps in data. In a paper publishing February 6 in the Cell Press journal Trends in Microbiology, scientists share insights gleaned from a “sisterhood” of thousands of citizen scientists and demonstrate how international collaboration can help illuminate the gaps in our knowledge about the vaginal microbiome, including which bacteria are helpful ...