(Press-News.org) In 2017, a tragic incident unfolded in a Nevada hospital. A woman, admitted for pneumonia, tragically succumbed to multiple organ failure and sepsis. The culprit? A strain of bacteria that had developed resistance to a staggering 26 different antibiotics. These superbugs, or antibiotic-resistant bacteria, stand as one of the most pressing public health threats globally.
Joining the effort to fight these deadly pathogens, researchers at Texas A&M have now shown that curcumin, the compound that gives turmeric its characteristic bright yellow color, can potentially be used to reduce antibiotic resistance.
The researchers showed that when curcumin is intentionally given to bacteria as food and then activated by light, it can trigger deleterious reactions within these microbes, eventually killing them. This process, they demonstrated, reduces the number of antibiotic-resistant strains and renders conventional antibiotics effective again.
The results of the study are published in the journal Scientific Reports.
Before antibiotics, infectious diseases were the leading cause of death and disability around the world. With the advent of these life-saving medications, the human lifespan has increased by 23 years on average. In the last several decades, while the discovery of novel antibiotics has plateaued, antibiotic resistant bacteria have simultaneously become more common, ushering in the era of superbugs, such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), vancomycin-resistant enterococcus, and pneumonia, which are all extremely hard to treat. In fact, infectious diseases are projected to be the main causes of human mortality once again, claiming up to 10 million lives annually.
“When bacteria start becoming resistant to conventional antibiotics, we have what we call an antibiotic catastrophe,” said Dr. Vanderlei Bagnato, professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering and senior author on the study. “To overcome this challenge, we need alternative ways to either kill the superbugs or find a novel way to modify natural processes within the bacteria so that antibiotics start to act again.”
Bacteria display natural variation within a given population. This heterogeneity introduces variations in cell behaviors, including response to antibiotics, which can directly contribute to treatment resistance if some strains survive antimicrobial medication and continue replicating. Thus, the researchers wanted to curb bacterial heterogeneity to control bacterial resistance.
Photodynamic inactivation, a technique that has shown promise in combating bacterial resistance, uses light and light-sensitive molecules, called photosensitizers, to produce reactive oxygen species that can kill microorganisms by disrupting their metabolic processes. In their experiments, the team used curcumin, which is also a natural food for bacteria. They tested this technique on strains of Staphylococcus aureus that are resistant to amoxicillin, erythromycin, and gentamicin.
The researchers exposed the bacteria to many cycles of light exposure and then compared the minimum concentration of antibiotics needed to kill the bacteria after light exposure versus those that did not get light exposure.
“When we have a mixed population of bacteria where some are resistant, we can use photodynamic inactivation to narrow the bacterial distribution, leaving behind strains that are more or less similar in their response to antibiotics,” said Bagnato. “It’s much easier now to predict the precise antibiotic dose needed to remove the infection.”
The team noted that photodynamic inactivation using curcumin has tremendous potential as an adjuvant or additional therapy with antibiotics for diseases, like pneumonia, caused by antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
“Photodynamic inactivation offers a cost-effective treatment option, which is crucial for reducing medical expenses not only in developing countries but also in the United States,” said Dr. Vladislav Yakovlev, professor in the Department of Biomedical Engineering and author on the study. “It also has potential applications in military medicine, where this technology could be used to treat battlefield wounds and prevent the development and spread of antimicrobial resistance, a significant concern in combat situations."
Contributors to the research include Dr. Jennifer Soares, who is the primary author on the paper, and Dr. Kate Blanco from Institute of Physics of São Carlos, University of São Paulo, Brazil.
This research was financially supported by São Paulo Research Foundation, National Council for Scientific and Technological Development, Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas, Governor’s University Research Initiative, the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, and the National Institutes of Health.
By Texas A&M University
###
END
Warding off superbugs with a pinch of turmeric
In a new study, researchers at Texas A&M have evaluated a low-cost yet effective technology called photodynamic inactivation using curcumin to curb bacterial resistance
2025-02-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Ophthalmic complications in patients on antidiabetic GLP-1 medications are concerning neuro-ophthalmologists
2025-02-06
BUFFALO, N.Y. — A small percentage of patients taking the extraordinarily popular GLP-1 medications have experienced vision problems, but a direct causal link with the drugs has not been established. That is the conclusion of a retrospective study published online on Jan. 30 in JAMA Ophthalmology.
The study focused on nine patients who had experienced vision problems while using semaglutide (brand names Wegovy and Ozempic) and tirzepatide (brand names Mounjaro and Zepbound).
The paper is one of several in the past ...
Physicians committee research policy director speaks today at hearing on taxpayer funded animal cruelty
2025-02-06
WASHINGTON, D.C. — Research Policy Director Elizabeth Baker from the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine, a national medical ethics and health advocacy group of 17,000 physicians, spoke today, Feb. 6, at a Congressional hearing focused on ending federally funded animal cruelty in research.
The U.S. House Oversight and Government Reform Subcommittee on Cybersecurity, Information Technology, and Government Innovation Chairwoman Nancy Mace (R-S.C.) announced the hearing in a news release on Monday, with plans to evaluate current animal cruelty funded by the federal government and explore opportunities ...
New technology lights way for accelerating coral reef restoration
2025-02-06
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Scientists have developed a novel tool designed to protect and conserve coral reefs by providing them with an abundance of feeding opportunities.
The device, dubbed the Underwater Zooplankton Enhancement Light Array (UZELA), is an autonomous, programmable underwater light that works to draw in nearby zooplankton, microscopic organisms that coral feed on.
After testing the submersible on two species of coral native to Hawaii over six months, researchers found that UZELA could ...
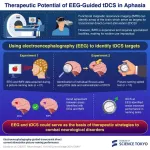
Electroencephalography may help guide treatments for language disorders
2025-02-06
Electroencephalography (EEG) may offer a more accessible alternative to functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) for guiding transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) when treating aphasia. Researchers from Institute of Science Tokyo found an 80% agreement between EEG and fMRI in identifying brain regions activated during language tasks. Furthermore, EEG-guided tDCS improved picture-naming speed in participants, indicating its potential for innovative therapies in language disorders.
Many neurological disorders are directly linked to damage or deterioration in specific regions of the brain. For example, ...
Multinational research project shows how life on Earth can be measured from space
2025-02-06
Measurements and data collected from space can be used to better understand life on Earth.
An ambitious, multinational research project funded by NASA and co-led by UC Merced civil and environmental engineering Professor Erin Hestir demonstrated that Earth’s biodiversity can be monitored and measured from space, leading to a better understanding of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Hestir led the team alongside University of Buffalo geography Professor Adam Wilson and Professor Jasper Slingsby from the University ...
Essential genome of malaria parasite Plasmodium knowlesi mapped
2025-02-06
Embargoed for release: Thursday, February 6, 2025, 2:00 PM ET
Key points:
Comprehensive genetic mapping of Plasmodium knowlesi, a zoonotic parasite that causes malaria, has revealed the genes required for malaria infection of the blood, and those driving drug resistance.
By identifying specific druggable targets and determinants of resistance, the map provides insights that could help the development of new therapeutics.
Boston, MA—A new, comprehensive map of all the genes essential for blood infections in Plasmodium knowlesi (P. ...
Ice streams move due to tiny ice quakes
2025-02-06
In brief:
• In Greenland, an international team of researchers led by ETH Zurich has discovered that countless tiny ice quakes take place deep inside ice streams.
• These quakes are responsible for the fact that ice streams also move with a continuous stick-slip motion and not only like viscous honey as previously considered.
• The researchers recorded seismic data from inside the ice stream using a fibre-optic cable in a 2,700-metre deep borehole.
The ...
Whale song has remarkable similarities to human speech in terms of efficiency
2025-02-06
Whale song can be as efficient as – and, in some cases, more efficient than – human communication, according to a new study in Science Advances. Meanwhile, new unrelated research in Science further investigates whale song’s adherence to a universal linguistic law, as observed in recordings of humpback whales.
Natural selection favors the pithy over the longwinded. For example, yelling “Duck!” is faster and far more effective than shouting “Be careful, there is an incoming projectile, and you need to move out of the way!” ...
Uncovered: How mice override instinctive fear responses
2025-02-06
Researchers have uncovered a neural mechanism in the brains of mice that enables them to override instinctive fear responses; dysfunction in this mechanism may contribute to inappropriate or excessive fear responses, they say. According to the findings, targeting these circuits could offer new therapeutic avenues for treating fear-related disorders like post-traumatic stress disorder and anxiety. Fear responses to visual threats, such as escaping from an approaching predator, are critical instinctive reactions for survival and are ...
A pathway that contributes to insulin resistance can be targeted, mouse study shows
2025-02-06
The hormone adrenomedullin disrupts insulin signaling in blood vessel cells, contributing to systemic insulin resistance in obesity-associated type 2 diabetes, according to a new study. Blocking adrenomedullin’s effects restores insulin function and improves glucose control in a mouse model, suggesting a potential new target for treating obesity-related metabolic disease. Diabetes is a leading global cause of illness, mortality, and healthcare expenditures, with most cases stemming from obesity-induced insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Insulin resistance primarily ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
[Press-News.org] Warding off superbugs with a pinch of turmericIn a new study, researchers at Texas A&M have evaluated a low-cost yet effective technology called photodynamic inactivation using curcumin to curb bacterial resistance