Study reveals how physical activity impacts sleep quality in older adults during COVID-19 pandemic
“[...] we found that PA may be associated with the sleep quality of older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic and that reduced levels of PA during the COVID-19 pandemic period had a negative association with the quality of sleep of older adults in..."
2025-02-11
(Press-News.org)
“[…] we found that PA may be associated with the sleep quality of older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic and that reduced levels of PA during the COVID-19 pandemic period had a negative association with the quality of sleep of older adults in social isolation.”
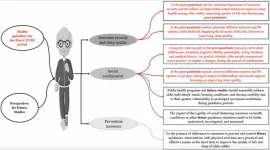
BUFFALO, NY—February 11, 2025 — A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on January 15, 2025, in Volume 17, Issue 1, titled “Association between physical activity practice and sleep quality of older people in social isolation during the COVID-19 pandemic and Health Guidelines and future studies for the post-COVID period: a systematic review.”
Researchers Alexandro Andrade, Ana Cecília Rosatelli de Freitas Bastos, Anderson D’Oliveira, and Guilherme Torres Vilarino from the Santa Catarina State University (UDESC) in Brazil, conducted a systematic review to examine the relationship between physical activity (PA) and sleep quality in older adults who experienced social isolation during the COVID-19 pandemic. Their findings reveal that a decline in PA levels during social isolation negatively impacted sleep health, emphasizing the need for regular movement in aging populations.
The study reviewed nine studies involving over 11,500 older adults of both sexes from China, Japan, Brazil, Scotland, Canada, Italy, and Spain. The results showed that reduced PA during the pandemic was linked to poorer sleep quality in four studies, while one study found that those who remained active had better sleep patterns. The four other studies showed no significant association.
Getting enough quality sleep is essential for healthy aging, as sleep disorders have been linked to cognitive decline, depression, and reduced mental well-being. The COVID-19 pandemic worsened sleep health due to increased stress, isolation, and anxiety. Researchers suggest that staying active through walking, stretching, and structured exercise routines may help improve sleep quality and overall mental health.
The researchers point out the importance of PA as an accessible way to enhance sleep quality in older adults, particularly during times of crisis. Encouraging regular exercise and movement may help prevent sleep disorders and improve overall well-being in aging populations.
“PA can be considered a safe and effective practice to improve sleep quality in older adults due to its well-documented benefits in the literature.”
As the world moves past the pandemic, the researchers call for public health policies that promote PA for seniors. Health professionals and caregivers should advocate for regular movement as a preventive measure against insomnia, poor sleep, and mental health issues while emphasizing the long-term consequences of physical inactivity. The study also highlights the need for further research on the most effective types and intensities of PA for improving sleep quality in older adults.
“The practice of exercise and PA, individually and in groups, is recommended for this post-COVID scenario, as a measure to reduce social isolation and its negative effects and improve the quality of sleep in older adults.”
Future studies should explore how different exercise routines impact sleep health, especially for older adults recovering from COVID-19 or facing ongoing sleep challenges.
Read the full paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.206180
Corresponding author: Alexandro Andrade – alexandro.andrade.phd@gmail.com
Keywords: aging, exercise, sleep quality, older people, SARS-CoV-2, long COVID
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Aging:
The journal Aging aims to promote 1) treatment of age-related diseases by slowing down aging, 2) validation of anti-aging drugs by treating age-related diseases, and 3) prevention of cancer by inhibiting aging. (Cancer and COVID-19 are age-related diseases.)
Aging is indexed by PubMed/Medline (abbreviated as “Aging (Albany NY)”), PubMed Central, Web of Science: Science Citation Index Expanded (abbreviated as “Aging‐US” and listed in the Cell Biology and Geriatrics & Gerontology categories), Scopus (abbreviated as “Aging” and listed in the Cell Biology and Aging categories), Biological Abstracts, BIOSIS Previews, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
Facebook
X
Instagram
YouTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker St., Suite 1
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-02-11
About The Study: In this cohort study of U.S. youths, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms were associated with the onset of nicotine and tobacco use. The findings highlight the importance of early diagnosis and effective treatment of ADHD to alleviate symptoms and reduce the risk of later nicotine and tobacco use.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Sean Esteban McCabe, PhD, email plius@umich.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
2025-02-11
About The Study: This study has 3 findings in a prepandemic context. First, approximately 1 in 9 U.S. residents used a dietary supplement for perceived immune benefits (supplements to prevent colds or boost the immune system), and such usage varied by several sociodemographic and health characteristics. Second, label claims related to immune benefits consistently appeared on over half of dietary supplements taken for perceived immune benefits. Lastly, the prevalence of dietary supplement use for perceived immune benefits due to a doctor recommendation and dietary supplement use exclusively for perceived immune benefits were both generally ...
2025-02-11
Study in experimental animals reveals fundamental differences in how immune system drives healing based on age
Newborn immune systems see, then eat dying cells, triggering production of bioactive lipids
Findings open the door to developing treatments that could ‘reprogram’ adult immune systems
CHICAGO --- Newborns with heart complications can rely on their newly developed immune systems to regenerate cardiac tissues, but adults aren’t so lucky. After a heart attack, most adults struggle to regenerate healthy heart tissue, leading ...
2025-02-11
A new type of soft robot can crawl like a worm, climb cables, and suddenly snap into a completely different shape to move in a new direction—all controlled by a single air input. This breakthrough, developed by researchers at Seoul National University, introduces a fundamentally new way for soft robots to move and adapt to their surroundings.
A Leap Forward in Soft Robotics
Soft robots, made from flexible materials, are known for their ability to bend and stretch. However, until now, they struggled to precisely control motion and required complex ...
2025-02-11
A new UCLA Health study has discovered in mouse models that genes associated with repairing mismatched DNA are critical in eliciting damages to neurons that are most vulnerable in Huntington's disease and triggering downstream pathologies and motor impairment, shedding light on disease mechanisms and potential new ways to develop therapies.
Huntington’s disease is one of the most common inherited neurodegenerative disorders that typically begins in adulthood and worsens over time. Patients begin to lose neurons in specific regions of the brain responsible for movement control, motor skill learning, language and ...
2025-02-11
Boston, MA – The Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute is proud to announce the launch of the Center for Sepsis Epidemiology and Prevention Studies (SEPSIS). This pioneering center of excellence is dedicated to advancing understanding, prevention, and management of sepsis, a life-threatening condition caused by a dysregulated immune response to infection.
The SEPSIS Center will be led by Dr. Chanu Rhee and Dr. Michael Klompas, internationally recognized leaders in sepsis surveillance, prevention, treatment, and policy. Both serve as faculty at Harvard Medical School and the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute and bring a wealth of expertise and a shared commitment ...
2025-02-11
Scientists from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and ShanghaiTech University have developed an innovative method for growing brain tumors of individual patients in the laboratory that mimic the original structure and the molecular property of the parental tumor as closely as possible. Drug tests in this model were found to correlate very well with actual patient responses, making it a valuable method for investigating therapies.
Tumor organoids, i.e. mini-tumors grown from surgical material in the culture dish, ...
2025-02-11
Laser diodes are semiconductors that generate light and amplify it using repeated reflection or ‘optical feedback’. Once the light has achieved desirable optical gain, laser diodes release it as powerful laser beams. Photonic crystal surface-emitting lasers (PCSELs) are advanced laser diodes where the optical gain is typically distributed laterally to the propagating light within a photonic crystal (PC) structure. They differ from traditional lasers by separating gain, feedback, and emission functions, offering scalable single-mode power and innovative ...
2025-02-11
There are reports of IT sabotage, cyber espionage, and other acts of hybrid warfare almost every day. Communication networks based on quantum physics could help eliminate threats of this kind. Researchers throughout Germany have already been working on developing those networks based on quantum repeaters for several years. In January 2025, the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) started funding a new research project, entitled Quantenrepeater.Net (QR.N), which aims to demonstrate the viability of quantum repeaters over test networks outside the protected lab environment. The BMBF will be providing a total of EUR 20 million over three years. ...
2025-02-11
The PhRMA Foundation announced the appointment to its Board of Directors of Dr. John C. Reed, MD, PhD, Executive Vice President of Innovative Medicine R&D at Johnson & Johnson (J&J), and Dr. Donatello Crocetta, MD, MBA, Chief Medical Officer and Head of Medical Communities at UCB.
The PhRMA Foundation is a 60-year-old nonprofit that fosters biopharmaceutical innovation and value-driven health care by investing in the frontiers of research. The Foundation catalyzes the careers of promising researchers through competitive, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study reveals how physical activity impacts sleep quality in older adults during COVID-19 pandemic
“[...] we found that PA may be associated with the sleep quality of older adults during the COVID-19 pandemic and that reduced levels of PA during the COVID-19 pandemic period had a negative association with the quality of sleep of older adults in..."

