(Press-News.org) Study in experimental animals reveals fundamental differences in how immune system drives healing based on age
Newborn immune systems see, then eat dying cells, triggering production of bioactive lipids
Findings open the door to developing treatments that could ‘reprogram’ adult immune systems
CHICAGO --- Newborns with heart complications can rely on their newly developed immune systems to regenerate cardiac tissues, but adults aren’t so lucky. After a heart attack, most adults struggle to regenerate healthy heart tissue, leading to scar-tissue buildup and, often, heart failure.
A new Northwestern Medicine study in experimental animals reveals a critical difference in how macrophages — a part of the immune system — help repair the heart in newborns versus adults after a heart attack. The study highlights a fundamental difference in how the immune system drives healing based on age.
The study will be published Feb. 11 in the journal Immunity.
“Understanding why newborns can regenerate their hearts while adults cannot will open the door to developing treatments that could ‘reprogram’ adult macrophages,” said first and co-corresponding author Connor Lantz, lead scientist of the bioinformatics core at the Comprehensive Transplant Center at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine.
In newborns, macrophages perform a process called efferocytosis, which recognizes and eats dying cells. This process triggers the production of a bioactive lipid called thromboxane, signaling nearby heart muscle cells to divide, and allowing the heart to regenerate damaged heart muscle, the study found. In adults, macrophages produce much less thromboxane, leading to a weaker repair signal.
“By mimicking the effects of thromboxane, we might one day improve tissue repair after a heart attack in adults,” Lantz said.
How the study worked
The study examined how the immune system responds to heart injury in mice of different ages, including newborn mice (one day old) and adult mice (eight weeks old). The researchers found the ability of macrophages to engulf dying cells was enhanced in newborn mice due to increased expression of MerTK, a receptor that recognizes dying cells. Therefore, when the scientists blocked this key receptor, newborn mice lost their ability to regenerate their hearts, resembling adult hearts after a heart attack.
Engulfment of dying cells by newborn macrophages triggered a chemical chain reaction that produced a molecule called thromboxane A2, which unexpectedly stimulated heart muscle cells to multiply and repair the damage, the study found. Additionally, nearby muscle heart cells in newborns are primed to respond to thromboxane A2, leading them to change their metabolism to support their growth and healing. But in adults, this process did not work the same way — after an injury, their macrophages did not produce enough thromboxane A2, limiting their ability to regenerate heart tissue.
The paper is titled, “Early Age Efferocytosis Directs Macrophage Arachidonic Acid Metabolism for Tissue Regeneration.” Edward B. Thorp, professor of experimental pathology at Feinberg, is a co-corresponding study author.
END
A new type of soft robot can crawl like a worm, climb cables, and suddenly snap into a completely different shape to move in a new direction—all controlled by a single air input. This breakthrough, developed by researchers at Seoul National University, introduces a fundamentally new way for soft robots to move and adapt to their surroundings.
A Leap Forward in Soft Robotics
Soft robots, made from flexible materials, are known for their ability to bend and stretch. However, until now, they struggled to precisely control motion and required complex ...
A new UCLA Health study has discovered in mouse models that genes associated with repairing mismatched DNA are critical in eliciting damages to neurons that are most vulnerable in Huntington's disease and triggering downstream pathologies and motor impairment, shedding light on disease mechanisms and potential new ways to develop therapies.
Huntington’s disease is one of the most common inherited neurodegenerative disorders that typically begins in adulthood and worsens over time. Patients begin to lose neurons in specific regions of the brain responsible for movement control, motor skill learning, language and ...
Boston, MA – The Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute is proud to announce the launch of the Center for Sepsis Epidemiology and Prevention Studies (SEPSIS). This pioneering center of excellence is dedicated to advancing understanding, prevention, and management of sepsis, a life-threatening condition caused by a dysregulated immune response to infection.
The SEPSIS Center will be led by Dr. Chanu Rhee and Dr. Michael Klompas, internationally recognized leaders in sepsis surveillance, prevention, treatment, and policy. Both serve as faculty at Harvard Medical School and the Harvard Pilgrim Health Care Institute and bring a wealth of expertise and a shared commitment ...
Scientists from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) and ShanghaiTech University have developed an innovative method for growing brain tumors of individual patients in the laboratory that mimic the original structure and the molecular property of the parental tumor as closely as possible. Drug tests in this model were found to correlate very well with actual patient responses, making it a valuable method for investigating therapies.
Tumor organoids, i.e. mini-tumors grown from surgical material in the culture dish, ...
Laser diodes are semiconductors that generate light and amplify it using repeated reflection or ‘optical feedback’. Once the light has achieved desirable optical gain, laser diodes release it as powerful laser beams. Photonic crystal surface-emitting lasers (PCSELs) are advanced laser diodes where the optical gain is typically distributed laterally to the propagating light within a photonic crystal (PC) structure. They differ from traditional lasers by separating gain, feedback, and emission functions, offering scalable single-mode power and innovative ...
There are reports of IT sabotage, cyber espionage, and other acts of hybrid warfare almost every day. Communication networks based on quantum physics could help eliminate threats of this kind. Researchers throughout Germany have already been working on developing those networks based on quantum repeaters for several years. In January 2025, the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) started funding a new research project, entitled Quantenrepeater.Net (QR.N), which aims to demonstrate the viability of quantum repeaters over test networks outside the protected lab environment. The BMBF will be providing a total of EUR 20 million over three years. ...
The PhRMA Foundation announced the appointment to its Board of Directors of Dr. John C. Reed, MD, PhD, Executive Vice President of Innovative Medicine R&D at Johnson & Johnson (J&J), and Dr. Donatello Crocetta, MD, MBA, Chief Medical Officer and Head of Medical Communities at UCB.
The PhRMA Foundation is a 60-year-old nonprofit that fosters biopharmaceutical innovation and value-driven health care by investing in the frontiers of research. The Foundation catalyzes the careers of promising researchers through competitive, ...
A special liquid diet, known as exclusive enteral nutrition, is an essential therapy for Crohn's disease. Patients consume only this formula for six to eight weeks, completely avoiding solid foods. However, the exact reasons why this is helpful were previously unclear. Researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and the LMU University Hospital Munich have now been able to decipher the mechanism behind this dietary therapy. Based on these results, they are launching a clinical study combining dietary therapy with faecal microbiome transfer to further enhance ...
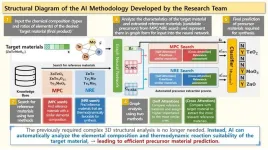
Researchers in Korea have developed a technology that automatically identifies the necessary precursor materials to synthesize specific target materials.
A joint research team led by Senior Researcher Gyoung S. Na from the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT) and Professor Chanyoung Park from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) has developed an AI-based retrosynthesis methodology that predicts the required precursor materials solely based on the chemical formula of the target material without expensive material descriptors ...
2024 was an exceptionally calm year for shark bites. Worldwide, there were only 47 unprovoked attacks, down 22 from the previous year and well below the 10-year average of 70. Four of last year’s attacks resulted in fatalities, also a significant reduction from recent years.
The International Shark Attack File, maintained by the Florida Museum of Natural History, provides data on what are considered unprovoked bites, defined as incidents in which a person does not initiate contact with a shark. Instances in which a person intentionally or unintentionally initiates contact, including spearfishing and releasing sharks ...