(Press-News.org) Darwin’s theory of natural selection provides an explanation for why organisms develop traits that help them survive and reproduce.
Because of this, death is often seen as a failure rather than a process shaped by evolution.
When organisms die, their molecules need to be broken down for reuse by other living things.
Such recycling of nutrients is necessary for new life to grow.
Now a study led by Professor Martin Cann of Durham University’s Department of Biosciences has shown that a type of E-coli bacteria produces an enzyme which breaks the contents of their cells down into nutrients after death.
The dead bacteria are therefore offering a banquet of nutrients to the cells that were their neighbours when they were living.
Professor Cann said: “We typically think of death being the end, that after something dies it just falls apart, rots and becomes a passive target as it is scavenged for nutrients.
“But what this paper has demonstrated is that death is not the end of the programmed biological processes that occur in an organism.
“Those processes continue after death, and they have evolved to do so.
“That is a fundamental rethink about how we view the death of an organism.”
The study has been published in the journal Nature Communications.
Co-author Professor Wilson Poon, from the School of Physics and Astronomy of the University of Edinburgh, inspired the research after posing what he believed were some unanswered questions about why organisms die the way they do.
The researchers assembled and realised they had stumbled across a potentially new area of biology; processes that have evolved to function after death.
Professor Cann said: “One problem remained; we couldn’t work out how an enzyme that functions after death could have evolved.
“Typically, we think of evolution acting on living organisms not dead ones.
“The solution is that neighbouring cells which gain nutrients from the dead cells are likely to be clonally related to the dead cell.
“Consequently, the dead cell is giving nutrients to its relatives, analogous to how animals will often help feed younger members of their family group.”
Co-author Professor Stuart West of the University of Oxford added: “This is like nothing we have observed before – it is equivalent to a dead meerkat suddenly turning into a pile of boiled eggs that the other members of its group could eat.”
The finding demonstrates that processes after death, like processes during life, can be biologically programmed and subject to evolution.
Biomolecules that regulate processes after death might be exploited in the future as novel targets to bacterial disease or as candidates to enhance bacterial growth in biotechnology.
Professor Poon suggests that modelling such processes using the tools of statistical physics may also provide design principles for humans as we move towards a more circular economy in which recycling needs to be built in from the beginning.
ENDS
Media Information
Interviews
Professor Martin Cann of Durham University’s Department of Biosciences is available for interview and can be contacted at m.j.cann@durham.ac.uk
Alternatively, please contact Durham University Marketing and Communications Office on communications.team@durham.ac.uk or +44(0)191 334 8623.
Source Information
‘Bacteria encode post-mortem protein catabolism that enables altruistic nutrient recycling’, Martin J. Cann et al., is published in the journal Nature Communications.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56761-6
The full study will be available via the following link once the embargo has lifted: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-56761-6
About Durham University
Durham University is a globally outstanding centre of teaching and research based in historic Durham City in the UK.
We are a collegiate university committed to inspiring our people to do outstanding things at Durham and in the world.
We conduct research that improves lives globally and we are ranked as a world top 100 university with an international reputation in research and education (QS World University Rankings 2025).
We are a member of the Russell Group of leading research-intensive UK universities and we are consistently ranked as a top 10 university in national league tables (Times and Sunday Times Good University Guide, Guardian University Guide and The Complete University Guide).
For more information about Durham University visit: www.durham.ac.uk/about/
END OF MEDIA RELEASE – issued by Durham University Communications Office.
END
Bacteria evolved to help neighboring cells after death, new research reveals
2025-02-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lack of discussion drives traditional gender roles in parenthood
2025-02-13
Conversations about parental duties continue to be led by mothers, even if both parents earn the same amount of money, finds a new study by a UCL researcher.
A new study by Dr Clare Stovell (IOE, UCL’s Faculty of Education & Society), published in the Journal of Family Studies, highlights how a lack of discussion between parents about important choices such as parental leave, work and childcare is perpetuating traditional gender roles.
The study found that women usually lead the conversations and there is little discussion about the man’s work schedule, even in cases where the woman earns as much or more than her partner.
Dr Stovell said: “These interviews ...
Scientists discover mechanism driving molecular network formation
2025-02-13
Covalent bonding is a widely understood phenomenon that joins the atoms of a molecule by a shared electron pair. But in nature, patterns of molecules can also be connected through weaker, more dynamic forces that give rise to supramolecular networks. These can self-assemble from an initial molecular cluster, or crystal, and grow into large, stable architectures.
Supramolecular networks are essential for maintaining the structure and function of biological systems. For example, to ‘eat’, cells rely ...
Comprehensive global study shows pesticides are major contributor to biodiversity crisis
2025-02-13
Pesticides are causing overwhelming negative effects on hundreds of species of microbes, fungi, plants, insects, fish, birds and mammals that they are not intended to harm – and globally their use is a major contributor to the biodiversity crisis.
That is the finding of the first study assessing the impacts of pesticides across all types of species in land and water habitats, carried out by an international research team that included the UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology (UKCEH) and the University of Sussex.
Multiple negative impacts
The scientists analysed over 1,700 existing lab and field studies of the impacts of 471 different ...
A simple supplement improves survival in patients with a new type of heart disease
2025-02-13
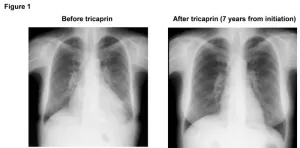
Osaka, Japan – Heart transplant is a scary and serious surgery with high cost, but for patients with heart failure it can be the only option for cure. Now, however, a multi-institutional research team led by Osaka University has found that simply taking a supplement might be all that is needed for certain patients with heart failure to recover – no surgery needed.
In a study published in Nature Cardiovascular Research, the research team found that tricaprin, a natural supplement, can improve long-term survival and recovery from heart failure in patients with triglyceride deposit cardiomyovasculopathy ...
Uncovering novel transcriptional enhancers in neuronal development and neuropsychiatric disorders
2025-02-13
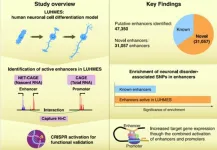
Neuropsychiatric disorders are becoming increasingly prevalent. Given their complex and multifactorial pathogenesis, there is an urgent need for effective and targeted therapies that can improve patients’ quality of life. Genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have identified various genetic alterations that contribute to the development and progression of neuropsychiatric disorders, ranging from mild dyslexia to more severe conditions such as schizophrenia.
While thousands of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)—changes in a single nucleotide position in the DNA—have been associated with neurological ...
IR Sant Pau study reveals immune system’s crucial role in ALS at cellular level
2025-02-13
A team of researchers from the Sant Pau Research Institute (IR Sant Pau) has published a study in the Journal of Neuroinflammation that, for the first time, examines in depth the role of the peripheral immune system in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) at the single-cell level. Their findings suggest that immune system cells—particularly two subpopulations of Natural Killer (NK) cells—may play a crucial part in the development and progression of this neurodegenerative disease.
ALS is a condition that causes the progressive degeneration of motor neurones, leading to a loss of muscle function and, eventually, affecting ...
Brain rhythms can predict seizure risk of Alzheimer’s disease patients, study finds
2025-02-13
A UCLA Health research team has identified changes in brain rhythms that indicate seizure activity in Alzheimer’s patients.
The findings, published in Brain Communications, build on UCLA neurologist and senior author Dr. Keith Vossel’s pioneering work that first linked silent epileptic activity to cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease.
Vossel’s previous studies showed that silent seizures, detected through overnight electroencephalography (EEG) and one-hour magnetoencephalography (MEG), occur in more than 40% of Alzheimer’s patients—beyond the 20% who experience overt seizures. His research has demonstrated ...
Scientists develop innovative DNA hydrogels for sustained drug release
2025-02-13
Hydrogels are polymeric materials with three-dimensional network structures containing large amounts of water. They serve as sustained-release drug delivery systems as they can encapsulate various bioactive substances, including drugs, antigens, and even cells. Hydrogels are better drug delivery alternatives than conventional systems, as they are more biocompatible, biodegradable, and easily administered as an injectable scaffold.
DNA has gained significant attention as a promising hydrogel material thanks to its customizable physicochemical properties, leading to the development of various DNA ...
Paramedics facing challenging end-of-life care demands
2025-02-13
Paramedics in England are experiencing wide-ranging challenges in responding to the increasing number of end-of-life care patients they are being called out to, according to a study from the University of Southampton.
The study published in BMC Palliative Care highlights the issues paramedics face when responding to patients at end-of-life, including a lack of patient information, barriers to administering medication, and insufficient training.
It was funded by Marie Curie and supported by National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Applied ...
Worm study shows hyperactivated neurons cause aging-related behavioral decline
2025-02-13
A study of nematodes by researchers at Nagoya University in Japan has found that aging-related decline in brain function is caused by the excessive activation of certain neurons over time, rather than a decline in neuronal activity. This finding, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, suggests that interventions aimed at reducing neuronal hyperactivation, such as dietary changes, could potentially mitigate age-related cognitive decline.
Proper brain function occurs when a large number of neurons are connected to each other and work ...