(Press-News.org) BINGHAMTON, N.Y. -- Binghamton University maintains its status as an R1 institution for its prolific research activity, according to a new list from the Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education.
Every three years, the Carnegie Classification looks at schools’ research expenditures and graduate programs to evaluate which campuses can be considered an R1 institution for “very high spending and doctorate production.”
Schools with this designation must spend at least $50 million on research and development and award at least 70 research doctorates. Binghamton wrapped up the fiscal year 2023 with more than $141 million in research expenditures, awarding an average of 167 doctorates every academic year since 2020.
This is the third time Binghamton has been named a top research institution, placing it among 187 world-class universities including Harvard, Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Johns Hopkins University.
“Binghamton was first recognized in 2019 as a major research university alongside some of today’s leading global institutions,” University President Harvey Stenger said. “Staying on that same list six years later is proof that our faculty and students have first-rate talent and the persistence to succeed in fields that demand tremendous creativity and dedication.”
Projects related to healthcare, electronics packaging and systems science are among those receiving significant external funding. But scholars from nearly all of Binghamton’s six schools and colleges have been recognized as top academics around the world, according to another study by Stanford University.
“This classification is an exciting achievement showcasing Binghamton’s growing leadership in research nationwide,” said Bahgat Sammakia, vice president for research. “It also cements the importance of supporting our scholars and inventors, as they discover new technologies and solutions addressing today’s societal challenges, whether it’s treating addiction or creating a more sustainable battery.”
Binghamton is a leader in multiple cross-sector coalitions, including SMART USA, which aims to advance semiconductor manufacturing in the United States, as well as New Energy New York, a state- and federally funded initiative to establish the region as a battery innovation and development hub.
Meanwhile, the University’s research capacities also continue to expand, with nearly 20 dedicated research centers in fields ranging from biofilms to cybersecurity to archaeology. The newest among them, the Natural Global Environmental Change Center or NAT-CHANGE, bridges disciplines to solve pressing issues related to climate change.
Students also are key participants in the University’s growing research enterprise, thanks in part to the expansion of schools like the Decker College of Nursing and Health Sciences as well as Binghamton’s signature First-year Research Immersion (FRI) program.
“Research is embedded into Binghamton’s mission. Both undergraduate and graduate students have the ability to contribute to cutting-edge work starting from their very first year on campus, and this continues until they leave with their bachelor’s, master’s or doctorate degrees,” said Donald Hall, provost and executive vice president for academic affairs. “This designation highlights the prowess of our academic community in not only uncovering new knowledge, but also sharing it with future generations.”
END
Binghamton University, State University of New York retains top research ranking among elite universities
Carnegie Classification again names Binghamton to list of R1 institutions
2025-02-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Breaking the pattern: How disorder toughens materials
2025-02-17
Cut open a bone and you’ll see a subtly disordered structure. Tiny beams, called trabeculae, connect to one another in irregular patterns, distributing stress and lending bones an impressive toughness. What if human-made materials could exhibit similar properties?
In a new paper in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Nexus, researchers at Penn Engineering, Penn Arts & Sciences and Aarhus University found that adding just the right amount of disorder to the structure of certain materials can make them more than twice as resistant to cracking.
The finding opens the door to more widespread use of so-called “mechanical metamaterials,” ...
A geometric deep learning method for decoding brain dynamics
2025-02-17
In the parable of the blind men and the elephant, several blind men each describe a different part of an elephant they are touching – a sharp tusk, a flexible trunk, or a broad leg – and disagree about the animal’s true nature. The story illustrates the problem of understanding an unseen, or latent object based on incomplete individual perceptions. Likewise, when researchers study brain dynamics based on recordings of a limited number of neurons, they must infer the latent patterns of brain dynamics that generate these recordings.
“Suppose you and I both engage in a mental task, ...
Novel catalyst development for sustainable ammonia synthesis
2025-02-17
As the world moves toward sustainability, the demand for efficient alternatives across industries continues to grow. Ammonia, a key chemical used in fertilizers, explosives, and various other products, is primarily synthesized through the energy-intensive Haber-Bosch process. This process requires extremely high temperatures and pressures, contributing to global carbon dioxide emissions. Conventional catalysts, such as iron and ruthenium, rely on these harsh conditions to drive the reaction. However, a recent study by researchers from Institute of Science Tokyo, the National Institute for Materials Science, and Tohoku University, Japan, led by Professor Masaaki Kitano, explores ...
Researchers identify DNA changes, biological pathways associated with inherited cancer risk
2025-02-17
Thousands of single changes in the nucleotides that make up the human genome have been associated with an increased risk of developing cancer. But until now, it’s not been clear which are directly responsible for the uncontrolled cellular growth that is the hallmark of the disease and which are simply coincidences or minor players.
Stanford researchers have conducted the first large-scale screen of these inherited changes, called single nucleotide variants, and homed in on fewer than 400 that are essential to initiate and drive cancer growth. These variants control several common biological ...
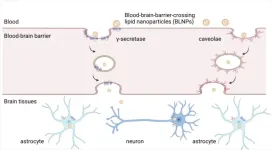
New lipid nanoparticle platform delivers mRNA to the brain through the blood-brain barrier
2025-02-17
New York, NY [February 17, 2025]—Scientists at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai have developed a lipid nanoparticle system capable of delivering messenger RNA (mRNA) to the brain via intravenous injection, a challenge that has long been limited by the protective nature of the blood-brain barrier.
The findings, in mouse models and isolated human brain tissue, were published in the February 17 online issue of Nature Materials [10.1038/s41563-024-02114-5]. They demonstrate the potential of this technology to pave the way for ...
Wildfires in the Andes cause severe soil degradation and hinder ecosystem recovery
2025-02-17
In September 2018, a wildfire burned nearly two thousand hectares of shrubland on the Pichu Pichu volcano, an ecologically significant area in the Peruvian Andes. Unlike Mediterranean ecosystems, where vegetation has evolved strategies to withstand fire, the volcanic soils of Arequipa—one of the driest regions in the world—are not adapted to wildfire disturbances. A Miguel Hernández University of Elche (UMH) research team collected and analyzed soil samples from the burned area at 3,700 meters above sea level to understand how these fragile ecosystems ...
Men and boys matter: Psychology professor reveals hidden issues we need to talk about
2025-02-17
These include those linked to body image, fatherhood and sexual relationships. His latest book - Current Issues Facing Men and Boys – also argues that men struggle to negotiate harmful notions of masculinity and are not included in conversations around gender.
Current Issues Facing Men and Boys urges the public, policymakers, practitioners and other key stakeholders to explore and support policies and practices that promote male wellbeing. This book comes as the UK government announces plans for the country's first men's health strategy, aiming ...
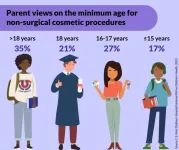
1 in 6 parents support teens getting non-surgical cosmetic procedures with parental consent
2025-02-17
For teens who may be self-conscious about issues such as acne scarring or discolored teeth, non-surgical cosmetic procedures are an increasingly popular way to address their concerns.
And some parents are supportive of this decision, a national poll suggests, with a sixth saying teenagers should be allowed to receive these types of aesthetic treatments for any reason as long as they have parental approval.
But half of parents only support teens getting non-surgical cosmetic procedures if there’s a valid reason – and their beliefs about which reasons count as valid differ – according to ...
Journalist travel grants available for 12th Heidelberg Laureate Forum
2025-02-17
This September, recipients of the Abel Prize, ACM A.M. Turing Award, ACM Prize in Computing, Fields Medal, IMU Abacus Medal and the Nevanlinna Prize are invited to gather in Heidelberg to meet with 200 young researchers from all over the world at the 12th Heidelberg Laureate Forum (HLF). In order to reach a broader, more diverse and international audience, the Heidelberg Laureate Forum Foundation (HLFF) encourages journalists to cover the event and affords them the chance to interact with the preeminent scientists of mathematics and computer science. The 12th HLF will take ...
Are we still primitive? How ancient survival instincts shape modern power struggles
2025-02-17
The evolutionary roots of human dominance and aggression remain central to social and political behaviour, and without conscious intervention these primal survival drives will continue to fuel inequality and division.
These are the arguments of a medical professor who, as global conflicts rise and democracies face growing challenges, says understanding how dominance and tribal instincts fuel division is more critical than ever.
In A New Approach to Human Social Evolution, Professor Jorge A. Colombo MD, PhD explores neuroscience, anthropology, and behavioural science to provide a new perspective on human social evolution.
He argues that fundamental behavioural drives ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
[Press-News.org] Binghamton University, State University of New York retains top research ranking among elite universitiesCarnegie Classification again names Binghamton to list of R1 institutions