(Press-News.org) These include those linked to body image, fatherhood and sexual relationships. His latest book - Current Issues Facing Men and Boys – also argues that men struggle to negotiate harmful notions of masculinity and are not included in conversations around gender.
Current Issues Facing Men and Boys urges the public, policymakers, practitioners and other key stakeholders to explore and support policies and practices that promote male wellbeing. This book comes as the UK government announces plans for the country's first men's health strategy, aiming to address health issues disproportionately affecting men.
Alongside health issues, the book explores everything from fatherhood and education to gaming addiction and homelessness, most of which are often ignored because men are too readily seen as ‘the problem’ rather than ‘having problems’, according to the leading academic.
Throughout the book, Professor Hine calls for an urgent shift in thinking and outlines ways to help men who struggle based on a series of principles. These include cultural and gender inclusivity, evidence-based approaches and early intervention, which he says will ultimately improve gender equality.
Benjamin Hine, Professor of Applied Psychology at the University of West London, a leading expert in this area, is also Chair of the Male Psychology Section of the British Psychological Society and co-founder of the Men and Boys Coalition. He believes that, “In today's rapidly shifting societal landscape, where the discourse around gender equality has gained significant momentum, the unique set of challenges faced by men and boys frequently goes unnoticed or is overshadowed.”
“However, it is essential to approach the subject of men's issues without automatically framing men as ‘the problem’. Men, like all individuals, are complex human beings with their own unique struggles, vulnerabilities, and challenges.”
“Moreover, the task of challenging and redefining the role of masculinity in these issues is not merely an academic exercise but a societal imperative. The health and wellbeing of men and boys depends on our collective ability to foster an understanding of masculinity that embraces vulnerability, values emotional literacy, and celebrates diversity.”
Crucially, inclusive, intersectional approaches for men and boys of all backgrounds, including across ethnic, religious, and gender/sexual identities, should be part of natural thinking for all organisations, including an immediate priority on men’s mental health and high suicide rate.
Professor Hine goes on to warn that it is really important how we have these conversations. If young men feel ‘excluded or alienated’ from gender discussions, which often justifiably focus on critical issues facing ‘women and marginalised groups’, this can leave men feeling resentful and lead to them feeling lonely, alienated, depressed, and engaging with extreme views, especially when they seek solace in toxic online spaces. Part of the problem, he argues, is that issues said to affect women and those which impact men have often been rigidly separated when they are in fact closely linked.
As a whistlestop tour of men’s issues, supported by a wealth of empirical evidence, Professor Hine covers everything from mental health, men in the media, education, fatherhood, sexual violence, homelessness, and much more, including gaming addiction, body image issues, and gang violence. This includes examining how different ‘actors’ in society influence these issues, from institutions like the army, prison and the police, to individual influencers like Andrew Tate and Harry Styles.
END
Men and boys matter: Psychology professor reveals hidden issues we need to talk about
Professor Benjamin Hine of the University of West London (UWL) says men and boys are facing a mental health crisis and they need support across a range of challenges.
2025-02-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
1 in 6 parents support teens getting non-surgical cosmetic procedures with parental consent
2025-02-17
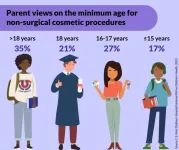
For teens who may be self-conscious about issues such as acne scarring or discolored teeth, non-surgical cosmetic procedures are an increasingly popular way to address their concerns.
And some parents are supportive of this decision, a national poll suggests, with a sixth saying teenagers should be allowed to receive these types of aesthetic treatments for any reason as long as they have parental approval.
But half of parents only support teens getting non-surgical cosmetic procedures if there’s a valid reason – and their beliefs about which reasons count as valid differ – according to ...
Journalist travel grants available for 12th Heidelberg Laureate Forum
2025-02-17
This September, recipients of the Abel Prize, ACM A.M. Turing Award, ACM Prize in Computing, Fields Medal, IMU Abacus Medal and the Nevanlinna Prize are invited to gather in Heidelberg to meet with 200 young researchers from all over the world at the 12th Heidelberg Laureate Forum (HLF). In order to reach a broader, more diverse and international audience, the Heidelberg Laureate Forum Foundation (HLFF) encourages journalists to cover the event and affords them the chance to interact with the preeminent scientists of mathematics and computer science. The 12th HLF will take ...
Are we still primitive? How ancient survival instincts shape modern power struggles
2025-02-17
The evolutionary roots of human dominance and aggression remain central to social and political behaviour, and without conscious intervention these primal survival drives will continue to fuel inequality and division.
These are the arguments of a medical professor who, as global conflicts rise and democracies face growing challenges, says understanding how dominance and tribal instincts fuel division is more critical than ever.
In A New Approach to Human Social Evolution, Professor Jorge A. Colombo MD, PhD explores neuroscience, anthropology, and behavioural science to provide a new perspective on human social evolution.
He argues that fundamental behavioural drives ...
Near-complete skull discovery reveals ‘top apex’, leopard-sized “fearsome” carnivore
2025-02-17
A rare discovery of a nearly complete skull in the Egyptian desert has led scientists to the “dream” revelation of a new 30-million-year-old species of the ancient apex predatory carnivore, Hyaenodonta.
Bearing sharp teeth and powerful jaw muscles, suggesting a strong bite, the newly-identified ‘Bastetodon’ was a leopard-sized “fearsome” mammal. It would have been at the top of all carnivores and the food chain when our own monkey-like ancestors were evolving.
Findings, published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology, detail ...
Reintroducing wolves to Scottish Highlands could help address climate emergency
2025-02-17
University of Leeds news
Embargoed until 05:01 GMT, 17 February
Reintroducing wolves to the Scottish Highlands could lead to an expansion of native woodland which could take in and store one million tonnes of CO2 annually, according to a new study led by researchers at the University of Leeds.
The team modelled the potential impact that wolves could have in four areas classified as Scottish Wild Land, where the eating of tree saplings by growing red deer populations is suppressing natural regeneration of trees and woodland.
They used a predator–prey model to ...
New antibody discovery platform can inform Alzheimer's and Parkinson's
2025-02-15
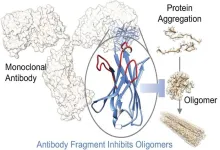
ROCKVILLE, MD – In diseases like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's, specific proteins misfold and clump together, forming toxic aggregates that damage brain cells. The process of proteins spontaneously clumping is called protein aggregation and researchers have developed novel methods to generate aggregate-specific antibodies as specific probes or modulators of the aggregation process.
This new method overcomes significant challenges in characterizing these complex and often transient protein structures. The work will be presented at the 69th Biophysical ...
The Biophysical Journal names Marcel P. Goldchen-Ohm the 2024 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
2025-02-15
ROCKVILLE, MD – Marcel P. Goldschen-Ohm, of the University of Texas at Austin, USA will be honored as the recipient of the Biophysical Journal Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator Award at the 69th Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society, held February 15-19 in Los Angeles, California. This award recognizes the work of outstanding early career investigators in biophysics. The winning paper is titled “GABAA Receptor Subunit M2-M3 Linkers Have Asymmetric Roles in Pore Gating and Diazepam Modulation.” The paper was published in Volume 123, Issue 14 of Biophysical Journal.
GABAA receptors mediate inhibitory synaptic signaling ...
A new system to study phytoplankton: Crucial species for planet Earth
2025-02-15
ROCKVILLE, MD – Phytoplankton, tiny plant-like organisms in the ocean, are incredibly important for life on Earth. They're a major food source for many sea creatures and produce almost half the oxygen we breathe. They also help control the climate by soaking up a lot of carbon dioxide, a gas that contributes to global warming.
Scientists want to learn more about how these phytoplankton use sunlight to make energy and oxygen, which can be useful in the context of environmental monitoring during ...
Scientists discover "genetic weak spot" in endangered Italian bear population
2025-02-15
ROCKVILLE, MD – The Apennine brown bear, also known as the Marsican brown bear (Ursus arctos marsicanus), is a unique and critically endangered subspecies of brown bear found only in the remote and rugged Apennine Mountains of central Italy.
A new study by the Italian Endemixit project (endemixit.com) reveals a potentially critical genetic flaw in the endangered Apennine brown bear population of Italy, offering insights that could help boost conservation efforts. The work will be presented at the 69th Biophysical Society Annual Meeting, to be held February 15 - 19, 2025 in Los Angeles.
This distinct population has been isolated for centuries, evolving unique physical ...
New insights into Alzheimer's brain inflammation
2025-02-15
ROCKVILLE, MD – Brain inflammation, while a crucial part of the body's immune response, takes on a detrimental role in Alzheimer's disease. Unlike the acute, short-lived inflammation that combats infection, the inflammation associated with Alzheimer's becomes chronic and persistent. Scientists have been trying to understand why this happens.
New research reveals key differences in how the brain's immune system responds to the disease compared to a bacterial infection. The work will be presented at the 69th ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
[Press-News.org] Men and boys matter: Psychology professor reveals hidden issues we need to talk aboutProfessor Benjamin Hine of the University of West London (UWL) says men and boys are facing a mental health crisis and they need support across a range of challenges.