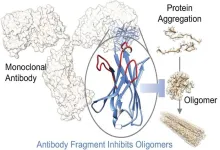
(Press-News.org) ROCKVILLE, MD – In diseases like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's, specific proteins misfold and clump together, forming toxic aggregates that damage brain cells. The process of proteins spontaneously clumping is called protein aggregation and researchers have developed novel methods to generate aggregate-specific antibodies as specific probes or modulators of the aggregation process.
This new method overcomes significant challenges in characterizing these complex and often transient protein structures. The work will be presented at the 69th Biophysical Society Annual Meeting, to be held February 15 - 19, 2025 in Los Angeles.
Most pathological aggregates, called oligomers, are difficult to study with traditional methods, due to their fleeting nature and structural variability. Antibodies, known for their precise target binding, offer a powerful tool for investigating these structures, but generating antibodies against such transitory targets has been a major hurdle.
This new platform integrates computational design and directed evolution to develop new antibodies, which are then screened for their ability to bind to target aggregates or inhibit aggregation process. “We can substantially speed up the process of discovery and production, which can save time and resources,” said Francesco Aprile, PhD, Associate Professor in Biological Chemistry at Imperial College London, who led the study.
Using this platform, Aprile and colleagues successfully generated single-domain antibodies (nanobodies) targeting intrinsically disordered proteins, or proteins that are not defined by one specific three-dimensional structure, but that are constantly changing. “What these intrinsically disordered proteins do is they start to self-assemble and form oligomers and aggregates such as amyloid fibrils, which are a hallmark of Alzheimer’s,” Aprile said.
The nanobodies the researchers developed can target different assemblies of amyloid-beta and alpha-synuclein, proteins associated with Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, respectively. These nanobodies can provide valuable insights into what makes these proteins form toxic oligomers.
“Our platform represents a significant advance in our ability to study protein self-assembly,” said Aprile. “By efficiently generating nanobodies against these challenging targets, we can now delve deeper into the mechanisms underlying these processes and their role in disease.”
Importantly, the research has identified specific regions within amyloid-beta and alpha-synuclein that could be promising therapeutic targets. This discovery opens new avenues for drug development aimed at treating Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Aprile noted, “By targeting these key protein assemblies, we may be able to slow or even prevent disease progression.”
Image Caption:
This new platform integrates computational design and directed evolution to develop new antibodies, which are screened for their ability to bind to toxic aggregates that form in diseases like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's. Courtesy of Francesco Aprile.
###
The Biophysical Society, founded in 1958, is a professional, scientific Society established to lead development and dissemination of knowledge in biophysics. The Society promotes growth in this expanding field through its annual meeting, publications, and committee and outreach activities. Its 7,000 members are located throughout the United States and the world, where they teach and conduct research in colleges, universities, laboratories, government agencies, and industry.
END
ROCKVILLE, MD – Marcel P. Goldschen-Ohm, of the University of Texas at Austin, USA will be honored as the recipient of the Biophysical Journal Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator Award at the 69th Annual Meeting of the Biophysical Society, held February 15-19 in Los Angeles, California. This award recognizes the work of outstanding early career investigators in biophysics. The winning paper is titled “GABAA Receptor Subunit M2-M3 Linkers Have Asymmetric Roles in Pore Gating and Diazepam Modulation.” The paper was published in Volume 123, Issue 14 of Biophysical Journal.
GABAA receptors mediate inhibitory synaptic signaling ...
ROCKVILLE, MD – Phytoplankton, tiny plant-like organisms in the ocean, are incredibly important for life on Earth. They're a major food source for many sea creatures and produce almost half the oxygen we breathe. They also help control the climate by soaking up a lot of carbon dioxide, a gas that contributes to global warming.
Scientists want to learn more about how these phytoplankton use sunlight to make energy and oxygen, which can be useful in the context of environmental monitoring during ...
ROCKVILLE, MD – The Apennine brown bear, also known as the Marsican brown bear (Ursus arctos marsicanus), is a unique and critically endangered subspecies of brown bear found only in the remote and rugged Apennine Mountains of central Italy.
A new study by the Italian Endemixit project (endemixit.com) reveals a potentially critical genetic flaw in the endangered Apennine brown bear population of Italy, offering insights that could help boost conservation efforts. The work will be presented at the 69th Biophysical Society Annual Meeting, to be held February 15 - 19, 2025 in Los Angeles.
This distinct population has been isolated for centuries, evolving unique physical ...
ROCKVILLE, MD – Brain inflammation, while a crucial part of the body's immune response, takes on a detrimental role in Alzheimer's disease. Unlike the acute, short-lived inflammation that combats infection, the inflammation associated with Alzheimer's becomes chronic and persistent. Scientists have been trying to understand why this happens.
New research reveals key differences in how the brain's immune system responds to the disease compared to a bacterial infection. The work will be presented at the 69th ...
ROCKVILLE, MD – In a surprising discovery, scientists have found that the heart possesses "sweet taste" receptors, similar to those on our tongues, and that stimulating these receptors with sweet substances can modulate the heartbeat. This research opens new avenues for understanding heart function and potentially for developing novel treatments for heart failure.
While taste receptors are traditionally associated with the tongue and our ability to perceive flavors, recent studies ...
ROCKVILLE, MD – Viruses, like those that cause COVID-19 or HIV, are formidable opponents once they invade our bodies. Antiviral treatments strive to block a virus or halt its replication. However, viruses are dynamic—constantly evolving and changing shape, which can make designing antiviral treatments a challenge.
But new research utilizes an innovative computational modeling approach to capture the complex and diverse shapes that viral proteins can adopt. The work will be presented at the 69th Biophysical Society Annual Meeting, to be held February 15 - 19, 2025 in Los Angeles.
This new approach, implemented in the open-source Integrative Modeling Platform ...
ROCKVILLE, MD – When scientists develop new molecules—whether for the purposes of agriculture, species control, or life-savings drugs—it’s important to know exactly what its targets are. Thoroughly understanding a molecule's interactions, both intended and unintended, is crucial for ensuring its safety and efficacy.
A cone snail toxin known to affect both insects and fish inspired Weizmann Institute scientists to develop a new way of finding molecular targets. By combining artificial intelligence with traditional ...
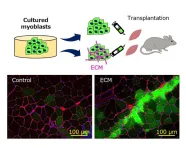
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a way to treat ageing-related muscular atrophy using regenerative medicine. Conventional methods to implant myoblasts, precursors to muscle fiber, required prior scarring for the new cells to graft properly. By adding extracellular matrix (ECM) fluid into the implant, the team successfully grafted myoblasts onto healthy muscle in mice. Their technique opens the way for using implantation to treat unscarred muscle atrophied by ageing.
Age-related muscular atrophy in skeletal muscle can have a devastating impact on people’s quality ...
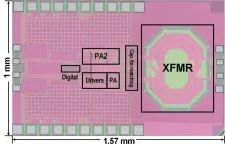
Three innovative design techniques substantially enhance wireless transmitter performance and can boost power efficiency and elevate data rates concurrently, as reported by the researchers from Science Tokyo, Japan. This effectively aligns with the growing demand for speed and efficiency, accelerating the widespread deployment of wireless devices. This enables synergistic operation of wireless electronic devices and better quality of modern life.
Background:
Integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into everyday life requires the interconnectedness of all electronic devices via a technology called the Internet of Things (IoT). The rapid expansion of the IoT market has ...
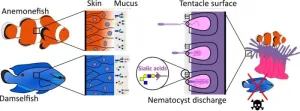
The clownfish-anemone living arrangement is one of the most widely recognized examples of symbiosis. Researchers have made a breakthrough in understanding how anemonefish can live safely among sea anemones without being stung by their venomous tentacles, solving a century-long mystery.
Scientists at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) and their international collaborators have discovered that anemonefish have evolved to maintain very low levels of sialic acid in their skin mucus to avoid triggering the release of nematocysts (stinging cells) in ...