(Press-News.org) ROCKVILLE, MD – In a surprising discovery, scientists have found that the heart possesses "sweet taste" receptors, similar to those on our tongues, and that stimulating these receptors with sweet substances can modulate the heartbeat. This research opens new avenues for understanding heart function and potentially for developing novel treatments for heart failure.
While taste receptors are traditionally associated with the tongue and our ability to perceive flavors, recent studies have shown that these receptors exist in other parts of the body, where they likely play different roles. This new study is the first to identify specific "sweet taste" receptors, known as TAS1R2 and TAS1R3, on the surface of heart muscle cells. The work will be presented at the 69th Biophysical Society Annual Meeting, to be held February 15 - 19, 2025 in Los Angeles.
The new research found that these receptors are not just present on heart muscle, but also functional. When the researchers stimulated these receptors in both human and mouse heart cells using aspartame, a common artificial sweetener, they observed a significant increase in the force of heart muscle contraction and accelerated calcium handling – key processes for a healthy heartbeat.
“After you eat a meal, it's been shown that your heart rate and blood pressure actually are increasing,” said Micah Yoder, a graduate student in the lab of Jonathan Kirk at Loyola University Chicago. “Previously, this was thought to be a neural axis that's being signaled. But we're proposing a more direct consequence, where we have a spike in our blood sugar after eating a meal, and that's binding to these sweet taste receptors on the heart muscle cells, causing a difference in the heartbeat,” he added.
Intriguingly, the researchers also found that these receptors are more abundant in the hearts of patients with heart failure, suggesting a possible link to disease. Further investigation revealed that stimulating the receptors triggers a cascade of molecular events within the heart cells, involving key proteins that control calcium flow and muscle contraction.
"During heart failure, the heart is changing its energetic landscape and prioritizing glucose uptake and glucose usage. So, it's possible that during this energetic change, the heart might need to change its nutrient sensing abilities to accommodate this switch,” Yoder explained.
Additionally, their research may explain why high consumption of artificially sweetened beverages is linked to arrhythmogenesis, or an irregular heartbeat. Not only are these sweet taste receptors particularly stimulated by artificial sweeteners like aspartame, Yoder noted, he found that overstimulation of these sweet taste receptors lead to a an increase in arrhythmic like behavior in the heart cells.
But further research is needed to fully understand the long-term effects of stimulating these receptors in the heart as well as how these receptors might be targeted to strengthen the heart in the case of heart failure.
Image Caption:
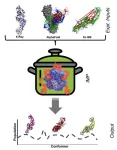
One of the two sweet taste receptors (T1R3) on an adult mouse heart muscle cell. Courtesy of Micah Yoder.
###
The Biophysical Society, founded in 1958, is a professional, scientific Society established to lead development and dissemination of knowledge in biophysics. The Society promotes growth in this expanding field through its annual meeting, publications, and committee and outreach activities. Its 7,000 members are located throughout the United States and the world, where they teach and conduct research in colleges, universities, laboratories, government agencies, and industry.
END
ROCKVILLE, MD – Viruses, like those that cause COVID-19 or HIV, are formidable opponents once they invade our bodies. Antiviral treatments strive to block a virus or halt its replication. However, viruses are dynamic—constantly evolving and changing shape, which can make designing antiviral treatments a challenge.
But new research utilizes an innovative computational modeling approach to capture the complex and diverse shapes that viral proteins can adopt. The work will be presented at the 69th Biophysical Society Annual Meeting, to be held February 15 - 19, 2025 in Los Angeles.
This new approach, implemented in the open-source Integrative Modeling Platform ...
ROCKVILLE, MD – When scientists develop new molecules—whether for the purposes of agriculture, species control, or life-savings drugs—it’s important to know exactly what its targets are. Thoroughly understanding a molecule's interactions, both intended and unintended, is crucial for ensuring its safety and efficacy.
A cone snail toxin known to affect both insects and fish inspired Weizmann Institute scientists to develop a new way of finding molecular targets. By combining artificial intelligence with traditional ...
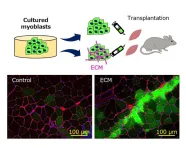
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University have developed a way to treat ageing-related muscular atrophy using regenerative medicine. Conventional methods to implant myoblasts, precursors to muscle fiber, required prior scarring for the new cells to graft properly. By adding extracellular matrix (ECM) fluid into the implant, the team successfully grafted myoblasts onto healthy muscle in mice. Their technique opens the way for using implantation to treat unscarred muscle atrophied by ageing.
Age-related muscular atrophy in skeletal muscle can have a devastating impact on people’s quality ...
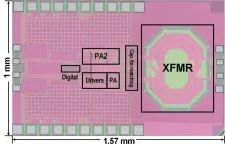
Three innovative design techniques substantially enhance wireless transmitter performance and can boost power efficiency and elevate data rates concurrently, as reported by the researchers from Science Tokyo, Japan. This effectively aligns with the growing demand for speed and efficiency, accelerating the widespread deployment of wireless devices. This enables synergistic operation of wireless electronic devices and better quality of modern life.
Background:
Integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into everyday life requires the interconnectedness of all electronic devices via a technology called the Internet of Things (IoT). The rapid expansion of the IoT market has ...
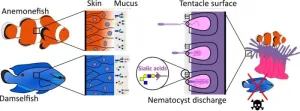
The clownfish-anemone living arrangement is one of the most widely recognized examples of symbiosis. Researchers have made a breakthrough in understanding how anemonefish can live safely among sea anemones without being stung by their venomous tentacles, solving a century-long mystery.
Scientists at the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) and their international collaborators have discovered that anemonefish have evolved to maintain very low levels of sialic acid in their skin mucus to avoid triggering the release of nematocysts (stinging cells) in ...
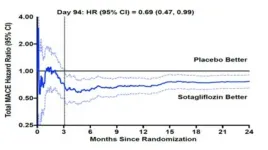
Sotagliflozin, a drug recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration to treat type 2 diabetes and kidney disease with additional cardiovascular risk factors, can significantly reduce heart attack and stroke among these patients, according to results from an international clinical trial led by a Mount Sinai researcher.
Sotagliflozin is a sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) inhibitor. It blocks the function of two proteins, known as SGLT1 and SGLT2, which move glucose and sodium across cell membranes and help control blood sugar levels. Other SGLT2 inhibitors do not as significantly block SGLT1.
The study, published ...
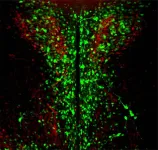
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Scientists discovered years ago that the hypothalamus — which helps to manage body temperature, hunger, sex drive, sleep and more — includes neurons that express the protein opsin 3 (OPN3). Far less clear, however, was what this light-sensing protein does so deep inside the brain.
A study published in PNAS suggests that OPN3 plays an important role in regulating food consumption.
“Our results uncover a mechanism by which the nonvisual opsin ...
New blood test could improve Alzheimer’s Disease diagnosis, research finds
Up to half of all people living with Alzheimer’s Disease in Ireland remain undiagnosed. Now, a new blood test may have the potential to transform patient care, allowing for better diagnosis, earlier interventions and more targeted treatments.
Researchers at Trinity College Dublin, the Tallaght Institute of Memory and Cognition and St James’s Hospital, Dublin are exploring the ability of a new blood test, plasma p-tau217, to detect Alzheimer’s Disease (AD). This test could potentially replace the current diagnostic method, a lumbar puncture/spinal tap (which ...
Cal Poly Assistant Professor Joni Roberts has been chosen, with two additional university faculty members, as the first Cal Poly Faculty Excellence Award honorees.
The inaugural Faculty Excellence Award — an honor recognizing outstanding contributions in teaching, research and service — is administered by the Office of the Provost and funded by generous donor contributions. The award reflects Cal Poly’s commitment to academic excellence and its Learn by Doing philosophy.
The ...
A new Colorado State University study of the interior U.S. West has found that tree ranges are generally contracting in response to climate change but not expanding into cooler, wetter climates – suggesting that forests are not regenerating fast enough to keep pace with climate change, wildfire, insects and disease.
As the climate becomes too warm for trees in certain places, tree ranges have been expected to shift toward more ideal conditions. The study analyzed national forest inventory data for more than 25,000 plots in ...