Professor Kazunari Domen: Groundbreaking contributions to photocatalytic water splitting
Novel materials and techniques for photocatalytic water splitting developed by Professor Kazunari Domen
2025-02-19
(Press-News.org)
Harnessing solar energy to produce hydrogen from water – the photocatalytic water splitting reaction, is a promising approach for the carbon-neutrality future. This process utilizes semiconductor materials to harvest sunlight for the splitting of water into hydrogen fuel with oxygen gas generated as by-product. The solar hydrogen, as a carbon-free energy source, holds immense potential for decarbonizing industries, addressing global energy demands and mitigating environmental challenges. However, realizing practical and economical implementation demands substantial innovative technologies to overcome challenges, in particular achieving efficient solar energy harvesting ability, enhancing charge utilization, ameliorating surface reaction kinetics as well as overcoming barriers for large-scale deployment.
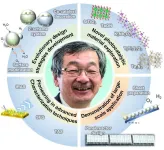
Professor Kazunari Domen, over 40 years of his research career, has established a new paradigm in the field of photocatalytic water splitting, bringing closer to the realization of a carbon-neutral hydrogen economy powered by sunlight and water. His research contributions emphasize the development of innovative materials and techniques that significantly advance the efficiency and scalability of solar hydrogen production, as highlighted in the article published in Chinese Journal of Catalysis (https://doi.org/10.1016/S1872-2067(24)60152-X). This article underscores the pivotal contributions by Professor Domen in shaping the future of artificial photosynthesis, providing a strategic blueprint for achieving a sustainable energy goal.
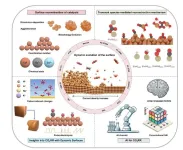
Central to the achievements by Professor Domen is the exploration of novel photocatalytic materials, capable of capturing visible light and driving water-splitting reactions efficiently. The state-of-the-art materials including oxides, (oxy)nitrides, and oxysulfides, have redefined the possibilities in photocatalytic research and ushered the beginning of the new era in the field. Leaping forward, the team led by Professor Domen introduced new modification strategies, such as cocatalyst engineering, surface modification and construction of Z-scheme system, to achieve evolutionary performance improvement. Another hallmark of Professor Domen’s research is the utilization of advanced characterization techniques, for instance the transient absorption spectroscopy and the interfacial sum-frequency generation spectroscopy, to unravel the underlying mechanisms behind photocatalytic processes. These insights have guided the strategic design of high-performance systems, seamlessly integrating core scientific principles with practical engineering solutions.
The legacy of Professor Domen lies not only in the groundbreaking development of technologies, but also the ability to translate these innovations into scalable solutions. His team revolutionizes cost-effective device fabrication techniques, culminating in the successful development of the first real-world hydrogen production panel system through photocatalytic overall water splitting under natural sunlight. The 100-square-metre panel stands as the largest solar hydrogen production unit to date. Besides marking a significant milestone, his work demonstrates the feasibility of large-scale solar-driven hydrogen production, paving the way for a clean energy future.
###
About the Journal
Chinese Journal of Catalysis is co-sponsored by Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Chinese Chemical Society, and it is currently published by Elsevier group. This monthly journal publishes in English timely contributions of original and rigorously reviewed manuscripts covering all areas of catalysis. The journal publishes Reviews, Accounts, Communications, Articles, Highlights, Perspectives, and Viewpoints of highly scientific values that help understanding and defining of new concepts in both fundamental issues and practical applications of catalysis. Chinese Journal of Catalysis ranks among the top one journals in Applied Chemistry with a current SCI impact factor of 15.7. The Editors-in-Chief are Profs. Can Li and Tao Zhang.
At Elsevier http://www.journals.elsevier.com/chinese-journal-of-catalysis
Manuscript submission https://mc03.manuscriptcentral.com/cjcatal
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-02-19
The continued massive consumption of fossil fuels in modern societies has led to a range of environmental issues, including excessive CO2 emissions. In this regard, electrochemical CO2 reduction can convert intermittent electricity into chemical fuels and other value-added products, which holds the potential to close the carbon cycle. Among the various catalysts, metals are the most extensively studied heterogeneous CO2RR electrocatalysts and can be classified into three categories based on the main products. Containing Bi, ...
2025-02-19
New Rochelle, NY, February 19, 2025—A new study in the peer-reviewed Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research (JICR) showed that a specific retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) agonist RNA (RAR) induces innate immune signaling and death of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro. Click here to read the article now.
Michael Gale, Jr., from the University of Washington School of Medicine, and coauthors, evaluated the actions of a specific RIG-I agonist RNA against two distinct human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. RAR is a synthetic-modified ...
2025-02-19
The Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC) is pleased to announce that registration is now open for its Annual Meeting, taking place May 28-31, 2025 in Phoenix, Arizona. This premier event is designed to provide healthcare professionals with the latest practical care strategies and scientific advancements in the field of multiple sclerosis and other CNS inflammatory conditions.
The CMSC Annual Meeting brings together leading MS specialists, researchers, and healthcare clinicians for a dynamic program featuring cutting-edge research, innovative treatment approaches, and interactive courses. Attendees will have the opportunity ...
2025-02-19
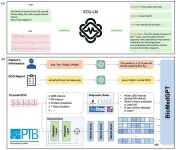
A team of researchers from Tsinghua University and Beijing Tsinghua Changgung Hospital has introduced a cutting-edge method to improve the interpretation of electrocardiogram (ECG) data. Their innovative model, called ECG-LM, leverages the power of large language models (LLMs) to interpret complex ECG signals more effectively and accurately. The groundbreaking research was published in Health Data Science, offering a transformative approach that promises to revolutionize heart-related diagnostics.
Electrocardiograms ...
2025-02-19
About The Study: In a representative study of adults experiencing homelessness in California, there was a high proportion of current drug use, history of overdose, and unmet need for treatment. Improving access to treatment tailored to the needs of people experiencing homelessness could improve outcomes.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ryan D. Assaf, PhD, MPH, email ryan.assaf@ucsf.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.27922)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
2025-02-19
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that it is possible to predict diagnostic transition to schizophrenia and bipolar disorder from routine clinical data extracted from electronic health records, with schizophrenia being notably easier to predict than bipolar disorder.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lasse Hansen, MSc, PhD, email lasse.hansen@clin.au.dk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2024.4702)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
2025-02-19
U.S. hospital occupancy after the end of the Covid-19 pandemic is significantly higher than it was before the pandemic, setting the stage for a hospital bed shortage as early as 2032, new research suggests.
In the decade leading up to the pandemic, U.S. average hospital occupancy was approximately 64%. In a study to be published in the peer-reviewed journal JAMA Network Open, the team of UCLA researchers found that the new post-pandemic national hospital occupancy average is 75% -- a full 11 percentage points ...
2025-02-19
About The Study: The U.S. has achieved a new post-pandemic hospital occupancy steady state 11 percentage points higher than it was pre-pandemic. This persistently elevated occupancy appears to be driven by a 16% reduction in the number of staffed U.S. hospital beds rather than by a change in the number of hospitalizations. Experts in developed countries have posited that a national hospital occupancy of 85% constitutes a hospital bed shortage (a conservative estimate). The findings of the current study show that the U.S. could reach this dangerous threshold as soon as 2032, with some ...
2025-02-19
About The Study: After more than 10 years of follow-up in the Swiss Multicenter Bypass or Sleeve Study randomized clinical trial, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass demonstrated superiority over sleeve gastrectomy for patient excess body mass index loss.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ralph Peterli, MD, email ralph.peterli@clarunis.ch.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2024.7052)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author ...
2025-02-19
In the next five years, integrating AI into country response systems could save more lives by anticipating the location and trajectory of disease outbreaks.
Global group of researchers call for better collaboration between academia, government and industry, to ensure safety, accountability and ethics in the use of AI in infectious disease research.
A study published in Nature today outlines for the first time how advances in AI can accelerate breakthroughs in infectious disease research and outbreak response.
The study – which ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Professor Kazunari Domen: Groundbreaking contributions to photocatalytic water splitting
Novel materials and techniques for photocatalytic water splitting developed by Professor Kazunari Domen