(Press-News.org) New Rochelle, NY, February 19, 2025—A new study in the peer-reviewed Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research (JICR) showed that a specific retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) agonist RNA (RAR) induces innate immune signaling and death of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro. Click here to read the article now.
Michael Gale, Jr., from the University of Washington School of Medicine, and coauthors, evaluated the actions of a specific RIG-I agonist RNA against two distinct human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. RAR is a synthetic-modified RNA motif derived from the hepatitis C virus genome that is specifically recognized by RIG-I and induces innate immune activation, including production of interferon (IFN)-b,when delivered to cells. The investigators showed that RAR-induced cell death is potentiated by addition of recombinant IFN-b.
Based on the current study and previously published work, the investigators propose a model for RAR-induced cell death. “We conclude that RAR treatment could contribute to strategies for the control of liver cancer and other cancer types.”
“The findings described in this report suggest a potential new mechanism for treating patients with hepatocellular carcinoma,” says Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research Executive Editor, Raymond Donnelly, PhD.
About the Journal
Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research (JICR) is an authoritative peer-reviewed journal published monthly online with open access options and in print that covers all aspects of interferons and cytokines from basic science to clinical applications. Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research is an official journal of the International Cytokine & Interferon Society. Complete tables of content and a sample issue may be viewed on the JICR website.
About the Publisher
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. is a global media company dedicated to creating, curating, and delivering impactful peer-reviewed research and authoritative content services to advance the fields of biotechnology and the life sciences, specialized clinical medicine, and public health and policy. For complete information, please visit the Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. website.
END
Synthetic RIG-I-agonist RNA induces death of hepatocellular carcinoma cells
2025-02-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Registration now open for CMSC Annual Meeting in Phoenix, AZ
2025-02-19
The Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers (CMSC) is pleased to announce that registration is now open for its Annual Meeting, taking place May 28-31, 2025 in Phoenix, Arizona. This premier event is designed to provide healthcare professionals with the latest practical care strategies and scientific advancements in the field of multiple sclerosis and other CNS inflammatory conditions.
The CMSC Annual Meeting brings together leading MS specialists, researchers, and healthcare clinicians for a dynamic program featuring cutting-edge research, innovative treatment approaches, and interactive courses. Attendees will have the opportunity ...
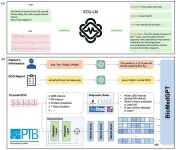
Breakthrough in heart health: A new approach to interpreting ECG data using large language models
2025-02-19
A team of researchers from Tsinghua University and Beijing Tsinghua Changgung Hospital has introduced a cutting-edge method to improve the interpretation of electrocardiogram (ECG) data. Their innovative model, called ECG-LM, leverages the power of large language models (LLMs) to interpret complex ECG signals more effectively and accurately. The groundbreaking research was published in Health Data Science, offering a transformative approach that promises to revolutionize heart-related diagnostics.
Electrocardiograms ...
Illicit substance use and treatment access among adults experiencing homelessness
2025-02-19
About The Study: In a representative study of adults experiencing homelessness in California, there was a high proportion of current drug use, history of overdose, and unmet need for treatment. Improving access to treatment tailored to the needs of people experiencing homelessness could improve outcomes.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ryan D. Assaf, PhD, MPH, email ryan.assaf@ucsf.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.27922)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, ...
Predicting diagnostic progression to schizophrenia or bipolar disorder via machine learning
2025-02-19
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that it is possible to predict diagnostic transition to schizophrenia and bipolar disorder from routine clinical data extracted from electronic health records, with schizophrenia being notably easier to predict than bipolar disorder.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lasse Hansen, MSc, PhD, email lasse.hansen@clin.au.dk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2024.4702)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
U.S. facing critical hospital bed shortage by 2032
2025-02-19
U.S. hospital occupancy after the end of the Covid-19 pandemic is significantly higher than it was before the pandemic, setting the stage for a hospital bed shortage as early as 2032, new research suggests.
In the decade leading up to the pandemic, U.S. average hospital occupancy was approximately 64%. In a study to be published in the peer-reviewed journal JAMA Network Open, the team of UCLA researchers found that the new post-pandemic national hospital occupancy average is 75% -- a full 11 percentage points ...
Health care staffing shortages and potential national hospital bed shortage
2025-02-19
About The Study: The U.S. has achieved a new post-pandemic hospital occupancy steady state 11 percentage points higher than it was pre-pandemic. This persistently elevated occupancy appears to be driven by a 16% reduction in the number of staffed U.S. hospital beds rather than by a change in the number of hospitalizations. Experts in developed countries have posited that a national hospital occupancy of 85% constitutes a hospital bed shortage (a conservative estimate). The findings of the current study show that the U.S. could reach this dangerous threshold as soon as 2032, with some ...
Long-term outcomes of laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass vs laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy for obesity
2025-02-19
About The Study: After more than 10 years of follow-up in the Swiss Multicenter Bypass or Sleeve Study randomized clinical trial, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass demonstrated superiority over sleeve gastrectomy for patient excess body mass index loss.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Ralph Peterli, MD, email ralph.peterli@clarunis.ch.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2024.7052)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author ...
Advances in AI can help prepare the world for the next pandemic, global group of scientists find
2025-02-19
In the next five years, integrating AI into country response systems could save more lives by anticipating the location and trajectory of disease outbreaks.
Global group of researchers call for better collaboration between academia, government and industry, to ensure safety, accountability and ethics in the use of AI in infectious disease research.
A study published in Nature today outlines for the first time how advances in AI can accelerate breakthroughs in infectious disease research and outbreak response.
The study – which ...
Emergency clinicians increase prescriptions of buprenorphine, effectively help patients get started on the path to recovery
2025-02-19
In the face of the alarming number of opioid-related deaths in the U.S., there have been national efforts to increase emergency clinician prescribing of buprenorphine, a medication used to treat opioid use disorder. In a new study published in JAMA, UCLA Health researchers report on the extent and success rate of such efforts in California.
Opioid-related emergency department (ED) visits, hospitalizations, and deaths have increased markedly since 1999, and the growing number of cases was declared a public health emergency in 2024. Combined ...
New sensor can take any gas and tell you what’s in it
2025-02-19
Expert sommeliers can take a whiff of a glass of wine and tell you a lot about what’s in your pinot noir or cabernet sauvignon.
A team of physicists at CU Boulder and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have achieved a similar feat of sensing, only for a much wider range of substances.
The group has developed a new laser-based device that can take any sample of gas and identify a huge variety of the molecules within it. It is sensitive enough to detect those molecules at minute concentrations all the way down to parts per trillion. ...