(Press-News.org) Toronto, ON - Preteens who spend more time on screens are more likely to develop manic symptoms years two-years later, according to a new study published in Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology.
The findings reveal that 10- to 11-year-olds who engage heavily with social media, video games, texting, and videos show a greater risk of symptoms such as inflated self-esteem, decreased need for sleep, distractibility, rapid speech, racing thoughts, and impulsivity — behaviors characteristic of manic episodes, a key feature of bipolar-spectrum disorders.
“Adolescence is a particularly vulnerable time for the development of bipolar-spectrum disorders,” said first author, Jason Nagata, MD, an associate professor of pediatrics at the University of California, San Francisco. “Given that earlier onset of symptoms is linked with more severe and chronic outcomes, it’s important to understand what might contribute to the onset or worsening of manic symptoms in teenagers.”
Symptoms of social media and video game addiction, characterized by the inability to stop despite trying, withdrawal, tolerance, conflict, and relapse, may play a role. “Screen addictions and irregular sleep patterns may exacerbate manic symptoms in susceptible teens,” said Nagata.
The study adds to the wealth of knowledge on the associations between screen use and poor mental health in adolescents. The study uses data from the nationwide Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) study, the largest long-term study of brain development in the United States.
“This study underscores the importance of cultivating healthy screen use habits early,” says co-author Kyle Ganson, PhD, assistant professor at the University of Toronto’s Factor-Inwentash Faculty of Social Work. “Future research can help us better understand the behaviors and brain mechanisms linking screen use with manic symptoms to help inform prevention and intervention efforts.”
The study collected data from 9,243 early adolescents aged 10-11 years. Study participants provided information about their typical screen habits, as well as whether they had experienced manic or hypomanic symptoms.
“Although screen time can have important benefits such as education and increased socialization, parents should be aware of the potential risks, especially to mental health,” said Nagata. “Families can develop a media plan which could include screen-free times before bedtime.”
END
Screen time linked to bipolar and manic symptoms in U.S. preteens
Social media, video games, texting, and videos tied to manic symptoms two years later
2025-02-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
In ancient stellar nurseries, some stars are born of fluffy clouds
2025-02-20
Fukuoka, Japan—How are stars born, and has it always been this way?
Stars form in regions of space known as stellar nurseries, where high concentrations of gas and dust coalesce to form a baby star. Also called molecular clouds, these regions of space can be massive, spanning hundreds of light-years and forming thousands of stars. And while we know much about the life cycle of a star thanks to advances in technology and observational tools, precise details remain obscure. For example, did stars form this way in the early universe?
Publishing in The Astrophysical Journal, researchers from Kyushu University, in collaboration with Osaka Metropolitan ...
Blood pressure drug could be a safer alternative for treating ADHD symptoms, finds study
2025-02-20
Blood pressure drug could be a safer alternative for treating ADHD symptoms, finds study
Repurposing amlodipine, a commonly used blood pressure medicine, could help manage attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms, according to an international study involving the University of Surrey.
In a study published in Neuropsychopharmacology, researchers tested five potential drugs in rats bred to exhibit ADHD-like symptoms. Among them, only amlodipine, a common blood pressure medication, significantly reduced hyperactivity.
To ...
Daily cannabis use linked to public health burden
2025-02-20
WASHINGTON (Feb. 20, 2025)--A new study analyzes the disease burden and the risk factors for severity among people who suffer from a condition called cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome. Researchers at the George Washington University say the condition occurs in people who are long-term regular consumers of cannabis and causes nausea, uncontrollable vomiting and excruciating pain in a cyclical pattern that often leads to repeated trips to the hospital.
“This is one of the first large studies to examine the burden of disease associated with this cannabis-linked syndrome,” says Andrew Meltzer, professor of emergency medicine ...
A new gene identified in the search for a therapy to treat malignant cardiac arrythmia
2025-02-20
Cardiac arrhythmias affect millions across the world and are responsible for a fifth of all deaths in the Netherlands. Currently there are multiple treatment options, ranging from life-long medication to invasive surgical procedures. Research from Amsterdam UMC and Johns Hopkins University, published today in the European Heart Journal, sets another important step in the hunt for a one-off gene therapy that could improve heart function and protect against arrhythmias.
"Arrhythmias often occur due to slowing of conduction of the electrical impulse through the heart. Rapid impulse conduction is needed for ...
‘Fog harvesting’ could yield water for drinking and agriculture in the world’s driest regions
2025-02-20
With less annual rainfall than 1 mm per year, Chile’s Atacama Desert is one of the driest places in the world. The main water source of cities in the region are underground rock layers that contain water-filled pore spaces which last recharged between 17,000 and 10,000 years ago.
Now, local researchers have assessed if ‘fog harvesting,’ a method where fog water is collected and saved, is a feasible way to provide the residents of informal settlements with much needed water.
“This research represents a notable shift in the ...
Unveiling the intricate mechanisms behind oxysterol-induced cell death
2025-02-20
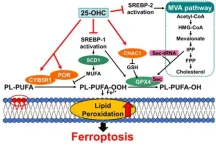
Oxysterols are a class of molecules derived from cholesterol via oxidation or as byproducts of cholesterol synthesis. Despite their relatively low concentration within our bodies, oxysterols are known to play many important biological roles, acting as transcriptional regulators, precursors for bile acid, and key players in brain development.
On the flip side, some pathologies are associated with imbalances in oxysterols. In particular, 25-hydroxycholesterol (25-OHC) has been shown to contribute to arteriosclerosis, cancer development, central nervous system ...
Closing the recycle loop: Waste-derived nutrients in liquid fertilizer
2025-02-20
Growing plants can be a joyous, yet frustrating process as plants require a delicate balance of nutrients, sun, and water to be productive.
Phosphorus and nitrogen, which are essential for plant growth, are often supplemented by chemical fertilizers to assure proper balance and output of produce. However, the amount of these nutrients on the planet is increasing due to excessive use, which in turn is causing various environmental problems. For this reason, there is a growing movement to promote sustainable agriculture through the recycling of phosphorus and nitrogen. In Japan, a target has been ...
vmTracking enables highly accurate multi-animal pose tracking in crowded environments
2025-02-20
Studying the social behavior of animals in their natural environments is necessary for advancing our understanding of neurological processes. To achieve this, tracking multiple individuals simultaneously and accurately as they interact in shared spaces is crucial. Traditional multi-animal tracking systems, such as multi-animal DeepLabCut (maDLC) and Social LEAP Estimates Animal Poses (SLEAP), use frame-by-frame identification to predict movements without the need for markers. While these tools effectively track poses, such as head direction, in simple scenarios, ...
A special collection to highlight recent advances in air pollution complex research in China
2025-02-20
Air pollution is a global environmental problem with serious impacts on human health, climate change, and ecological systems. In China, rapid development in the last several decades has led to a drastic increase in coal consumption and the number of vehicles. As a result, air pollution in China is complicated by the coexistence of high concentrations of primary and secondary trace gases and aerosol particles from multiple sources.
Air pollution complex is a term used to characterize the formation mechanisms of air pollution, and was first proposed by Professor Xiaoyan Tang in 1997. A better understanding of these complex mechanisms is critical for meeting the urgent societal ...
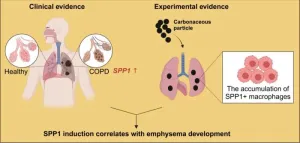
Macrophages express high level of Spp1, linking the environmental particle pollution exposure and the development of emphysema - an important finding for COPD
2025-02-20
This study is led by Dr. Lianyong Han and Dr. Tobias Stoeger in Germany (Institute of Lung Health and Immunity (LHI), Comprehensive Pneumology Center (CPC), Helmholtz Zentrum München, German Research Center for Environmental Health).
By analyzing multiple emphysema and COPD patient datasets, SPP1 is significantly upregulated in the lungs of patients, compared to healthy individuals. “These findings pointed out the clinical relevance of SPP1 induction during COPD development and has motivated us to understand their contributions ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Screen time linked to bipolar and manic symptoms in U.S. preteensSocial media, video games, texting, and videos tied to manic symptoms two years later