(Press-News.org) Investigators at Mass General Brigham have developed a tool that can identify older adults at increased risk of emergency healthcare needs, rehospitalization or death. The tool measured patient frailty, an aging-related syndrome, by integrating the health records of more than 500,000 individuals collected across multiple hospitals at Mass General Brigham. These findings, published in Journal of the American Geriatric Society, could help clinicians care for high-risk patients even without the availability of comprehensive primary care records.
“Frailty is associated with higher risk of falls, hospitalization and potentially preventable healthcare system costs,” said co-first author Bharati Kochar MD, MS, of the Gastroenterology Unit and the Mongan Institute Center for Aging and Serious Illness at Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham healthcare system. “But it can be challenging to measure frailty using routinely collected data in electronic health records (EHRs). Patients often receive care across multiple healthcare systems, which can lead to incomplete information on aging-related health deficits. Our study demonstrates we can overcome these challenges to help identify patients at risk for adverse health outcomes.”
In this study, researchers examined EHR data from patients who received care at hospitals within the Mass General Brigham system. The analysis included patients aged 60 and above, who had experienced between 1-2 outpatient visits within a 2- or 3-year period prior to 2017, as well as a sub-cohort that received primary care within the same time window. The investigators developed a frailty index that classified patients as robust, pre-frail, frail or very frail based on the presence or absence of 31 age-related health deficits in their EHR data.
Among 518,449 patients with a mean age of 71.94 years, the research team identified 72.9% as robust, 15.8% as pre-frail, 6.9% as frail and 2.8% as very frail. Compared to robust individuals, very frail individuals had increased rates of death and hospital readmission within a 90-day window. Rates of worse outcomes increased from pre-frail to very frail individuals, relative to robust individuals.
“Our study shows that frailty can be measured in EHRs, even when data is incomplete,” said senior author Ariela R. Orkaby, MD, MPH, of the Division of Aging at Brigham and Women’s Hospital. “For hospitals caring for an older and sicker population, an automated frailty tool, such as the Mass General Brigham-Electronic Frailty Index, is a rapid way to identify patients at highest risk of an adverse health outcome. We hope that this tool will help improve care of all older adults entering the healthcare system.”
The authors note that while the work was made possible through cross-system collaboration at Mass General Brigham, the tool could also help other health systems identify older adults at risk of outcomes that adversely impact overall health and well-being.
Authorship: In addition to Kochar, Mass General Brigham authors include David Cheng, Elizabeth Araka, Christine S. Ritchie, and Ariela R. Orkaby. Additional authors include Hanna-Riikka Lehto, Nelia Jain, and Rachelle Bernacki.
Disclosures: Kochar reports consulting fees for Pfizer, Inc & Bristol-Meyers Squibb, relationships ended. Jain is now affiliated with Devoted Health, Waltham, Massachusetts, USA.
Funding: National Institutes of Health (R03AG074059, K76AG083309, R03AG060169, IK2CX001800, P30AG031679, R01AG081287), Paivikki and Sakari Sohlberg Foundation.
Paper cited: Kochar B et al. “Application of an electronic frailty index to identify high risk older adults using electronic health record data” Journal of the American Geriatrics Society DOI: 10.1111/jgs.19389
END
New frailty measurement tool could help identify vulnerable older adults in epic
Investigators at Mass General Brigham have developed a tool that can identify older adults at increased risk of emergency healthcare needs, rehospitalization or death
2025-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Co-prescribed stimulants, opioids linked to higher opioid doses
2025-02-21
COLUMBUS, Ohio – The combination of prescribed central nervous system stimulants, such as drugs that relieve ADHD symptoms, with prescribed opioid medications is associated with a pattern of escalating opioid intake, a new study has found.
The analysis of health insurance claims data from almost 3 million U.S. patients investigated prescribed stimulants’ impact on prescription opioid use over 10 years, looking for origins of the so-called “twin epidemic” of combining the two classes of drugs, which can increase the risk for overdose deaths.
“Combining the two drugs is associated ...
What if we could revive waste carbon dioxide?
2025-02-21
As the severity of climate change and carbon emissions becomes a global concern, technologies to convert carbon dioxide (CO₂) into resources such as chemical fuels and compounds are urgently needed. Dr. Dahee Park’s research team from the Nano Materials Research Division at the Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS), has collaborated with Professor Jeong-Young Park’s team from the Department of Chemistry at KAIST to develop a catalyst technology that significantly enhances the efficiency of carbon dioxide (CO2) conversion.
Conventional ...
Mechanochemistry strikes again – A facile means for generating organolithium molecules
2025-02-21
Mechanochemistry using a ball mill demonstrates versatility for generating academically and industrially significant organolithium compounds.
Organolithium compounds, molecules containing a carbon–lithium bond, are excellent precursors for building new carbon–carbon and other carbon–heteroatom bonds. They are widely utilized in both academia and industry for their applications in polymer synthesis, pharmaceuticals, and general organic synthesis. A conventional method for generating organolithiums is done ...
Breakthrough in high-performance oxide-ion conductors using rubidium
2025-02-21
Rubidium could be the next key player in oxide-ion conductors. Researchers at Institute of Science Tokyo have discovered a rare rubidium (Rb)-containing oxide-ion conductor, Rb₅BiMo₄O₁₆, with exceptionally high conductivity. Identified through computational screening and experiments, its superior performance stems from low activation energy and structural features like large free volume and tetrahedral motion. Its stability under various conditions offers a promising direction for solid oxide fuel cells and clean energy technologies.
Oxide-ion ...
Hurricane-proofed downtown skyscrapers unexpectedly vulnerable to ‘bouncing’ winds
2025-02-21
Houston, we have a problem. The ‘Space City’ boasts 50 buildings over 150 meters tall. These were designed to withstand hurricanes, to which Texas is prone. But on May 16th, 2024, a derecho – a wide, long-lived windstorm associated with rapidly moving showers or thunderstorms – managed to cause unexpected damage to many of the tall buildings downtown. The socio-economic impact was significant, due to traffic disruptions, businesses temporarily closing, and the need for repairs.
Why ...
Microcomb chips help pave the way for thousand times more accurate GPS systems
2025-02-21
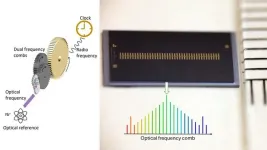
Optical atomic clocks can increase the precision of time and geographic position a thousandfold in our mobile phones, computers, and GPS systems. However, they are currently too large and complex to be widely used in society. Now, a research team from Purdue University, USA, and Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, has developed a technology that, with the help of on-chip microcombs, could make ultra-precise optical atomic clock systems significantly smaller and more accessible – with significant benefits for navigation, autonomous vehicles, and geo-data monitoring.
Today, our mobile phones, computers, ...
Illuminating the proton’s inner workings
2025-02-21
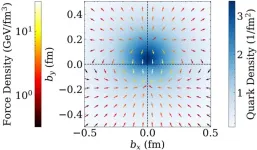
Scientists have now mapped the forces acting inside a proton, showing in unprecedented detail how quarks—the tiny particles within—respond when hit by high-energy photons.
The international team includes experts from the University of Adelaide who are exploring the structure of sub-atomic matter to try and provide further insight into the forces that underpin the natural world.
“We have used a powerful computational technique called lattice quantum chromodynamics to map the forces acting inside ...
Genetic therapy gives infants life-changing improvements in sight
2025-02-21
Four young children have gained life-changing improvements in sight following treatment with a pioneering new genetic medicine through UCL Institute of Ophthalmology and Moorfields Eye Hospital, with the support of MeiraGTx.
The children were born with a severe impairment to their sight due to a rare genetic deficiency that affects the AIPL1 gene. The condition, a form of retinal dystrophy, means those affected are born with only sufficient sight to distinguish between light and darkness. The gene defect causes ...
Impacts of workplace bullying on sleep can be “contagious” between partners
2025-02-21
Workplace bullying affects not only the employee’s sleep but their partner’s too, according to new research published today.
Exposure to bullying by superiors and/or colleagues has been linked to a variety of negative health outcomes, such as sleep problems.
Now research by the University of East Anglia (UEA) in the UK, and Complutense University of Madrid and Seville University in Spain, sheds light on the short-term consequences of workplace bullying on various indicators of sleep.
These include waking up too early (sleep severity), interference with daily life (sleep impact) and dissatisfaction with own sleep (sleep satisfaction).
Writing in ...
UK peatland fires are supercharging carbon emissions as climate change causes hotter, drier summers
2025-02-21
A new study led by the University of Cambridge has revealed that as our springs and summers get hotter and drier, the UK wildfire season is being stretched and intensified. More fires, taking hold over more months of the year, are causing more carbon to be released into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
Fires on peatlands, which are carbon-rich, can almost double global fire-driven carbon emissions. Researchers found that despite accounting for only a quarter of the total UK land area that burns each year, dwarfed by moor and heathland, peatland fires have caused up to 90% of annual UK fire-driven carbon emissions since 2001 – with emissions ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
[Press-News.org] New frailty measurement tool could help identify vulnerable older adults in epicInvestigators at Mass General Brigham have developed a tool that can identify older adults at increased risk of emergency healthcare needs, rehospitalization or death