(Press-News.org) An autonomous underwater vehicle can propel itself efficiently by using the energy in nearby water currents. Underwater and aerial vehicles must make their way through a complex environment of gusts and currents, fighting against many flows as they attempt to stay on course. Peter Gunnarson and John O. Dabiri designed an underwater robot that makes use of these flows to cut down on the energy needed to travel, “surfing” vortices to make its way to its destination. The palm-sized robot, CARL, was equipped with an onboard inertial measurement unit, ten motors to allow movement in all three axes, and a simple but effective algorithm: if the magnitude of the acceleration in the crossflow-direction exceeded a threshold, CARL would swim in the same direction as the acceleration. The robot was tested in a 1.5 m deep and 5 m long tank, in which vortex rings were generated by pulsing a wall-mounted thruster. Using the algorithm, CARL was able to surf the vortex from one end of the tank to another using one-fifth of the energy as a robot without the same programming. According to the authors, CARL’s success surfing a prototypical flow structure, suggests that with further elaboration, a similar technique could be used to allow autonomous vehicles to improve their efficiencies significantly by interacting with background flows.
END
Submersible robot surfs water currents
2025-02-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Using brain scans to forecast human choice at scale
2025-02-25
Neuroimaging can capture brain activity in response to stimuli before a person decides how to respond. Initial affective responses—broadly good or bad feelings about a stimulus—have been associated with activity in evolutionarily conserved subcortical and cortical circuits including the Nucleus Accumbens (NAcc) and Anterior (AIns). Activity then continues through integrative circuits associated with more deliberative and reflective processing. Previous work has suggested that the early affective responses may be more ...
AI’s emotional blunting effect
2025-02-25
Ask a Large language model (LLM) such as ChatGPT to summarize what people are saying about a topic, and although the model might summarize the facts efficiently, it might give a false impression of how people feel about the topic. LLMs play an increasingly large role in research, but rather than being a transparent window into the world, they can present and summarize content with a different tone and emphasis than the original data, potentially skewing research results. Yi Ding and colleagues compared a climate dataset of 18,896,054 tweets that mentioned "climate change" from January 2019 to December 2021 to rephrased tweets prepared by LLMs. The authors found that the ...
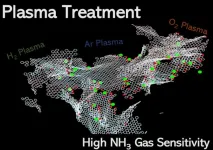
Modifying graphene with plasma to produce better gas sensors
2025-02-25
Gas sensing technologies play a vital role in our modern world, from ensuring our safety in homes and workplaces to monitoring environmental pollution and industrial processes. Traditional gas sensors, while effective, often face limitations in their sensitivity, response time, and power consumption.
To account for these drawbacks, recent developments in gas sensors have focused on carbon nanomaterials, including the ever-popular graphene. This versatile and relatively inexpensive material can provide exceptional sensitivity ...
Study reveals Africa will reach 1.5C climate change threshold by 2040 even under low emission scenarios
2025-02-25
New research highlighted in the journal CABI Reviews suggests that all five subregions of Africa will breach the 1.5°C climate change threshold – the limit stipulated by the Paris Agreement – by 2040 even under low emission scenarios.
A team of scientists, from the University of Zimbabwe, and the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) in Kenya, conducted a literature review to develop a framework for just transition pathways for Africa’s agriculture towards low emission and climate resilient development under 1.5°C of global warming.
They found that despite Africa ...
Researchers discover 16 new Alzheimer’s disease susceptibility genes
2025-02-25
Investigators from Mass General Brigham have conducted a multi-ancestry, whole genome sequencing association study of Alzheimer’s disease and found evidence for 16 new susceptibility genes, expanding the study of Alzheimer’s disease in underrepresented groups. Their results are published in Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association.
For the study, co-led by Julian Daniel Sunday Willett, MD, PhD, and Mohammad Waqas, of the Genetics and Aging Research ...
We need a new definition of dyslexia, research says
2025-02-25
A new definition of dyslexia is needed to more accurately describe the learning disorder and give those struggling with dyslexia the specific support they require, says new research.
Dyslexia has had several different definitions over the years and this murky and complicated history means it can be a postcode lottery for children who may have dyslexia, or those who have been diagnosed but can’t access the support they need.
The first step to fixing this issue, new research has argued, is to redefine dyslexia and adopt the new definition across the UK.
The research was conducted by the University of Birmingham, the SpLD Assessment Standards Committee (SASC), Kings College London, ...
Young women suffering menopause symptoms in silence, study reveals
2025-02-25
More than half of women ages 30 to 35 are already suffering moderate to severe symptoms associated with menopause, yet most women are waiting decades before seeking treatment, new research from UVA Health and the Flo women’s health app reveals.
The research sheds important light on “perimenopause,” the transition period leading to menopause. Many women in perimenopause assume they’re too young to be suffering symptoms related to menopause, believing that symptoms won’t appear until they reach their 50s. But this ...
Rebels of health care use technology to connect with clinicians, information, and each other
2025-02-25
Rebels of health care use technology to connect with clinicians, information, and each other
Cambridge, MA – February 25, 2025 – The future of health care is being forged in the crucible of rare disease. A new survey led by Susannah Fox, author of Rebel Health: A Field Guide to the Patient-Led Revolution in Medical Care (The MIT Press), finds that 15% of U.S. households are affected by rare disease or an undiagnosed illness. Their lives are characterized by extreme stress, often matched by their resourcefulness.
“People living with rare diseases push the edges of what is possible by using technology ...
Smart is sexy: evolution of intelligence partly driven by love
2025-02-25
The Beatles said it best: Love is all you need. And according to new research from The Australian National University (ANU), the same is true in the animal kingdom. Well, at least for mosquitofish – a matchstick-sized fish endemic to Central America and now found globally.
According to the ANU scientists, male mosquitofish possess impressive problem-solving skills and can successfully navigate mazes and other tests. Males that perform better have a higher chance of mating.
Lead author Dr Ivan Vinogradov said male mosquitofish ...
Have we been wrong about why Mars is red?
2025-02-25
Mars is easily identifiable in the night sky by its prominent red hue. Thanks to the fleet of spacecraft that have studied the planet over the last decades, we know that this red colour is due to rusted iron minerals in the dust. That is, iron bound up in Mars’s rocks has at some point reacted with liquid water, or water and oxygen in the air, similar to how rust forms on Earth.
Over billions of years this rusty material – iron oxide – has been broken down into dust and spread all around the planet by winds, a process that continues today.
But iron ...