(Press-News.org) On February 7, 2025, the U.S. National Institutes of Health announced a decision to cap indirect cost reimbursement—which supports the critical infrastructure and staff that make biomedical research possible—at 15%. In a commentary published February 28 in the Cell Press journal Cell, molecular biologist Tom Maniatis of the New York Genome Center (NYGC) and Columbia University's Zuckerman Institute reflects on the impact NIH funding has had on his own career and science, explores the value indirect investment has brought to U.S. science over the last five decades, and calls for urgent, unified action from the scientific community to prevent the cap from taking effect.
“The U.S. scientific ecosystem has long been an engine of innovation, fueled by strategic investment and collaborative effort,” writes Maniatis. “We must act swiftly and decisively to safeguard the future of science in the United States and ensure that research institutions have the resources they need to continue their essential work.”
Although the NIH decision has been temporarily blocked by a federal judge, it continues to raise significant concern in the scientific community because the proposed cap is significantly lower than the rate currently negotiated between the agency and many of the research institutions it funds. Maniatis was invited by Cell to share his perspective on this issue after the launch of a petition he created with his team at the NYGC; the petition has already garnered its targeted 5,000 signatures.
Maniatis believes that small, independent institutions will be harmed the most by this decision—and that that is cause for concern for everyone. In the commentary, he writes: “The NYGC has an over-decade-long history of bringing together broad, multidisciplinary collaborations … that are beyond the scope of any single institution. If the NIH indirect cost reimbursement rates are capped at 15%, small independent research institutions, like the NYGC, will be shuttered, stifling technological innovation, scientific progress, and collaboration.”
His commentary also expands on the bipartisan history of the NIH, including how it has been funded over time and the impact it has had on U.S. innovation, healthcare, and economic growth. In addition to inviting the scientific community and the public to sign the NYGC petition, he suggests the following:
Bringing together stakeholders from across universities, independent research institutes, medical centers, and professional societies to speak against this decision
Engaging with policymakers to ensure they understand why indirect cost reimbursement exists in its current form and the consequences this decision would have
Collaborating with industry leaders, foundations, and philanthropists to bring attention to the broader economic and societal impact of weakening the U.S. scientific enterprise
“Advances in technology and the resulting deepened understanding of human biology at the molecular level have been beyond anything we could have imagined in 1971,” he writes, looking back at when he was awarded his first NIH grant. “My scientific career, and that of most scientists I know, would not have been possible without the steady support from the NIH, not only for salaries and supplies for my lab, but also providing funds to support the building, infrastructure, and utilities where my labs have been located, as well as the essential administrative support that has made our work possible.”
###
Cell, Maniatis, “Safeguarding the Future of Biomedical Science in the United States” https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(25)00212-0 DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.02.024
Cell (@CellCellPress), the flagship journal of Cell Press, is a bimonthly journal that publishes findings of unusual significance in any area of experimental biology, including but not limited to cell biology, molecular biology, neuroscience, immunology, virology and microbiology, cancer, human genetics, systems biology, signaling, and disease mechanisms and therapeutics. Visit http://www.cell.com/cell. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact press@cell.com.
END
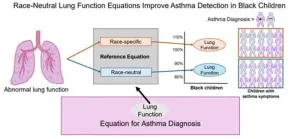
Despite ongoing progress, structural racism and health disparities continue to shape healthcare practices in ways healthcare providers may not even realize. A recent study in JAMA Network Open, published Feb. 28, 2025, shows that continued use of race-specific equations in the diagnostic process of children with asthma symptoms limits the identification of reduced lung function in Black children.
“This finding is important because when these children are not identified as having reduced lung function, they may not receive further testing. This can lead to under-diagnosis, ...
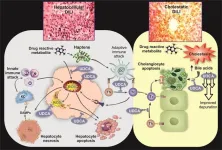
Hepatic steatosis, often triggered by non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is a leading cause of liver dysfunction globally, affecting approximately 30% of the population. The progression from steatosis to hepatic fibrosis, which may ultimately lead to cirrhosis, is a significant concern in liver disease management. This review highlights the critical role of solute carrier (SLC) family transporters in both hepatic steatosis and fibrosis. SLC transporters are membrane-bound proteins responsible for transporting a variety of molecules, including fatty acids, ...
Scientists have a new target to prevent cold sores after University of Virginia School of Medicine researchers discovered an unexpected way the herpes virus re-activates in the body. The finding could also have important implications for genital herpes caused by the same virus.
The discovery from UVA’s Anna Cliffe, PhD, and colleagues seems to defy common sense. She and her team found that the slumbering herpes virus will make a protein to trigger the body’s immune response as part of its escape from dormancy. You’d think this would be bad for the virus – that activating the body’s ...
Glenview, Illinois – The American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST), the PF Warriors, the Rare Disease Diversity Coalition (RDDC)—a program at the Black Woman's Health Imperative—and the National Association of Community Health Workers (NACHW) announce their collaboration to address idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) as a chronic disease on Rare Disease Day 2025.
Together, the organizations will employ designated activities that will build a knowledge base on the current IPF landscape ...
The study, which examined 121 babies aged three to twelve months in Accra, the capital of Ghana, demonstrates a remarkable variety of language input in the early months of life. The children are regularly exposed to two to six languages. Strikingly, the number of caregivers the children have also ranges between two and six, and babies who have more adults in their daily lives who regularly take care of them also hear more different languages. In Ghana, families often live in so-called “compound buildings”, where many ...
Virginia Tech is spearheading a research coalition to reveal the untapped potential of the greater Appalachian Mountains region.
This coalition aims to accelerate the identification and characterization of unconventional critical mineral resources throughout the area. It brings together academic institutions, research laboratories, federal and state natural resource offices, and consultancies, all collaborating with the end goal of boosting regional economic growth and creating new jobs.
The research team, led by Richard Bishop, professor of practice in ...
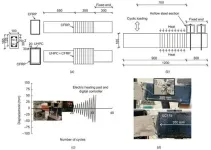
A recent study published in Engineering delves into the behavior of reinforced concrete beams strengthened with Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymer (CFRP) and Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC) under thermocyclic loading. This research, conducted by Ju-Hyung Kim and Yail J. Kim, aims to understand the effects of multi-hazard loading on these strengthened structures, which is crucial for the maintenance and rehabilitation of existing buildings.
Multi-hazards, such as the combination of seismic events and high temperatures, pose ...
Paul Armsworth, Distinguished Service Professor in the Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, has received a 2025 Southeastern Conference Faculty Achievement Award for excellence in teaching, research and service.
He and the 15 other recipients this year — one from each SEC member university — are now nominated for the SEC Professor of the Year Award, which will be announced later in the spring.
“I am thrilled to receive this recognition, but it is also very humbling to be celebrated in this ...
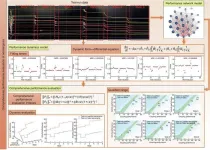
A recent study published in Engineering presents a groundbreaking method for comprehensively evaluating the performance of aeroengines, the crucial components powering aircraft. Authored by Shubin Si and other researchers from esteemed institutions in China, this research addresses long-standing challenges in aeroengine performance assessment.
Aeroengines are complex systems, and their performance directly impacts flight safety and efficiency. Traditional evaluation methods, such as airlines relying on single-parameter indicators like exhaust gas temperature or manufacturers conducting ...
A study led by UMass Chan researchers demonstrated that a gene therapy to correct a mutation that causes maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) prevented newborn death, normalized growth, restored coordinated expression of the affected genes and stabilized biomarkers in a calf as well as in mice.
“Simply put, we believe the gene therapy demonstrated in both animal species, especially in the cow, very well showcases the therapeutic potential for MSUD, in part because the diseased cow, without treatment, has a very similar metabolic profile as the patients,” said Dan Wang, PhD, assistant ...