(Press-News.org) COLUMBUS, Ohio – Novel technology intends to redefine the virtual reality experience by expanding to incorporate a new sensory connection: taste.
The interface, dubbed ‘e-Taste’, uses a combination of sensors and wireless chemical dispensers to facilitate the remote perception of taste – what scientists call gustation. These sensors are attuned to recognize molecules like glucose and glutamate — chemicals that represent the five basic tastes of sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami. Once captured via an electrical signal, that data is wirelessly passed to a remote device for replication.
Field testing done by researchers at The Ohio State University confirmed the device’s ability to digitally simulate a range of taste intensities, while still offering variety and safety for the user.
“The chemical dimension in the current VR and AR realm is relatively underrepresented, especially when we talk about olfaction and gustation,” said Jinghua Li, co-author of the study and an assistant professor of materials science and engineering at Ohio State. “It’s a gap that needs to be filled and we’ve developed that with this next-generation system.”
The system, whose development was inspired by previous biosensor work of Li’s, utilizes an actuator with two parts: an interface to the mouth and a small electromagnetic pump. This pump connects to a liquid channel of chemicals that vibrates when an electric charge passes through it, pushing the solution through a special gel layer into the mouth of the subject.
Depending on the length of time that the solution interacts with this gel layer, the intensity and strength of any given taste can easily be adjusted, said Li.
“Based on the digital instruction, you can also choose to release one or several different tastes simultaneously so that they can form different sensations,” she said.
The study was published today in the journal Science Advances.
Taste is a subjective sense that can change from one moment to another. Yet this complex feeling is the product of two of the body’s chemical sensing systems working in tandem to ensure what you eat is safe and nutritious, the gustation and the olfactory (or smell) senses.
“Taste and smell are greatly related to human emotion and memory,“ said Li. “So our sensor has to learn to capture, control and store all that information.”
Despite the difficulty involved in replicating similar taste sensations for a majority of people, researchers found that in human trials, participants could distinguish between different sour intensities in the liquids generated by the system with an accuracy rate of about 70%.
Further tests assessing e-Taste’s ability to immerse players in a virtual food experience also analyzed its long-range capabilities, showing that remote tasting could be initiated in Ohio from as far away as California. Another experiment involved subjects trying to identify five food options they perceived, whether it was lemonade, cake, fried egg, fish soup or coffee.
While these results open up opportunities to pioneer new VR experiences, this team’s findings are especially significant because they could potentially provide scientists with a more intimate understanding of how the brain processes sensory signals from the mouth, said Li.
Plans to enhance the technology revolve around further miniaturizing the system and improving the system’s compatibility with different chemical compounds in food that produce taste sensations. Beyond helping to build a better and more dynamic gaming experience, the study notes that the work could be useful in promoting accessibility and inclusivity in virtual spaces for individuals with disabilities, like those with traumatic brain injuries or Long Covid, which brought gustatory loss to mainstream attention.
“This will help people connect in virtual spaces in never-before-seen ways,” said Li. “This concept is here and it is a good first step to becoming a small part of the metaverse.”
Other Ohio State co-authors include Shulin Chen, Yizhen Jia, Tzu-Li Liu, Qi Wang and Prasad Nithianandam and Chunyu Yang, including Bowen Duan and Zhaoqian Xie from Dalian University of Technology, Xiao Xiao and Changsheng Wu from the National University of Singapore, Xi Tian from Tsinghua University.
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation, the National Institute Of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, the Chronic Brain Injury Pilot Award Program at Ohio State, the Center for Emergent Materials; the Center for Exploration of Novel Complex Materials, the Institute for Materials Research, the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Dalian Outstanding Young Talents in Science and Technology.
#
Contact: Jinghua Li, Li. 1107@osu.edu
Written by Tatyana Woodall, Woodall.52@osu.edu
END
URBANA, Ill. – Nanozymes are synthetic materials that have enzyme-like catalytic properties, and they are broadly used for biomedical purposes, such as disease diagnostics. However, inorganic nanozymes are generally toxic, expensive, and complicated to produce, making them unsuitable for the agricultural and food industries. A University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign research team has developed organic-material-based nanozymes that are non-toxic, environmentally friendly, and cost effective. In two new studies, they introduce ...
ITHACA, N.Y. – When people go along with opinions that go against their better judgment, they feel more culpable for the decision if things go wrong than if they hadn’t received another opinion, new research from Cornell University finds.
The effect may seem counterintuitive, but going against one’s better judgment increases thoughts about better decisions that could have been made, which amplify feelings of control over the situation.
“If you have another person in the ...
HOUSTON – (Feb. 28, 2025) – A team of researchers at the George R. Brown School of Engineering and Computing at Rice University has developed an innovative artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled, low-cost device that will make flow cytometry ⎯ a technique used to analyze cells or particles in a fluid using a laser beam ⎯ affordable and accessible.
The prototype identifies and counts cells from unpurified blood samples with similar accuracy as the more expensive and bulky conventional flow cytometers, provides results within minutes and is significantly cheaper and compact, making it highly attractive for point-of-care clinical ...
In a study published today in Biofunctional Materials, Prof. Dr. Haidar, Founder and CEO of BioMAT’X I+D+I LABs in Santiago, Chile, unveils a groundbreaking advancement in dental care: Copper-incorporated microvesicles (CiMs). This innovative technology combines the healing power of copper with microvesicles to enhance tissue regeneration, promote healing, and combat oral diseases. With potential applications in dentistry, cranio-maxillo-facial surgery and beyond, CiMs; a promising leap forward in biomedical technology.
In an exciting breakthrough ...
NEW YORK, NY (February 28, 2025) -- Primary care practices that employ nurse practitioners (NPs) are more likely to serve socioeconomically disadvantaged communities than practices with no NPs on staff, Columbia University School of Nursing researchers report in JAMA Network Open. Assistant Professor Monica O’Reilly-Jacob, PhD, led the study, published online February 28, 2025.
To better understand the distribution of NPs—who are increasingly critical to improving access to primary care—O’Reilly-Jacob and her colleagues looked ...
The Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center is conducting a research study that will look at whether calcium, vasopressin, or both early in the course of treatment would help severely injured patients that lose a lot of blood survive their injuries.
The CAlcium and VAsopressin following Injury Early Resuscitation (CAVALIER) trial will include approximately 1,050 people aged 18 to 90. Patients who have traumatic injuries with loss of blood may be enrolled by participating emergency medical personnel during their transportation to the hospital or after arrival to University Medical Center Hospital.
CAVALIER is an Exception from Informed Consent (EFIC) trial, meaning that, the trial ...
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – Who, or rather what, will be the next top model?
Data scientists and developers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility are trying to find out, exploring some of the latest artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to help make high-performance computers more reliable and less costly to run.
The models in this case are artificial neural networks trained to monitor and predict the behavior of a scientific computing cluster, where torrents of numbers are constantly crunched. The goal is to help system administrators quickly identify and ...
DALLAS, Feb. 28, 2025 — Cardiovascular disease disproportionately affects Black communities, with more than 57% of non-Hispanic Black adults living with some form of the disease. To drive solutions that address these disparities, the American Heart Association, a global force changing the future of health for all, launched the Heart of Innovation HBCU Challenge to empower the next generation of health tech entrepreneurs from Historically Black Colleges and Universities (HBCUs).
On Monday, Shadrach ...
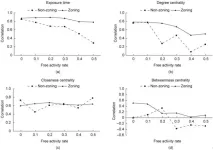
A recent study published in the journal Engineering delves into the complex world of assessing the transmission risk of infectious diseases in indoor spaces. With the ongoing impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, understanding how to accurately evaluate the effectiveness of non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) has become crucial.
Governments worldwide implemented NPIs to control the spread of COVID-19. Many studies used simulations to measure the risk of infection transmission before and after implementing these measures. However, the choice of metric to quantify ...
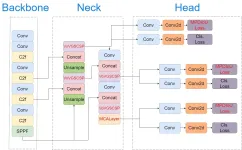
Researchers have unveiled a groundbreaking AI-driven approach to improve the early diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder by analyzing micro-expressions in movies. Micro-expressions, which are fleeting facial movements that reveal hidden emotions, are particularly challenging to detect in individuals with ASD. By employing the Cinemetrics method, the team successfully extracted micro-expressions from films featuring ASD patients and utilized an enhanced YOLOv8-SMART algorithm for precise detection. This advanced model significantly outperformed existing methods, achieving remarkable ...