Research supports move toward better tailoring stroke rehabilitation
Georgetown and MedStar Health research hope new MRI technique to help predict and guide patients’ recovery
2025-03-03
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON – A new Georgetown University Medical Center study in collaboration with MedStar Health and the National Institutes of Health exploring a new brain imaging technique is bringing stroke experts a step closer to better tailoring rehabilitation.
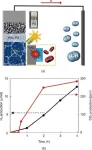
Neurologists often use MRI images of the brain’s white matter to glean information about a person’s ability to recover, but a new imaging technique added to MRI allows clinicians to better see the condition of white matter tracts leading to the limbs, an observation usually only seen after death during an autopsy.
“A white matter tract called the corticospinal tract provides the main wiring that goes from your brain down to your spinal cord to help power your arms and legs,” explains study leader, Matthew A. Edwardson, MD, an associate professor of neurology at Georgetown University School of Medicine and a vascular neurologist and a member of the stroke team at MedStar Georgetown University Hospital. “If those cables are severed or atrophied, the person is not going to be able to regain meaningful use of their arms and legs – they wouldn’t have much motor strength.”
The imaging technique used by Edwardson and his colleagues is called diffusion tensor-based morphometry (DTBM). It combines directional information about the structures in the brain with the shape and size of the structures being imaged. Previously it was difficult to separate the white matter cables from the gray matter using morphometry approaches because they did not include the directional information. This two-part technique allows researchers to map and quantify changes over time in the white matter tracts.
“To our knowledge, this is the first study to allow us to measure atrophy of these tracts in stroke survivors,” says Edwardson, a member of the Center for Brain Plasticity and Recovery, a joint collaboration between Georgetown University and MedStar National Rehabilitation Network.
He and colleagues from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) describe their findings in March 3, 2025 in the journal Neurology (“Association between changes in white matter volume detected with diffusion tensor-based morphometry and motor recovery after stroke”).
“Now, we can see if the cables have shrunk in size which would indicate that a stroke has caused enough damage to the brain to lead to the wiring becoming atrophied,” says Edwardson. “That observation is strongly correlated with how well somebody will recover. If there's a lot of atrophy in the brain in those cables, they're not going to have much ability to recover their arm function after a stroke.”
Edwardson says further studies would be needed before the observations could be used to tailor stroke rehabilitation.
“It would be helpful for the therapist to know at the time of admission to inpatient rehabilitation whether there's some likelihood of their patient regaining function,” he says. “If it is determined that the patient isn’t likely to recover meaningful motor use, then the therapist could change their strategy to perhaps focus on the unimpaired side with strategies to compensate for the disability.”
###
Along with Edwardson co-authors of the publication are Amritha Nayak, ME, M. Okan Irfanoglu, PhD; and Carlo Pierpaoli, MD, PhD; of NIH’s National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering; and . Marie Luby, PhD; and Lawrence L. Latour, PhD; of NIH’s National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
The authors report having no personal financial interests related to the study.
Funding was received from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (UL1TR000101), and Georgetown’s Clinical and Translational Science Award.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-03-03
Learning to think more about specific events in the future appears to reduce impulsivity, improve decision-making, and shows potential as a therapy for alcohol use disorder, a new Virginia Tech study found.
The study, which involved 24 participants whose brains were scanned during both resting-state and task-based fMRI, showed brain connections were altered by future thinking.
The research, published recently in the journal Brain Connectivity, was among the last led by the late Warren Bickel, professor and director of the Addiction Recovery Research Center at the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute ...
2025-03-03
A recent study published in Engineering presents an innovative strategy for converting plastic waste into useful products. The research, led by a team of scientists from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) and other institutions, focuses on polystyrene (PS), a commonly used plastic that poses significant challenges for waste management.
Plastic pollution has become a pressing environmental issue due to the increasing production and improper disposal of plastic products. PS, in particular, is difficult to degrade naturally and often ends up in landfills or the environment, contributing to the spread of microplastics. Current methods for treating ...
2025-03-03
When sea otters were reintroduced along the coastlines of islands in Southern California and British Columbia, researchers saw kelp forests return to areas that were destroyed by sea urchins. But how slow or fast they grew back depended on the location — and until now, scientists didn’t understand why.
New CU Boulder research found sea otters, an important keystone species, play a vital role in kelp forest recovery, but their level of influence depends on what other species they interact with in salty Pacific Ocean waters. The study, published ...
2025-03-03
A new study from Tulane University suggests that repeated collapse and reopening of tiny alveoli—air sacs in the lungs essential for breathing—during mechanical ventilation may cause microscopic tissue damage, playing a key role in ventilator-related injuries that contribute to thousands of deaths annually.
Published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), the study sheds light on ventilator-induced lung injury, a complication that gained increased attention during the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to a surge in patients requiring ...
2025-03-03
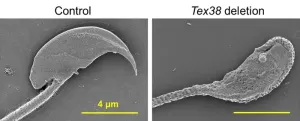
Osaka, Japan – The human body is full of checks and balances that ensure correct growth, development, and function of all our different systems. Now, researchers from Japan have reported a newly discovered protein interaction that regulates sperm development.
In a study to be published soon in PNAS, a multi-institutional research team led by Osaka University has revealed that the interaction between two specific proteins is crucial for ensuring that sperm cells develop properly.
Sperm formation is a highly complex process that involves many changes ...
2025-03-03
A Yale-led research team has uncovered how a naturally occurring biological mechanism found in mammals is able to prevent sperm cells from interacting with an egg, preventing fertilization.
The discovery, identified in rodent models, offers a new path for scientific research to help people grappling with infertility issues, while also opening a new line of study for developing contraceptive therapies. The findings appear in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“This will have direct implications ...
2025-03-03
In a recent study published in Engineering, researchers have developed an innovative analytical framework for ecological security assessment, prediction, and zoning management. Guided by the Social–Economic–Natural Complex Ecosystems (SENCE) theory, this framework aims to enhance ecological security for sustainable development.
The Daqing River Basin in the North China Plain was chosen as a case study due to its ecological significance and the increasing human-land conflicts. The research team established an assessment index system based on the pressure-state-response ...
2025-03-03
A recent study published in Engineering introduces an innovative design paradigm for reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs), aiming to enhance their design efficiency and versatility. This research, led by a team of scientists from Southeast University and Guangzhou University, offers a fresh approach to address the challenges in RIS design.
RISs, enabled by digital coding technology, are crucial for manipulating electromagnetic (EM) waves in real-time. They play a significant role in 5G and 6G research. However, traditional automatic RIS design methods face issues. Most involve extensive numerical simulations ...
2025-03-03
Researchers have widely accepted that impulsivity increases the risk of drug addiction, but the evidence to support this belief is mixed. Exploring the relationship between impulsivity and cocaine use in rats, Yihong Yang and colleagues from the National Institute on Drug Abuse found evidence that contradicts the prevailing view that high impulsivity predicts cocaine use.
One classification of impulsivity is impulsive choice, which can be studied with risky choice tasks and delay-discounting tasks (DDT). During DDT, impulsive individuals prefer smaller, ...
2025-03-03
London’s Ultra Low Emission Zone (ULEZ) is transforming children’s journeys to school by making streets safer, improving perceptions of air quality and encouraging children to live healthier lives. A new study published today in BMJ Open, and funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR), highlights its benefits, with many families noticing cleaner air and safer roads. However, it also reveals challenges, particularly for those living in outer boroughs who are more reliant on the car and may struggle to adapt.
Road traffic is a major source of air pollution in London, posing serious health risks. One in 11 children in the city has asthma, a condition ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Research supports move toward better tailoring stroke rehabilitation
Georgetown and MedStar Health research hope new MRI technique to help predict and guide patients’ recovery