(Press-News.org) In a crowning achievement, the University of Auckland Business School is one of the best in the world, successfully gaining triple crown accreditation - a mark of excellence held by only one percent of business schools globally.
The Business School was the first in Australasia to attain triple crown status in 2004, a recognition it has maintained for two decades.
Triple crown status is achieved if a business school can meet the strict requirements of three international accreditation bodies – the Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business (AACSB), the Association of MBAs (AMBA) and the European Quality Improvement System (EQUIS).
The Business School is the longest-standing triple crown accredited school in the region, with all three international accrediting bodies praising many aspects of its operations in the latest round of accreditation awards.
The European Quality Improvement System awarded accreditation to the School based on overall quality, viability and a commitment to continuous improvement. It also considered internationalisation and corporate connections.
The Business School's commitment to excellence, academic quality and innovative programme design were among several areas that impressed assessors from the Association of MBAs, an institution known for stringent criteria that evaluate teaching, curriculum and student interaction.
Meanwhile, accreditation from the Association to Advance Collegiate Schools of Business is achieved by just six percent of the world's business schools and is considered the gold standard in global business education.
Business schools that earn this accreditation must demonstrate a commitment to excellence in teaching, research, curriculum development and student success. In the latest accreditation renewal, the organisation commended the Business School for its outstanding research engagement, research-led teaching and strong commitment to positive societal impact through faculty and departmental research centres.
It said: "The recent establishment of the Energy Centre and Inclusive Capitalism Centre as faculty-level research centres has brought increased emphasis to research agendas of critical significance for New Zealand and the Asia-Pacific region."
It also praised the Business School for actively driving initiatives to improve research impact, such as the national research translation competition, which sees academics translate complex studies into relatable reads.
“Additionally, the experience of the School in developing a wide range of research engagements and collaborations with industry partners, such as with prominent Māori owned seafood company, Moana New Zealand, lead the way in informing classroom learning through rich case study development that prioritises local issues and solutions.”
Business School Dean, Professor Susan Watson
Business School Dean Susan Watson says the triple crown achievement is a testament to the School's exceptional performance across teaching, research, student success and industry engagement.
"With the successful completion of all three accreditations in an exceptionally compressed timeframe, the Business School continues to demonstrate remarkable organisational capability and sustained excellence," she says.
"This recognises our innovative programme design, impactful research and meaningful industry engagement - both in New Zealand and on the world stage."
She says the Business School also earned accolades for its cultural leadership.
"Our unique integration of Māori perspectives and commitment to diversity sets u
END
Business School celebrates triple crown
In a crowning achievement, the University of Auckland Business School is one of the best in the world, successfully gaining triple crown accreditation - a mark of excellence held by only one percent of business schools globally.
2025-03-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Can Rhizobium + low P increase the yield of common bean in Ethiopia?
2025-03-04
Common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) is a leguminous plant that can form a symbiotic relationship with rhizobia in the soil. Rhizobia convert nitrogen in the atmosphere into ammonia, providing nitrogen nutrition for leguminous plants. However, due to the low effectiveness of rhizobia in the soil, common bean has one of the lowest nitrogen fixation efficiencies among food legumes. Some studies have shown that pre-inoculating common bean seeds with elite rhizobial strains can enhance nitrogen fixation, thereby promoting the plant growth of common bean and increasing the grain yield. As one of the most important food legumes in Ethiopia, the grain yield of common bean is quite low, because of the lack ...
Research Security Symposium on March 12
2025-03-04
In recent years, with the increasing openness and internationalization of research, the risks of inappropriate exploiting openness of research have become more apparent. With the growing importance of research security, the issue of how to safely promote cutting-edge research and international collaboration while respecting research freedom is becoming more important in many countries.
The Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) organizes the symposium aiming to create an opportunity to deepen discussion on efforts necessary to protect research freedom. The symposium will consist of ...
Special type of fat tissue could promote healthful longevity and help maintain exercise capacity in aging
2025-03-04
Rutgers Health researchers have made discoveries about brown fat that may open a new path to helping people stay physically fit as they age.
A team from Rutgers New Jersey Medical School found that mice lacking a specific gene developed an unusually potent form of brown fat tissue that expanded lifespan and increased exercise capacity by roughly 30%. The team is working on a drug that could mimic these effects in humans.
“Exercise capacity diminishes as you get older, and to have a technique ...
Researchers develop high-water-soluble pyrene tetraone derivative to boost energy density of aqueous organic flow batteries
2025-03-04
Aqueous organic flow batteries (AOFBs) hold promise for renewable energy integration and electricity grid storage due to their inherent safety, as well as the availability of naturally abundant and synthetically tunable organic redox-active molecules (ORAMs). However, challenges such as low energy density, poor stability at high concentrations, and high synthesis costs hinder their commercial viability.
Developing ORAMs that offer both high energy density and ultra-stable cycling performance is essential for advancing stationary energy storage ...
Who gets the lion’s share? HKU ecologists highlight disparities in global biodiversity conservation funding
2025-03-04
The extensive loss of biodiversity represents one of the major crises of our time, threatening not only entire ecosystems but also our current and future livelihoods. As scientists realise the magnitude and scale of ongoing extinctions, it is vital to ascertain the resources available for conservation and whether funds are being effectively distributed to protect species most in need.
A team of researchers from the School of Biological Sciences, The University of Hong Kong (HKU), addressed these questions in a recent paper in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), USA, by compiling information ...
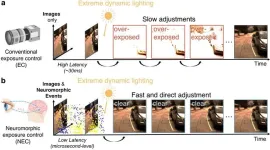
HKU researchers unveil neuromorphic exposure control system to improve machine vision in extreme lighting environments
2025-03-04
A research team led by Professor Jia Pan and Professor Yifan Evan Peng from the Department of Computer Science and Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering under the Faculty of Engineering at the University of Hong Kong (HKU), in collaboration with the researcher at Australian National University, has recently developed a groundbreaking neuromorphic exposure control (NEC) system that revolutionizes machine vision under extreme lighting variations. Published in Nature Communications, this biologically inspired system mimics human peripheral vision to achieve unprecedented speed and robustness in dynamic perception environments.
Traditional automatic exposure (AE) ...
Researchers develop highly robust, reconfigurable, and mechanochromic cellulose photonic hydrogels
2025-03-04
Inspired by the natural Bouligand structure, researchers have been developing advanced materials for applications in impact-resistant bioplastics, ceramic armor, and biomimetic alloy composites. Most existing materials are still composed of single-scale brittle units despite the progress in improving the plasticity of materials. The lack of hierarchical active interfaces and autonomous response capabilities limits their ductility and overall functionality.
Therefore, researchers aim to develop Bouligand-structured materials with multi-level active ...
Researchers develop new in-cell ultraviolet photodissociation top-down mass spectrometry method
2025-03-04
Proteins in cells are highly flexible and often exist in multiple conformations, each with unique abilities to bind ligands. These conformations are regulated by the organism to control protein function. Currently, most studies on protein structure and activity are conducted using purified proteins in vitro, which cannot fully replicate the complex of the intracellular environment and maybe influenced by the purification process or buffer conditions.
In a study published in Journal of the American Chemical Society, a team led by Prof. WANG Fangjun ...
Researchers develop innovative tool for rapid pathogen detection
2025-03-04
Researchers from the Zhang Liye Laboratory have developed a groundbreaking tool that revolutionizes the way researchers design primers for detecting pathogens. This new pipeline, which scans entire genomes to identify the most effective primer sets, could significantly enhance the speed and accuracy of diagnosing infectious diseases. The findings, published on 15 Feb 2025 in Frontiers of Computer Science, address a critical challenge in quantitative PCR (qPCR) primer design.
Unlike existing software that requires manual selection of specific genes or regions, this new tool automatically ...
New insights into how cancer evades the immune system
2025-03-04
Research into immunotherapy against cancer typically focuses on better recognition of cancer cells by the body's own immune system. Researchers at Amsterdam UMC and Moffitt Cancer Center have taken a different approach. They investigated how cancer affects the energy management of a patient’s T cells and showed for the first time that contact with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) cells leads to a serious energy crisis in these cells. These findings are published today in Cellular & Molecular Immunology, building on a publication earlier this month in Blood Advances. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
[Press-News.org] Business School celebrates triple crownIn a crowning achievement, the University of Auckland Business School is one of the best in the world, successfully gaining triple crown accreditation - a mark of excellence held by only one percent of business schools globally.