Enhancing climate action: satellite insights into fossil fuel CO2 emissions
2025-03-04
(Press-News.org)
Reliable and accurate monitoring of CO2 emissions is a cornerstone of effective climate change mitigation strategies. While traditional methods largely depend on ground-based measurements and bottom-up inventories, these approaches are often resource-intensive and prone to errors. Satellite Technology has emerged as a promising alternative, but the challenge remains in distinguishing anthropogenic emissions from natural processes. The long atmospheric lifetime of CO2 makes it difficult to pinpoint localized sources of emissions and track changes over time. Additionally, natural emissions and background concentrations can obscure signals from human activity. To overcome these hurdles, new, more advanced monitoring techniques are needed.
On October 18, 2024, a team from Tsinghua University published a review (DOI: 10.1007/s11783-025-1922-x) in Frontiers of Environmental Science & Engineering, presenting a novel method to monitor fossil fuel CO2 emissions by utilizing satellite observations of NO2. This method offers a more reliable and scalable solution for tracking emissions, from localized sources like power plants to broader national levels.
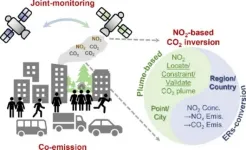
The review introduces two primary methodologies to use NO2 as a proxy for CO2 emissions, taking advantage of its shorter atmospheric lifetime and enhanced detectability. The first method, the plume-based approach, uses NO2 observations to locate and validate CO2 plumes, providing a precise way to identify emissions from point sources such as power plants and industrial facilities. By tracking the movement of NO2 plumes, researchers can more accurately determine the origin and magnitude of CO2 emissions. This method is particularly useful in urban environments with multiple emission sources, as it allows for the differentiation of emissions from various facilities.
The second method, the emission ratio-based approach, involves estimating NOx emissions from NO2 data and converting these estimates into CO2 emissions using known CO2-to-NOx emission ratios. This technique is especially effective for larger spatial scales, such as national or regional assessments, where direct CO2 observations might be compromised by high background concentrations. By incorporating emission ratios, this method accounts for variations in fuel types and combustion processes, offering a more reliable estimation of CO2 emissions. The study also addresses the uncertainties inherent in these methods, including structural uncertainties in the relationship between NO2 and emissions, as well as data-related challenges like retrieval errors and the accuracy of prior emissions inventories. To reduce these uncertainties, the researchers recommend the deployment of next-generation satellites with enhanced capabilities and the development of more sophisticated inversion systems.
Dr. Bo Zheng, an associate professor at Tsinghua University and a leading author of the study, commented, "This research marks a significant leap forward in our ability to monitor and verify CO2 emissions. By utilizing NO2 as a proxy, we can achieve much greater accuracy and reliability in emission estimates, which is crucial for implementing effective climate policies."
The study’s findings have far-reaching implications for global climate policy and environmental management. Accurate emissions monitoring is critical for countries to assess their progress toward meeting their climate commitments under the Paris Agreement. This new technology can support the development of more targeted and effective mitigation strategies, strengthening international efforts to combat climate change. Moreover, it provides researchers and policymakers with a valuable tool for understanding CO2 emission dynamics and their environmental consequences, paving the way for more informed decision-making in climate action.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-03-04
The teaching and research section is the fundamental organizational unit for teaching and research in a university, and the virtual teaching and research section (VTRS) is a crucial exploration for the digital transformation of new basic teaching organization construction in the information age. However, this new type of organization transcends university and spatial boundaries, and motivating participants and sustaining their engagement is a key challenge in VTRS operation. The VTRS for database courses (VTRS-DB) proposes an open community-based operating model, founded on the core concepts of "openness, dedication, competition, and orderliness." ...
2025-03-04
Six out of every ten people globally lack access to safe medical oxygen, resulting in hundreds of thousands of preventable deaths each year and reducing quality of life for millions more, an international report co-authored by the University of Auckland has found.
Associate Professor Stephen Howie from the University’s Faculty of Medical and Health Sciences (FMHS) was an adviser to the Lancet Global Health Commission on Medical Oxygen Security and co-author of its report Reducing global inequities in medical oxygen access released 18 February.
A key finding shows global access to medical oxygen is highly inequitable. Five billion ...
2025-03-04
In a crowning achievement, the University of Auckland Business School is one of the best in the world, successfully gaining triple crown accreditation - a mark of excellence held by only one percent of business schools globally.
The Business School was the first in Australasia to attain triple crown status in 2004, a recognition it has maintained for two decades.
Triple crown status is achieved if a business school can meet the strict requirements of three international accreditation bodies – the Association to Advance ...
2025-03-04
Common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) is a leguminous plant that can form a symbiotic relationship with rhizobia in the soil. Rhizobia convert nitrogen in the atmosphere into ammonia, providing nitrogen nutrition for leguminous plants. However, due to the low effectiveness of rhizobia in the soil, common bean has one of the lowest nitrogen fixation efficiencies among food legumes. Some studies have shown that pre-inoculating common bean seeds with elite rhizobial strains can enhance nitrogen fixation, thereby promoting the plant growth of common bean and increasing the grain yield. As one of the most important food legumes in Ethiopia, the grain yield of common bean is quite low, because of the lack ...
2025-03-04
In recent years, with the increasing openness and internationalization of research, the risks of inappropriate exploiting openness of research have become more apparent. With the growing importance of research security, the issue of how to safely promote cutting-edge research and international collaboration while respecting research freedom is becoming more important in many countries.
The Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST) organizes the symposium aiming to create an opportunity to deepen discussion on efforts necessary to protect research freedom. The symposium will consist of ...
2025-03-04
Rutgers Health researchers have made discoveries about brown fat that may open a new path to helping people stay physically fit as they age.
A team from Rutgers New Jersey Medical School found that mice lacking a specific gene developed an unusually potent form of brown fat tissue that expanded lifespan and increased exercise capacity by roughly 30%. The team is working on a drug that could mimic these effects in humans.
“Exercise capacity diminishes as you get older, and to have a technique ...
2025-03-04
Aqueous organic flow batteries (AOFBs) hold promise for renewable energy integration and electricity grid storage due to their inherent safety, as well as the availability of naturally abundant and synthetically tunable organic redox-active molecules (ORAMs). However, challenges such as low energy density, poor stability at high concentrations, and high synthesis costs hinder their commercial viability.
Developing ORAMs that offer both high energy density and ultra-stable cycling performance is essential for advancing stationary energy storage ...
2025-03-04
The extensive loss of biodiversity represents one of the major crises of our time, threatening not only entire ecosystems but also our current and future livelihoods. As scientists realise the magnitude and scale of ongoing extinctions, it is vital to ascertain the resources available for conservation and whether funds are being effectively distributed to protect species most in need.
A team of researchers from the School of Biological Sciences, The University of Hong Kong (HKU), addressed these questions in a recent paper in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), USA, by compiling information ...
2025-03-04
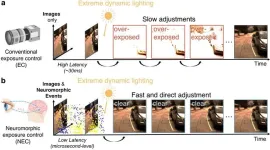
A research team led by Professor Jia Pan and Professor Yifan Evan Peng from the Department of Computer Science and Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering under the Faculty of Engineering at the University of Hong Kong (HKU), in collaboration with the researcher at Australian National University, has recently developed a groundbreaking neuromorphic exposure control (NEC) system that revolutionizes machine vision under extreme lighting variations. Published in Nature Communications, this biologically inspired system mimics human peripheral vision to achieve unprecedented speed and robustness in dynamic perception environments.
Traditional automatic exposure (AE) ...
2025-03-04
Inspired by the natural Bouligand structure, researchers have been developing advanced materials for applications in impact-resistant bioplastics, ceramic armor, and biomimetic alloy composites. Most existing materials are still composed of single-scale brittle units despite the progress in improving the plasticity of materials. The lack of hierarchical active interfaces and autonomous response capabilities limits their ductility and overall functionality.
Therefore, researchers aim to develop Bouligand-structured materials with multi-level active ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Enhancing climate action: satellite insights into fossil fuel CO2 emissions