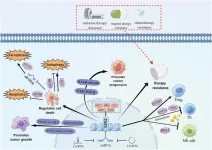
(Press-News.org) The critical role of EZH2, an essential epigenetic regulator, in cancer progression and treatment is underscored in this new review article published in Genes & Diseases. The study highlights the transformative potential of EZH2 inhibition, paving the way for a new generation of targeted therapies aimed at disrupting tumor growth and overcoming treatment resistance.
EZH2, a core component of the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2), plays a fundamental role in silencing tumor suppressor genes through histone methylation. Its overexpression has been implicated in a variety of malignancies, including breast cancer, prostate cancer, glioblastoma, and lymphoma. The ability of EZH2 inhibitors to reverse these effects represents a major advance in cancer therapy, offering new hope for patients with aggressive and treatment-resistant tumors.
Inhibition of EZH2 disrupts key signaling pathways that drive tumor proliferation, invasion, and survival. Beyond its canonical role in H3K27 trimethylation, EZH2 has been found to regulate non-histone proteins, activating pathways that promote metastasis and chemotherapy resistance. By targeting EZH2, researchers aim to counteract these mechanisms, restoring the expression of tumor suppressor genes and sensitizing cancer cells to conventional treatments.
The first FDA-approved EZH2 inhibitor, tazemetostat, has already demonstrated significant clinical benefits in epithelioid sarcoma and follicular lymphoma, marking an important milestone in the development of epigenetic-based cancer treatments. Ongoing research is expanding the scope of EZH2-targeting strategies, including combination therapies that integrate immune checkpoint inhibitors, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. These approaches aim to enhance treatment efficacy, reduce drug resistance, and improve long-term survival rates.
Despite the promise of EZH2 inhibitors, challenges remain in optimizing their use. Tumor heterogeneity, adaptive resistance mechanisms, and potential off-target effects highlight the need for further investigation into the precise role of EZH2 in different cancer types. Advanced biomarker studies are being pursued to identify predictive indicators that can guide patient selection and personalized treatment approaches.
The growing body of evidence supporting EZH2 as a therapeutic target is revolutionizing the field of oncology, offering a powerful tool for combating some of the most aggressive and treatment-resistant cancers.
# # # # #
Genes & Diseases publishes rigorously peer-reviewed and high quality original articles and authoritative reviews that focus on the molecular bases of human diseases. Emphasis is placed on hypothesis-driven, mechanistic studies relevant to pathogenesis and/or experimental therapeutics of human diseases. The journal has worldwide authorship, and a broad scope in basic and translational biomedical research of molecular biology, molecular genetics, and cell biology, including but not limited to cell proliferation and apoptosis, signal transduction, stem cell biology, developmental biology, gene regulation and epigenetics, cancer biology, immunity and infection, neuroscience, disease-specific animal models, gene and cell-based therapies, and regenerative medicine.
Scopus CiteScore: 7.3
Impact Factor: 6.9
# # # # # #
More information: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/
Editorial Board: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/editorial-board/
All issues and articles in press are available online in ScienceDirect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/genes-and-diseases ).
Submissions to Genes & Disease may be made using Editorial Manager (https://www.editorialmanager.com/gendis/default.aspx ).
Print ISSN: 2352-4820
eISSN: 2352-3042
CN: 50-1221/R
Contact Us: editor@genesndiseases.com
X (formerly Twitter): @GenesNDiseases (https://x.com/GenesNDiseases )
# # # # # #
Reference
Mengfei Xu, Chunyan Xu, Rui Wang, Qing Tang, Qichun Zhou, Wanyin Wu, Xinliang Wan, Handan Mo, Jun Pan, Sumei Wang, Treating human cancer by targeting EZH2, Genes & Diseases, Volume 12, Issue 3, 2025, 101313, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101313
END
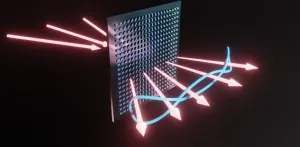
Quantum information processing is a field that relies on the entanglement of multiple photons to process vast amounts of information. However, creating multiphoton entanglement is a challenging task. Traditional methods either use quantum nonlinear optical processes, which are inefficient for large numbers of photons, or linear beam-splitting and quantum interference, which require complex setups prone to issues like loss and crosstalk.
A team of researchers from Peking University, Southern University of Science and Technology, and the University of Science and Technology of China recently made ...
Up to 10% of cancers are caused by genes that can be easily detected by commercially available tests. These include such common cancers as cancer of the breast, ovary, colon, stomach, uterus and pancreas.
“We don’t routinely screen for cancer susceptibility genes in primary-care settings because genetic testing is often considered too complicated and primary care doctors already have so many things they need to address,” noted lead author Dr. Elizabeth Swisher, a UW Medicine gynecological oncologist. "But it is an opportunity lost.”
In the JAMA Network Open study published ...
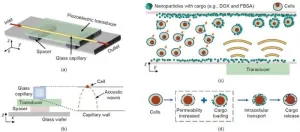
A recent study published in Engineering presents an innovative acoustofluidics-based approach for intracellular nanoparticle delivery. This method offers a new way to transport various functional nanomaterials into different cell types, potentially revolutionizing therapeutic applications and biophysical studies.
The efficient delivery of biomolecular cargos into cells is crucial for biomedical research, including gene therapies and drug delivery. However, traditional delivery methods such as endocytosis of nano-vectors, microinjection, and electroporation have limitations. They may require time-consuming processes, complex operations, or expensive equipment. ...
Sulfate-reducing bacteria break down a large proportion of the organic carbon in oxygen-free zones of the Earth, and in the seabed in particular. Among these important microbes, the Desulfobacteraceae family of bacteria stands out because its members are able to break down a wide variety of compounds – including some that are poorly degradable – to their end product, carbon dioxide (CO2).
A team of researchers led by Dr Lars Wöhlbrand and Prof. Dr Ralf Rabus from the University of Oldenburg, Germany, has investigated the role ...
When spiders spin their webs, they use their hind legs to pull silk threads from their spinnerets. This pulling action doesn’t just help the spider release the silk, it’s also a crucial step in strengthening the silk fibers for a more durable web.
In a new study, Northwestern University researchers have discovered why the role of stretching is so important. By simulating spider silk in a computational model, the team discovered the stretching process aligns the protein chains within the fibers and increases the number of bonds between those ...
On ten thousand to million years time scales, climate dynamics on the Earth’s surface are driven by both external and internal processes. Earth`s interior provides heat from radioactive decay and chemical compounds by volcanic degassing, such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Quasiperiodic changes in Earth’s orbit around the sun regulate the amount of incoming solar radiation on the planet’s surface as well as its distribution across latitudes, affecting the length and intensity ...
High levels of ammonia kill liver cells by damaging the mitochondria that power the cells. But this can be prevented using an existing drug due to start clinical trials, finds a new study in mice led by researchers from UCL.
The study, published in Science Advances, is the first to observe that build-up of ammonia (hyperammonaemia) can harm liver cells and describe how this damage occurs in mouse models that are clinically relevant for humans.
Hyperammonaemia is known to cause brain dysfunction in those with liver disease, ...
Philadelphia, March 7, 2025 – After many decades of research, the dairy sector has a significant body of peer-reviewed research showing that feed additives can effectively reduce methane, the greenhouse gas that makes up most of dairy’s environmental footprint. Yet the practical use of this knowledge on farms—as well as general awareness around additive effectiveness and safety—is still gaining momentum. At this critical point in the dairy sector’s pathway to a net-zero future, the Journal of Dairy Science, the leading general dairy research journal from ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — Eradivir, a clinical-stage small molecule immunotherapy biotech company, announced it has begun a Phase 2 challenge study with its antiviral therapeutic, EV25. The study will provide safety and efficacy data gathered from otherwise healthy participants infected with influenza then later treated with EV25.
EV25 was built on a platform created in Philip Low’s lab. Low is the Presidential Scholar for Drug Discovery and the Ralph C. Corley Distinguished Professor of Chemistry in Purdue University’s College of Science. Low is Eradivir’s chief scientific officer and on its board of directors.
The European Medicines ...
Puerto Madryn, Argentina – A new study published in PeerJ Life and Environment reveals that the teeth of South American sea lions (Otaria byronia) hold valuable clues about past population dynamics. Researchers from the Instituto de Biología de Organismos Marinos, the Centro para el Estudio de Sistemas Marinos, and the Universidad Nacional de la Patagonia San Juan Bosco analysed changes intooth size and growth layer groups (GLGs) over the ...