(Press-News.org)
A recent study published in Engineering delves into the latest progress in intracortical neural interface technologies for freely moving animals. These interfaces, which establish a connection between the nervous system and external devices, have the potential to revolutionize neuroscience research and clinical medicine.
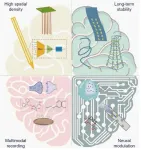
The researchers, led by Xinxia Cai, Zhaojie Xu and Yirong Wu, analyzed four key technological directions for ideal implantable neural interface devices: higher spatial density, improved biocompatibility, enhanced multimodal detection of electrical/neurotransmitter signals, and more effective neural modulation.
In terms of high spatial density, microelectrode array (MEA) designs have evolved significantly. The Utah array and Michigan array, two classic MEA structures, have been reconfigured with new processes and materials. For example, the Utah graded electrode array achieved a higher channel density by tilting the electrode needles and integrating longitudinal multisite on a needle. The Michigan array, on the other hand, has explored methods like electron beam lithography and dual-layer wiring to increase the number of recording sites. CMOS technology has also enabled the integration of neural electrodes with amplifier circuits, reducing the size of the backend circuit.
Long-term stability of MEAs is crucial but challenged by tissue damage and immune responses. To address this, flexible substrates such as polyimide, parylene, and PDMS are being used. These materials have a lower Young’s modulus, similar to that of brain tissue, reducing the immune response. Surface preparation methods, including electrode coatings and electroplated layers at the electrode sites, are also being employed to enhance the quality and longevity of recorded signals.
Multimodal recording MEAs are another area of focus. These devices can detect both electrophysiological and neurotransmitter signals. Electrochemical methods, such as amperometry and fast-scan cyclic voltammetry, are used to measure neurotransmitter concentrations. Different sensitive layers are constructed for various neurotransmitters, with materials like carbon-based materials, conductive polymers, and enzymes. However, challenges remain in achieving high-resolution and selective detection, as well as integrating the detection circuits.
Bidirectional neural probes that can both record and modulate neural activity are also being developed. Electrical stimulation (ES), optical modulation, and microfluidic delivery are the main modulation methods. ES has limitations in specificity, while optical modulation offers higher cellular specificity. Microfluidic delivery can precisely deliver drugs or chemical molecules to specific brain regions.
These technological advancements in intracortical neural interfaces have wide-ranging applications. They can help researchers better understand neural circuit functions, the mechanisms of neural encoding and decoding, and the pathogenesis of clinical disorders. In the future, they may also contribute to the development of more effective and personalized therapies for neurological diseases, as well as the restoration of motor and sensory functions. However, challenges such as the maturity of flexible CMOS fabrication technologies and the management of thermal and electrical noise still need to be overcome.
The paper “Recent Advances in Intracortical Neural Interfaces for Freely Moving Animals: Technologies and Applications,” authored by Xinxia Cai, Zhaojie Xu, Jingquan Liu, Robert Wang, and Yirong Wu. Full text of the open access paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2024.12.012. For more information about the Engineering, follow us on X (https://twitter.com/EngineeringJrnl) & like us on Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/EngineeringJrnl).
END
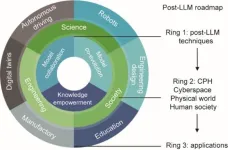
A recent paper published in the journal Engineering delves into the future of artificial intelligence (AI) beyond large language models (LLMs). LLMs have made remarkable progress in multimodal tasks, yet they face limitations such as outdated information, hallucinations, inefficiency, and a lack of interpretability. To address these issues, researchers explore three key directions: knowledge empowerment, model collaboration, and model co-evolution.
Knowledge empowerment aims to integrate external knowledge into LLMs. This can be achieved through various methods, including integrating knowledge ...
Tokyo, Japan – The XRISM collaboration have discovered flows of hot gas in the core of the Centaurus Cluster. By comparing state-of-the-art X-ray measurements from the XRISM satellite with numerical simulations, they showed this is evidence for collisions between galaxy clusters, causing gas inside to “slosh”. This solves the longstanding mystery of how cluster cores stay hot, and sheds light on how our universe continues to evolve.
Astronomers have long envisioned how vast gravitational forces ...
Incidents of children in the U.S. being poisoned by the synthetic opioid fentanyl “increased and became more severe”, a new study reveals.
Launched today as Congress continues to review the HALT Fentanyl Act, the research follows an analysis of nonfatal fentanyl pediatric (aged 0-19) exposures reported to poison centers in 49 U.S. states from 2015 through to 2023.
In total, some 3,009 cases were detailed across the eight-year period.
In 2023 alone, 44.6% were life-threatening incidents in which there was extreme harm ...
Humans may not be the only ones who aid their friends when they’re hurt. Mice may do it, too, as shown by a new research study led by scientists at the Keck School of Medicine of USC published recently in Science.
Scientists have been trying to understand why social mammals appear to help injured members of their species. There are numerous factors that determine empathetic behavior and social bonding in mammals, said Li Zhang, the principal investigator of the study and professor of physiology and neuroscience ...
An ambitious project led by Vanderbilt University Medical Center investigators aims to use artificial intelligence technologies to generate antibody therapies against any antigen target of interest.
VUMC has been awarded up to $30 million from the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H) to build a massive antibody-antigen atlas, develop AI-based algorithms to engineer antigen-specific antibodies, and apply the AI technology to identify and develop potential therapeutic antibodies.
ARPA-H is an ...
A new review article highlights the transformative role of circular RNA (circRNA) in cancer, revealing its potential as both a key player in tumor biology and a promising avenue for future therapies. Once thought to be noncoding RNA, circRNA has now been shown to encode functional proteins, challenging conventional RNA biology and opening up novel therapeutic possibilities.
Unlike traditional messenger RNA, circRNAs form a continuous loop, lacking the typical 5' cap and 3' tail. This unique structure was originally believed to preclude them from protein translation. However, recent discoveries demonstrate that specific internal ribosome entry sites (IRES) and N6-methyladenosine ...
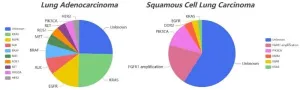
Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality, with lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) representing the most prevalent subtypes of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Despite their classification under the same umbrella, these two forms of lung cancer exhibit distinct genetic landscapes, therapeutic targets, and treatment responses.
Recent advancements in next-generation gene sequencing have identified key driver genes that differentiate LUAD and LUSC, influencing their respective clinical management approaches. LUAD is frequently associated ...
A study published March 6 in The Lancet Regional Health — Americas highlights a growing divide in cardiovascular health in the U.S., showing that wealth and education play a significant role in heart disease risk.
The research, led by Salma Abdalla, MBBS, DrPH, an assistant professor of public health at Washington University in St. Louis, reveals that the top 20% of high-income, college-educated Americans have far lower rates of cardiovascular disease than the rest of the population — disparities ...
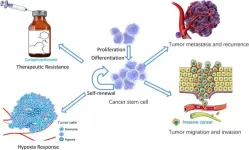
This review highlights the critical role of ubiquitination in governing the functionality of cancer stem cells (CSCs), shedding light on potential therapeutic targets for combating tumor progression, recurrence, and drug resistance. Published in Genes & Diseases, this article explores the intricate mechanisms through which the ubiquitin (Ub) system regulates key pathways essential for CSC maintenance and survival.
Ubiquitination, a fundamental post-translational modification, plays a pivotal role in protein stability, cellular signaling, and gene expression, particularly in the context of CSCs. Dysregulation ...
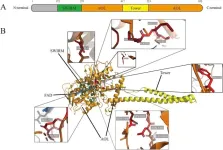
A new review highlights the pivotal role of LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) in regulating critical cellular processes and its implications for human diseases. This article sheds light on how post-translational modifications (PTMs) influence LSD1 activity, impacting its function in gene regulation and disease progression.
LSD1 is a histone demethylase that plays a significant role in chromatin remodeling and gene expression by modifying histone H3 lysine residues. It interacts with various protein complexes, allowing it to serve as both a transcriptional activator and repressor. The intricate modifications ...