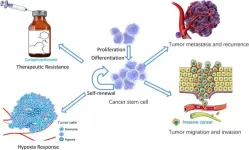
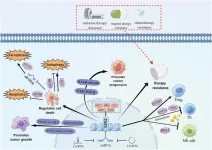
(Press-News.org) This review highlights the critical role of ubiquitination in governing the functionality of cancer stem cells (CSCs), shedding light on potential therapeutic targets for combating tumor progression, recurrence, and drug resistance. Published in Genes & Diseases, this article explores the intricate mechanisms through which the ubiquitin (Ub) system regulates key pathways essential for CSC maintenance and survival.
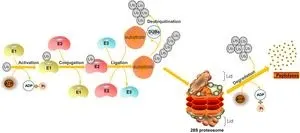
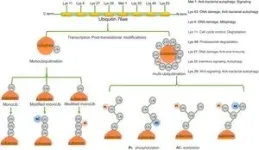
Ubiquitination, a fundamental post-translational modification, plays a pivotal role in protein stability, cellular signaling, and gene expression, particularly in the context of CSCs. Dysregulation of the Ub system has been identified as a driving force behind tumorigenesis and metastasis, making it a crucial area of study for developing novel anti-cancer therapies. The review delves into the E3 ubiquitin ligases, a specialized class of enzymes responsible for targeting specific proteins for degradation, and their interaction with CSCs. These ligases, alongside deubiquitinases, modulate transcription factors such as SOX2, OCT4, KLF4, and c-Myc, all of which play a crucial role in CSC self-renewal and differentiation.
The study further examines the interplay between ubiquitination and key signaling pathways, including Notch, Wnt/β-catenin, Hedgehog, and Hippo-YAP, which regulate stem-like properties in cancer cells. By influencing these pathways, ubiquitination emerges as a potentially powerful therapeutic target to disrupt the aggressive nature of CSCs. The involvement of the Ub-proteasome system (UPS) in maintaining CSC characteristics highlights an opportunity for drug development focused on modulating ubiquitin ligases and deubiquitinases to selectively degrade or stabilize proteins essential for CSC survival.
This review underscores the need for targeted therapies aimed at exploiting the vulnerabilities of the Ub system in CSCs. Existing proteasome inhibitors, such as bortezomib and carfilzomib, have shown promise in certain cancers, but further research into specific E3 ligases and DUBs could pave the way for more precise and effective cancer treatments. The potential of combining Ub-targeted therapies with traditional chemotherapy, immunotherapy, and targeted drugs represents a novel frontier in oncological treatment strategies.
As cancer research advances, understanding the molecular mechanisms behind CSC regulation through ubiquitination offers new hope for improved therapeutic interventions. By identifying key regulatory factors and pathways, this review provides a comprehensive framework for the development of next-generation anti-cancer therapies, marking an important step toward overcoming cancer recurrence and treatment resistance.
# # # # #
Genes & Diseases publishes rigorously peer-reviewed and high quality original articles and authoritative reviews that focus on the molecular bases of human diseases. Emphasis is placed on hypothesis-driven, mechanistic studies relevant to pathogenesis and/or experimental therapeutics of human diseases. The journal has worldwide authorship, and a broad scope in basic and translational biomedical research of molecular biology, molecular genetics, and cell biology, including but not limited to cell proliferation and apoptosis, signal transduction, stem cell biology, developmental biology, gene regulation and epigenetics, cancer biology, immunity and infection, neuroscience, disease-specific animal models, gene and cell-based therapies, and regenerative medicine.
Scopus CiteScore: 7.3
Impact Factor: 6.9
# # # # # #
More information: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/
Editorial Board: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/editorial-board/
All issues and articles in press are available online in ScienceDirect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/genes-and-diseases ).
Submissions to Genes & Disease may be made using Editorial Manager (https://www.editorialmanager.com/gendis/default.aspx ).
Print ISSN: 2352-4820
eISSN: 2352-3042
CN: 50-1221/R
Contact Us: editor@genesndiseases.com
X (formerly Twitter): @GenesNDiseases (https://x.com/GenesNDiseases )
# # # # # #
Reference
Qianqian Guo, Hai Qin, Zelong Chen, Wenzhou Zhang, Lufeng Zheng, Tingting Qin, Key roles of ubiquitination in regulating critical regulators of cancer stem cell functionality, Genes & Diseases, Volume 12, Issue 3, 2025, 101311, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101311
END
A new review highlights the pivotal role of LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) in regulating critical cellular processes and its implications for human diseases. This article sheds light on how post-translational modifications (PTMs) influence LSD1 activity, impacting its function in gene regulation and disease progression.
LSD1 is a histone demethylase that plays a significant role in chromatin remodeling and gene expression by modifying histone H3 lysine residues. It interacts with various protein complexes, allowing it to serve as both a transcriptional activator and repressor. The intricate modifications ...
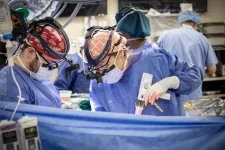
Surgeons and teams with Vanderbilt Lung Transplant performed 99 lung transplants in 2024, the most ever in one year. Two of the procedures involved combined organ transplants.
For the second calendar year in a row, Vanderbilt Lung Transplant has the busiest program in the Southeast and leads the nation in innovation in organ preservation and regeneration.
The Vanderbilt Transplant Center is now home to the nation’s eighth largest lung transplant program by volume, and is among the best in long-term outcomes, demonstrating the ...
The critical role of EZH2, an essential epigenetic regulator, in cancer progression and treatment is underscored in this new review article published in Genes & Diseases. The study highlights the transformative potential of EZH2 inhibition, paving the way for a new generation of targeted therapies aimed at disrupting tumor growth and overcoming treatment resistance.
EZH2, a core component of the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2), plays a fundamental role in silencing tumor suppressor genes through histone methylation. Its overexpression has been ...
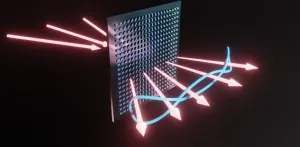
Quantum information processing is a field that relies on the entanglement of multiple photons to process vast amounts of information. However, creating multiphoton entanglement is a challenging task. Traditional methods either use quantum nonlinear optical processes, which are inefficient for large numbers of photons, or linear beam-splitting and quantum interference, which require complex setups prone to issues like loss and crosstalk.
A team of researchers from Peking University, Southern University of Science and Technology, and the University of Science and Technology of China recently made ...
Up to 10% of cancers are caused by genes that can be easily detected by commercially available tests. These include such common cancers as cancer of the breast, ovary, colon, stomach, uterus and pancreas.
“We don’t routinely screen for cancer susceptibility genes in primary-care settings because genetic testing is often considered too complicated and primary care doctors already have so many things they need to address,” noted lead author Dr. Elizabeth Swisher, a UW Medicine gynecological oncologist. "But it is an opportunity lost.”
In the JAMA Network Open study published ...
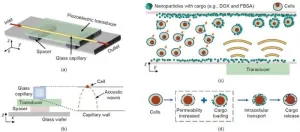
A recent study published in Engineering presents an innovative acoustofluidics-based approach for intracellular nanoparticle delivery. This method offers a new way to transport various functional nanomaterials into different cell types, potentially revolutionizing therapeutic applications and biophysical studies.
The efficient delivery of biomolecular cargos into cells is crucial for biomedical research, including gene therapies and drug delivery. However, traditional delivery methods such as endocytosis of nano-vectors, microinjection, and electroporation have limitations. They may require time-consuming processes, complex operations, or expensive equipment. ...
Sulfate-reducing bacteria break down a large proportion of the organic carbon in oxygen-free zones of the Earth, and in the seabed in particular. Among these important microbes, the Desulfobacteraceae family of bacteria stands out because its members are able to break down a wide variety of compounds – including some that are poorly degradable – to their end product, carbon dioxide (CO2).
A team of researchers led by Dr Lars Wöhlbrand and Prof. Dr Ralf Rabus from the University of Oldenburg, Germany, has investigated the role ...
When spiders spin their webs, they use their hind legs to pull silk threads from their spinnerets. This pulling action doesn’t just help the spider release the silk, it’s also a crucial step in strengthening the silk fibers for a more durable web.
In a new study, Northwestern University researchers have discovered why the role of stretching is so important. By simulating spider silk in a computational model, the team discovered the stretching process aligns the protein chains within the fibers and increases the number of bonds between those ...
On ten thousand to million years time scales, climate dynamics on the Earth’s surface are driven by both external and internal processes. Earth`s interior provides heat from radioactive decay and chemical compounds by volcanic degassing, such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Quasiperiodic changes in Earth’s orbit around the sun regulate the amount of incoming solar radiation on the planet’s surface as well as its distribution across latitudes, affecting the length and intensity ...
High levels of ammonia kill liver cells by damaging the mitochondria that power the cells. But this can be prevented using an existing drug due to start clinical trials, finds a new study in mice led by researchers from UCL.
The study, published in Science Advances, is the first to observe that build-up of ammonia (hyperammonaemia) can harm liver cells and describe how this damage occurs in mouse models that are clinically relevant for humans.
Hyperammonaemia is known to cause brain dysfunction in those with liver disease, ...