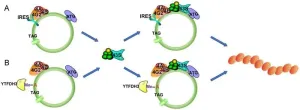
(Press-News.org) A new review article highlights the transformative role of circular RNA (circRNA) in cancer, revealing its potential as both a key player in tumor biology and a promising avenue for future therapies. Once thought to be noncoding RNA, circRNA has now been shown to encode functional proteins, challenging conventional RNA biology and opening up novel therapeutic possibilities.
Unlike traditional messenger RNA, circRNAs form a continuous loop, lacking the typical 5' cap and 3' tail. This unique structure was originally believed to preclude them from protein translation. However, recent discoveries demonstrate that specific internal ribosome entry sites (IRES) and N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications enable circRNAs to undergo cap-independent translation. The resulting proteins influence a range of cellular processes, including those linked to cancer progression and suppression.
Emerging evidence underscores the significance of circRNA-encoded proteins in multiple types of cancer, including glioblastoma, breast cancer, gastric cancer, liver cancer, and colorectal cancer. These proteins interact with critical signaling pathways, such as PI3K/Akt, Wnt/β-catenin, and TGF-β/Smad, influencing cell proliferation, migration, and apoptosis. In glioblastoma, for instance, circRNA-derived proteins contribute to tumorigenicity, while in colorectal cancer, they regulate metabolic processes that drive malignancy.
Beyond their role in cancer progression, translatable circRNAs are poised to redefine RNA-based therapeutics. Their stability and potential for long-lasting protein expression make them promising candidates for protein replacement therapies, vaccines, and targeted drug development. Advances in bioengineering have further enhanced circRNA synthesis, enabling more efficient protein production and laying the foundation for circRNA-based immunotherapies. These innovations could lead to highly potent treatments with improved delivery mechanisms and greater precision in targeting malignant cells.
Despite their vast potential, significant challenges remain in understanding the regulatory mechanisms governing circRNA translation. Key questions include how these proteins achieve tissue-specific functions and how circRNA synthesis can be optimized for clinical applications. Current research aims to refine the techniques used to design and manufacture artificial circRNAs, ensuring their efficacy and safety in medical treatments.
This new understanding of circRNAs as hidden protein sources represents a major shift in molecular biology and oncology. By further exploring their coding potential, researchers and clinicians may unlock new ways to detect, treat, and ultimately prevent cancer.
# # # # #
Genes & Diseases publishes rigorously peer-reviewed and high quality original articles and authoritative reviews that focus on the molecular bases of human diseases. Emphasis is placed on hypothesis-driven, mechanistic studies relevant to pathogenesis and/or experimental therapeutics of human diseases. The journal has worldwide authorship, and a broad scope in basic and translational biomedical research of molecular biology, molecular genetics, and cell biology, including but not limited to cell proliferation and apoptosis, signal transduction, stem cell biology, developmental biology, gene regulation and epigenetics, cancer biology, immunity and infection, neuroscience, disease-specific animal models, gene and cell-based therapies, and regenerative medicine.
Scopus CiteScore: 7.3
Impact Factor: 6.9
# # # # # #
More information: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/
Editorial Board: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/editorial-board/
All issues and articles in press are available online in ScienceDirect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/genes-and-diseases ).
Submissions to Genes & Disease may be made using Editorial Manager (https://www.editorialmanager.com/gendis/default.aspx ).
Print ISSN: 2352-4820
eISSN: 2352-3042
CN: 50-1221/R
Contact Us: editor@genesndiseases.com
X (formerly Twitter): @GenesNDiseases (https://x.com/GenesNDiseases )
# # # # # #
Reference
Yuan Lin, Yawen Wang, Lixin Li, Kai Zhang, Coding circular RNA in human cancer, Genes & Diseases,
Volume 12, Issue 3, 2025, 101347, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101347
END
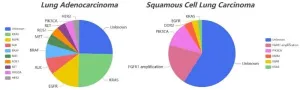
Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality, with lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) representing the most prevalent subtypes of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Despite their classification under the same umbrella, these two forms of lung cancer exhibit distinct genetic landscapes, therapeutic targets, and treatment responses.
Recent advancements in next-generation gene sequencing have identified key driver genes that differentiate LUAD and LUSC, influencing their respective clinical management approaches. LUAD is frequently associated ...
A study published March 6 in The Lancet Regional Health — Americas highlights a growing divide in cardiovascular health in the U.S., showing that wealth and education play a significant role in heart disease risk.
The research, led by Salma Abdalla, MBBS, DrPH, an assistant professor of public health at Washington University in St. Louis, reveals that the top 20% of high-income, college-educated Americans have far lower rates of cardiovascular disease than the rest of the population — disparities ...
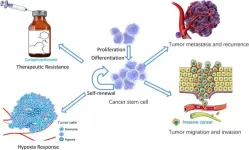
This review highlights the critical role of ubiquitination in governing the functionality of cancer stem cells (CSCs), shedding light on potential therapeutic targets for combating tumor progression, recurrence, and drug resistance. Published in Genes & Diseases, this article explores the intricate mechanisms through which the ubiquitin (Ub) system regulates key pathways essential for CSC maintenance and survival.
Ubiquitination, a fundamental post-translational modification, plays a pivotal role in protein stability, cellular signaling, and gene expression, particularly in the context of CSCs. Dysregulation ...
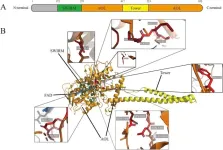
A new review highlights the pivotal role of LSD1 (lysine-specific demethylase 1) in regulating critical cellular processes and its implications for human diseases. This article sheds light on how post-translational modifications (PTMs) influence LSD1 activity, impacting its function in gene regulation and disease progression.
LSD1 is a histone demethylase that plays a significant role in chromatin remodeling and gene expression by modifying histone H3 lysine residues. It interacts with various protein complexes, allowing it to serve as both a transcriptional activator and repressor. The intricate modifications ...
Surgeons and teams with Vanderbilt Lung Transplant performed 99 lung transplants in 2024, the most ever in one year. Two of the procedures involved combined organ transplants.
For the second calendar year in a row, Vanderbilt Lung Transplant has the busiest program in the Southeast and leads the nation in innovation in organ preservation and regeneration.
The Vanderbilt Transplant Center is now home to the nation’s eighth largest lung transplant program by volume, and is among the best in long-term outcomes, demonstrating the ...
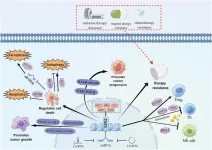
The critical role of EZH2, an essential epigenetic regulator, in cancer progression and treatment is underscored in this new review article published in Genes & Diseases. The study highlights the transformative potential of EZH2 inhibition, paving the way for a new generation of targeted therapies aimed at disrupting tumor growth and overcoming treatment resistance.
EZH2, a core component of the Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2), plays a fundamental role in silencing tumor suppressor genes through histone methylation. Its overexpression has been ...
Quantum information processing is a field that relies on the entanglement of multiple photons to process vast amounts of information. However, creating multiphoton entanglement is a challenging task. Traditional methods either use quantum nonlinear optical processes, which are inefficient for large numbers of photons, or linear beam-splitting and quantum interference, which require complex setups prone to issues like loss and crosstalk.
A team of researchers from Peking University, Southern University of Science and Technology, and the University of Science and Technology of China recently made ...
Up to 10% of cancers are caused by genes that can be easily detected by commercially available tests. These include such common cancers as cancer of the breast, ovary, colon, stomach, uterus and pancreas.
“We don’t routinely screen for cancer susceptibility genes in primary-care settings because genetic testing is often considered too complicated and primary care doctors already have so many things they need to address,” noted lead author Dr. Elizabeth Swisher, a UW Medicine gynecological oncologist. "But it is an opportunity lost.”
In the JAMA Network Open study published ...
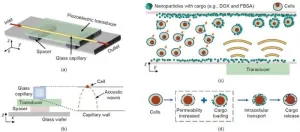
A recent study published in Engineering presents an innovative acoustofluidics-based approach for intracellular nanoparticle delivery. This method offers a new way to transport various functional nanomaterials into different cell types, potentially revolutionizing therapeutic applications and biophysical studies.
The efficient delivery of biomolecular cargos into cells is crucial for biomedical research, including gene therapies and drug delivery. However, traditional delivery methods such as endocytosis of nano-vectors, microinjection, and electroporation have limitations. They may require time-consuming processes, complex operations, or expensive equipment. ...
Sulfate-reducing bacteria break down a large proportion of the organic carbon in oxygen-free zones of the Earth, and in the seabed in particular. Among these important microbes, the Desulfobacteraceae family of bacteria stands out because its members are able to break down a wide variety of compounds – including some that are poorly degradable – to their end product, carbon dioxide (CO2).
A team of researchers led by Dr Lars Wöhlbrand and Prof. Dr Ralf Rabus from the University of Oldenburg, Germany, has investigated the role ...