(Press-News.org) The megalodon has long been imagined as an enormous great white shark, but new research suggests that perception is all wrong. The study finds the prehistoric hunter had a much longer body—closer in shape to a lemon shark or even a large whale.
The study team, which included researchers from University of California, Riverside and across the globe, used a novel approach to estimate the shark’s total body length, moving beyond traditional methods that rely primarily on tooth size. By examining megalodon’s vertebral column and comparing it to over 100 species of living and extinct sharks, they determined a more accurate proportion for the head, body, and tail.
The findings, published today in the journal Palaeontologia Electronica, suggest the prehistoric predator may have reached about 80 feet, or about two school buses in length. It also likely weighed an estimated 94 tons, comparable to a large blue whale, but with a body designed for energy-efficient cruising rather than continuous high-speed pursuit.
“This study provides the most robust analysis yet of megalodon’s body size and shape,” said Phillip Sternes, a shark biologist who completed his Ph.D. at UCR. “Rather than resembling an oversized great white shark, it was actually more like an enormous lemon shark, with a more slender, elongated body. That shape makes a lot more sense for moving efficiently through water.”
Great white sharks have a stocky, torpedo-shaped body built for bursts of speed, with a broad midsection that tapers sharply toward the tail. In contrast, lemon sharks have a leaner, more uniform body shape, with a less pronounced taper. Their longer, more cylindrical build allows for smoother, more energy-efficient swimming. If megalodon had a body structure more like a lemon shark, as this study suggests, it would have looked much sleeker than the bulky predator often depicted in popular media.
Sharks, like airplanes or Olympic swimmers, must minimize drag to move smoothly and easily.
“You lead with your head when you swim because it’s more efficient than leading with your stomach,” said Tim Higham, UCR biologist who contributed insights to the study on how animals move through water. “Similarly, evolution moves toward efficiency, much of the time.”
The study highlights how large aquatic animals including sharks, whales, or even extinct marine reptiles, follow similar patterns when it comes to body proportions. “The physics of swimming limit how stocky or stretched out a massive predator can be,” Higham said.
The research also sheds light on megalodon’s swimming capabilities. While debates have raged over whether it was a high-speed predator or a slower, cruising hunter, the new findings suggest a balance. The shark likely swam at moderate speeds, with the ability to burst forward when attacking prey. Given its sheer size and energy demands, constant high-speed swimming wouldn’t have been efficient.
The study also indicates that as a newborn, a megalodon could have been nearly 13 feet long, roughly the size of an adult great white shark. “It is entirely possible that megalodon pups were already taking down marine mammals shortly after being born,” Sternes said.
A key breakthrough of this study was identifying the lemon shark as the best living analog for megalodon’s proportions. Unlike the great white, lemon sharks have a more elongated body. When the researchers scaled up the proportions of a lemon shark to megalodon’s estimated length, it was a near-perfect match.
“This research not only refines our understanding of what megalodon looked like, but it also provides a framework for studying how size influences movement in marine animals,” Sternes said.
Beyond reshaping our understanding of megalodon, the study offers insight into why only certain animals can evolve to massive sizes.
“Gigantism isn’t just about getting bigger—it’s about evolving the right body to survive at that scale,” Sternes said. “And megalodon may have been one of the most extreme examples of that.”
END
A longer, sleeker super predator: Megalodon’s true form
Novel study paints more accurate picture of extinct, gigantic shark
2025-03-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Walking, moving more may lower risk of cardiovascular death for women with cancer history
2025-03-09
Research Highlights:
Increased physical activity including taking more daily steps was linked to a lower risk of death from cardiovascular disease among postmenopausal women with a history of cancer.
The study found that engaging in one hour per day of moderate to vigorous physical activity reduced participants’ risk of death from any cause by 40% and risk of death from cardiovascular disease by 60%.
Each additional 2,500 steps per day for a participant was associated with a 34% reduction in risk of death from cardiovascular disease.
Note: The study featured in this news release is a research abstract. Abstracts presented ...
Intracortical neural interfaces: Advancing technologies for freely moving animals
2025-03-09
A recent study published in Engineering delves into the latest progress in intracortical neural interface technologies for freely moving animals. These interfaces, which establish a connection between the nervous system and external devices, have the potential to revolutionize neuroscience research and clinical medicine.
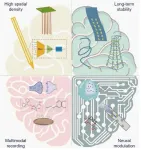
The researchers, led by Xinxia Cai, Zhaojie Xu and Yirong Wu, analyzed four key technological directions for ideal implantable neural interface devices: higher spatial density, improved biocompatibility, enhanced multimodal detection of electrical/neurotransmitter signals, and more effective neural modulation.
In terms of high spatial density, microelectrode ...
Post-LLM era: New horizons for AI with knowledge, collaboration, and co-evolution
2025-03-08
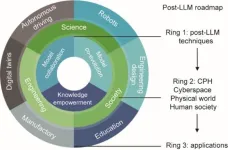
A recent paper published in the journal Engineering delves into the future of artificial intelligence (AI) beyond large language models (LLMs). LLMs have made remarkable progress in multimodal tasks, yet they face limitations such as outdated information, hallucinations, inefficiency, and a lack of interpretability. To address these issues, researchers explore three key directions: knowledge empowerment, model collaboration, and model co-evolution.
Knowledge empowerment aims to integrate external knowledge into LLMs. This can be achieved through various methods, including integrating knowledge ...
“Sloshing” from celestial collisions solves mystery of how galactic clusters stay hot
2025-03-08
Tokyo, Japan – The XRISM collaboration have discovered flows of hot gas in the core of the Centaurus Cluster. By comparing state-of-the-art X-ray measurements from the XRISM satellite with numerical simulations, they showed this is evidence for collisions between galaxy clusters, causing gas inside to “slosh”. This solves the longstanding mystery of how cluster cores stay hot, and sheds light on how our universe continues to evolve.
Astronomers have long envisioned how vast gravitational forces ...
Children poisoned by the synthetic opioid, fentanyl, has risen in the U.S. – eight years of national data shows
2025-03-08
Incidents of children in the U.S. being poisoned by the synthetic opioid fentanyl “increased and became more severe”, a new study reveals.
Launched today as Congress continues to review the HALT Fentanyl Act, the research follows an analysis of nonfatal fentanyl pediatric (aged 0-19) exposures reported to poison centers in 49 U.S. states from 2015 through to 2023.
In total, some 3,009 cases were detailed across the eight-year period.
In 2023 alone, 44.6% were life-threatening incidents in which there was extreme harm ...
USC researchers observe mice may have a form of first aid
2025-03-08
Humans may not be the only ones who aid their friends when they’re hurt. Mice may do it, too, as shown by a new research study led by scientists at the Keck School of Medicine of USC published recently in Science.
Scientists have been trying to understand why social mammals appear to help injured members of their species. There are numerous factors that determine empathetic behavior and social bonding in mammals, said Li Zhang, the principal investigator of the study and professor of physiology and neuroscience ...
VUMC to develop AI technology for therapeutic antibody discovery
2025-03-07
An ambitious project led by Vanderbilt University Medical Center investigators aims to use artificial intelligence technologies to generate antibody therapies against any antigen target of interest.
VUMC has been awarded up to $30 million from the Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H) to build a massive antibody-antigen atlas, develop AI-based algorithms to engineer antigen-specific antibodies, and apply the AI technology to identify and develop potential therapeutic antibodies.
ARPA-H is an ...
Unlocking the hidden proteome: The role of coding circular RNA in cancer
2025-03-07
A new review article highlights the transformative role of circular RNA (circRNA) in cancer, revealing its potential as both a key player in tumor biology and a promising avenue for future therapies. Once thought to be noncoding RNA, circRNA has now been shown to encode functional proteins, challenging conventional RNA biology and opening up novel therapeutic possibilities.
Unlike traditional messenger RNA, circRNAs form a continuous loop, lacking the typical 5' cap and 3' tail. This unique structure was originally believed to preclude them from protein translation. However, recent discoveries demonstrate that specific internal ribosome entry sites (IRES) and N6-methyladenosine ...
Advancing lung cancer treatment: Understanding the differences between LUAD and LUSC
2025-03-07
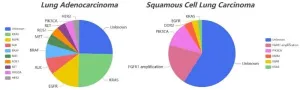
Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related mortality, with lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) representing the most prevalent subtypes of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Despite their classification under the same umbrella, these two forms of lung cancer exhibit distinct genetic landscapes, therapeutic targets, and treatment responses.
Recent advancements in next-generation gene sequencing have identified key driver genes that differentiate LUAD and LUSC, influencing their respective clinical management approaches. LUAD is frequently associated ...
Study reveals widening heart disease disparities in the US
2025-03-07
A study published March 6 in The Lancet Regional Health — Americas highlights a growing divide in cardiovascular health in the U.S., showing that wealth and education play a significant role in heart disease risk.
The research, led by Salma Abdalla, MBBS, DrPH, an assistant professor of public health at Washington University in St. Louis, reveals that the top 20% of high-income, college-educated Americans have far lower rates of cardiovascular disease than the rest of the population — disparities ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
[Press-News.org] A longer, sleeker super predator: Megalodon’s true formNovel study paints more accurate picture of extinct, gigantic shark