Growing consumption of the American eel may lead to it being critically endangered like its European counterpart
A study by a Yale-NUS research team finds the endangered American eel being sold in Singapore as ‘eel’or ‘unagi’ – findings call for more attention to monitor the eel trade
2025-03-10
(Press-News.org)
High demand for eel combined with decline in stock have resulted in soaring prices for this food item, which in many cultures, is considered a delicacy. This has fuelled a concern globally as the prized food item is now being illegally traded from Europe to Asia.
Current research has focused on the critically endangered Anguilla anguilla, commonly known as the European eel. While its export outside the European Union is tightly regulated, large quantities of A. anguilla juveniles continue to be smuggled out of the EU to Asia where they are grown in eel farms until reaching a marketable size.
To investigate the prevalence and consumption of endangered eels – particularly the European eel – a Yale-NUS College research team examined 327 individual eel products purchased across 86 retailers throughout Singapore. However, instead of prevalence of the European eel, the team identified 70% of another species in the sample – Anguilla rostrata, commonly known as the American eel. While not critically endangered like the European eel, the American eel is also considered an endangered species. The findings suggested a possible shift in trade and consumption of eel to the American eel.
Given these findings, the research team called for specific attention to the American eel, with increased enforcement and monitoring needed as proactive steps necessary to avoid the same dramatic population declines that have been documented in other eel species like the European eel.
The paper was a result of Yale-NUS alumnus Joshua Choo (Class of 2024)’s Environment Studies capstone, which he did under the supervision of Yale-NUS Assistant Professor of Science (Marine Biology) Benjamin Wainwright. The paper was published in Conservation Science and Practice. In July 2024, Joshua presented the research at the 2024 International Eel Science Symposium in Liverpool, UK.
Joshua said, “It was sad to connect Singaporean unagi with the history of anguillid eel exploitation – where a crash in one anguillid’s stock repeatedly leads to another’s overexploitation and crash. It was, however, heartening to see so many researchers and Indigenous groups invested in anguillid recovery in Liverpool – from Japan to Aotearoa to the EU and UK. There’s room for Southeast Asian perspectives in eel science – it’s important to protect tropical anguillids from the endangerment plaguing their temperate cousins, and to explore conservation solutions for our food that can bypass profit-driven overexploitation.”
Joshua and the research team performed DNA barcoding of the samples of eel meat, sold as ‘eel’ or ‘unagi’ by supermarkets, restaurants, and wholesalers. Their findings found three pieces of the critically endangered European eel (which is banned from export outside the EU), and that 217 of the 257 products he tested were the endangered, though not internationally regulated, American eel.
“The mislabelling of seafood products is a significant global problem that contributes to ongoing biodiversity losses in the oceans. This deliberate mislabelling can have negative consequences for the health of human consumers and presents numerous opportunities for organised crime to prosper. The trade in eels is described as the greatest wildlife crime on Earth, it supports vast criminal networks that illegally traffic many hundreds of millions of glass eels (juvenile eels) to Asia each year,” said Asst Prof Wainwright.
He further explained, “What we show with this work is a likely shift in trade, this shift could be the consequence of EU enforced rules and regulations making it harder to smuggle the European eel to Asia, consequently suppliers have now shifted their focus to the less regulated American eel. If the American eel is to avoid a similar fate to that suffered by the European eels, it will be important to closely monitor the American eel trade and introduce rules and regulations designed to prevent overexploitation.”
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-03-10
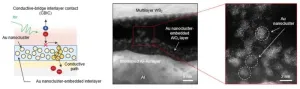
Next-generation imaging technology is rapidly expanding beyond smartphones into intelligent devices, robotics, extended reality (XR) devices, healthcare, CCTV, and various other industries. At the core of these technological advances are highly efficient, ultra-compact image sensors that convert light signals into electrical signals. Image sensors capture and process visual information from objects and environments, enabling precise reconstruction of their shape, size, and spatial position.
Currently, commercial image sensors are primarily based on silicon semiconductors. ...
2025-03-10
A new study examining the effects of sleep patterns and shift work on the immune system has found that sleep debt and night shifts increase the risk of several common infections in nurses.
Modern society relies on shift work, which requires employees to work outside of traditional hours. While essential in sectors such as healthcare, growing evidence suggests that these work patterns may negatively impact worker’s health.
This study, which analysed self-reported data from 1,335 Norwegian nurses, found that shift work – particularly night shifts – was associated with a higher risk of several infections, including the ...
2025-03-09
CHICAGO — A new scientific study provides many new insights into the biology of the prehistoric gigantic shark, Megalodon or megatooth shark, which lived nearly worldwide 15-3.6 million years ago. Paleobiology professor Kenshu Shimada of DePaul University led the study along with 28 other shark, fossil, and vertebrate anatomy experts around the globe. Findings from the study will be published in the journal “Palaeontologia Electronica.”
Formally called Otodus megalodon, it is primarily known only from its serrated teeth, vertebrae, ...
2025-03-09
The megalodon has long been imagined as an enormous great white shark, but new research suggests that perception is all wrong. The study finds the prehistoric hunter had a much longer body—closer in shape to a lemon shark or even a large whale.
The study team, which included researchers from University of California, Riverside and across the globe, used a novel approach to estimate the shark’s total body length, moving beyond traditional methods that rely primarily on tooth size. By examining megalodon’s vertebral column and comparing ...
2025-03-09
Research Highlights:
Increased physical activity including taking more daily steps was linked to a lower risk of death from cardiovascular disease among postmenopausal women with a history of cancer.
The study found that engaging in one hour per day of moderate to vigorous physical activity reduced participants’ risk of death from any cause by 40% and risk of death from cardiovascular disease by 60%.
Each additional 2,500 steps per day for a participant was associated with a 34% reduction in risk of death from cardiovascular disease.
Note: The study featured in this news release is a research abstract. Abstracts presented ...
2025-03-09
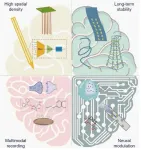
A recent study published in Engineering delves into the latest progress in intracortical neural interface technologies for freely moving animals. These interfaces, which establish a connection between the nervous system and external devices, have the potential to revolutionize neuroscience research and clinical medicine.
The researchers, led by Xinxia Cai, Zhaojie Xu and Yirong Wu, analyzed four key technological directions for ideal implantable neural interface devices: higher spatial density, improved biocompatibility, enhanced multimodal detection of electrical/neurotransmitter signals, and more effective neural modulation.
In terms of high spatial density, microelectrode ...
2025-03-08
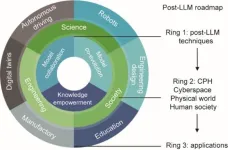
A recent paper published in the journal Engineering delves into the future of artificial intelligence (AI) beyond large language models (LLMs). LLMs have made remarkable progress in multimodal tasks, yet they face limitations such as outdated information, hallucinations, inefficiency, and a lack of interpretability. To address these issues, researchers explore three key directions: knowledge empowerment, model collaboration, and model co-evolution.
Knowledge empowerment aims to integrate external knowledge into LLMs. This can be achieved through various methods, including integrating knowledge ...
2025-03-08
Tokyo, Japan – The XRISM collaboration have discovered flows of hot gas in the core of the Centaurus Cluster. By comparing state-of-the-art X-ray measurements from the XRISM satellite with numerical simulations, they showed this is evidence for collisions between galaxy clusters, causing gas inside to “slosh”. This solves the longstanding mystery of how cluster cores stay hot, and sheds light on how our universe continues to evolve.
Astronomers have long envisioned how vast gravitational forces ...
2025-03-08
Incidents of children in the U.S. being poisoned by the synthetic opioid fentanyl “increased and became more severe”, a new study reveals.
Launched today as Congress continues to review the HALT Fentanyl Act, the research follows an analysis of nonfatal fentanyl pediatric (aged 0-19) exposures reported to poison centers in 49 U.S. states from 2015 through to 2023.
In total, some 3,009 cases were detailed across the eight-year period.
In 2023 alone, 44.6% were life-threatening incidents in which there was extreme harm ...
2025-03-08
Humans may not be the only ones who aid their friends when they’re hurt. Mice may do it, too, as shown by a new research study led by scientists at the Keck School of Medicine of USC published recently in Science.
Scientists have been trying to understand why social mammals appear to help injured members of their species. There are numerous factors that determine empathetic behavior and social bonding in mammals, said Li Zhang, the principal investigator of the study and professor of physiology and neuroscience ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Growing consumption of the American eel may lead to it being critically endangered like its European counterpart
A study by a Yale-NUS research team finds the endangered American eel being sold in Singapore as ‘eel’or ‘unagi’ – findings call for more attention to monitor the eel trade