Patients’ affinity for AI messages drops if they know the technology was used
A survey of patients showed a slight preference for AI messages over messages written by their clinician, but overall satisfaction was high for both communications
2025-03-11
(Press-News.org) DURHAM, N.C. – In a Duke Health-led survey, patients who were shown messages written either by artificial intelligence (AI) or human clinicians indicated a preference for responses drafted by AI over a human. That preference was diminished, though not erased, when told AI was involved.
The study, publishing March 11 in JAMA Network Open, showed high overall satisfaction with communications written both by AI and humans, despite their preference for AI. This suggests that letting patients know AI was used does not greatly reduce confidence in the message.
“Every health system is grappling with this issue of whether we disclose the use of AI and how,” said senior author Anand Chowdhury, M.D., assistant professor in the Department of Medicine at Duke University School of Medicine. “There is a desire to be transparent, and a desire to have satisfied patients. If we disclose AI, what do we lose? That is what our study intended to measure.”
Chowdhury and colleagues sent a series of surveys to members of the Duke University Health System patient advisory committee. This is a group of Duke Health patients and community members who help inform how Duke Health communicates with and cares for patients. More than 1,400 people responded to at least one of the surveys.
The surveys focused on three clinical topics, including routine medication refill request (a low seriousness topic), medication side effect question (moderate seriousness), and potential cancer on imaging (high seriousness).
Human responses were provided by a multidisciplinary team of physicians who were asked to write a realistic response to each survey scenario based on how they typically draft responses to patients. The generative AI responses were written using ChatGPT and were reviewed for accuracy by the study physicians who made minimal changes to the responses.
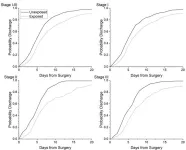
For each survey, participants were asked to review a vignette that presented one of the clinical topics. Each vignette included a response from either AI or human clinicians, along with either a disclosure or no disclosure telling them who the author was. They were then asked to rate their overall satisfaction with the response, usefulness of the information, and how cared for they felt during the interaction.
Comparing authors, patients preferred AI-drafted messages by an average difference of 0.30 points on 5-point scale for satisfaction. The AI communications tended to be longer, included more details, and likely seemed more empathetic than human-drafted messages.
“Our study shows us that patients have a slight preference for messages written by AI, even though they are slightly less satisfied when the disclosure informs them that AI was involved,” said first author Joanna S. Cavalier, M.D., assistant professor in the Department of Medicine at Duke University School of Medicine.
When they looked at the difference in satisfaction when participants were told AI was involved, disclosing AI led to lower satisfaction, though not by much: 0.1 points on the 5-point scale. Regardless of the actual author, patients were overall more satisfied with messages when they were not told AI was involved in drafting the response.
“These findings are particularly important in the context of research showing that patients have higher satisfaction when they can connect electronically with their clinicians,” Chowdhury said.
“At the same time, clinicians express burnout when their in-basket is full, making the use of automated tools highly attractive to ease that burden,” Chowdhury said. “Ultimately these findings give us confidence to use technologies like this to potentially help our clinicians reduce burnout, while still doing the right thing and telling our patients when we use AI.”
In addition to Chowdhury and Cavalier, study authors include Benjamin A. Goldstein, Vardit Ravitsky, Jean-Christophe Bélisle-Pipon, Armando Bedoya, Jennifer Maddocks, Sam Klotman, Matt Roman, Jessica Sperling, Chun Xu, and Eric G Poon.
###
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-03-11
Due to the physical, psychological, and socioeconomic consequences of a cancer diagnosis and treatment, people with cancer are especially vulnerable during extreme weather events like hurricanes, tornadoes, and wildfires, which are becoming more common and damaging with climate change. A new national study led by American Cancer Society (ACS) and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health researchers finds patients whose facility was impacted by a wildfire disaster during recovery from lung cancer surgery had longer length of stay (LOS) than similar patients treated at the same facility, but at times when no disaster occurred. The findings are out today in the Journal ...
2025-03-11
A research team led by the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has discovered “berkelocene,” the first organometallic molecule to be characterized containing the heavy element berkelium.
Organometallic molecules, which consist of a metal ion surrounded by a carbon-based framework, are relatively common for early actinide elements like uranium (atomic number 92), but they are scarcely known for later actinides like berkelium (atomic number 97).
“This is the first time that evidence for the formation of a chemical bond between berkelium and carbon has been obtained. The discovery provides ...
2025-03-11
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is a common and potentially life-threatening condition that requires prompt and accurate diagnosis. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and colonoscopy are the primary diagnostic modalities, but initial examinations may sometimes fail to identify the bleeding source. In such cases, repeated endoscopic evaluations can improve detection rates. This review explores the role of repeat EGD and colonoscopy in diagnosing GI bleeding, highlighting the conditions under which they are most beneficial and the challenges associated with their use.
Incidence and Causes of Gastrointestinal ...
2025-03-11
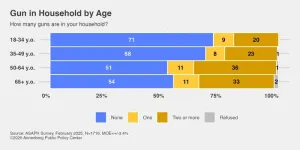
PHILADELPHIA – Since 2017, firearm-related injuries in the United States have been the most common cause of death from injury among children through young adults, ages 1 to 24, surpassing motor vehicle accidents, according to a 2022 study. Access to firearms in one’s home increases the risk of suicide and accidental death.
But over a third of Americans with guns in their homes say they do not store all of them in a locked location (37%), according to the latest health survey from the Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) of the University of Pennsylvania. ...
2025-03-11
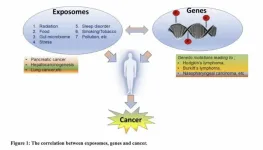
“Environmental exposures may cause genetic damage, lead to mutations in key genes, and/or block the DNA repair mechanisms increasing the risk of cancer.”
BUFFALO, NY – March 11, 2025 – A new editorial was published in Oncotarget, Volume 16, on March 10, 2025, titled “EXPOSOMES and GENES: The duo influencing CANCER initiation and progression.”
In this editorial, Drs. Uzma Saqib, Katherine E. Ricks, Alexander G. Obukhov, and Krishnan Hajela from Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya (DAVV) in Indore, India, discuss how environmental factors, known as exposomes, interact with genes to influence cancer risk. The authors highlight how pollution, diet, ...
2025-03-11
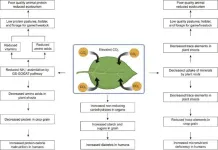
A recent study published in Engineering delves into the complex impacts of elevated CO2 levels on food security, plant growth, and crop quality. As the global atmospheric CO2 concentration continues to rise, understanding these effects is crucial for ensuring future food supplies.
On one hand, elevated CO2 can have some positive effects on plants. For C3 plants, it can stimulate photosynthesis, leading to increased dry matter yield and grain production. In legumes, it enhances N2 fixation, which is beneficial for reducing reliance on chemical fertilizers. Additionally, ...
2025-03-11
Researchers from RMIT University and the University of Melbourne have discovered that water generates an electrical charge up to 10 times greater than previously understood when it moves across a surface.
The team, led by Dr Joe Berry, Dr Peter Sherrell and Professor Amanda Ellis, observed when a water droplet became stuck on a tiny bump or rough spot, the force built up until it “jumped or slipped” past an obstacle, creating an irreversible charge that had not been reported before.
The new understanding of this “stick-slip” motion of water over a surface paves the way for surface design with controlled electrification, with ...
2025-03-11
Miami (March 11, 2025) – People with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and arthritis have a higher risk of death than people with arthritis who do not have COPD, according to a new study. The study is published in the January 2025 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
COPD is an inflammatory lung disease, comprising several conditions, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, and can be caused by genetics and irritants like smoke or pollution. The disease affects more than 30 million Americans and is the fourth leading cause of death ...
2025-03-11
WASHINGTON, DC – The Editorial Board of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) has selected six papers published by PNAS in 2024 to receive the Cozzarelli Prize, an award that recognizes outstanding contributions to the scientific disciplines represented by the National Academy of Sciences (NAS). Papers were chosen from more than 3,200 research articles that appeared in the journal last year and represent the six broadly defined classes under which the NAS is organized. Additionally, the Editorial Board has recognized six papers—one ...
2025-03-11
The American Meteorological Society continuously publishes research on climate, weather, and water in its 12 journals. Many of these articles are available for early online access–they are peer-reviewed, but not yet in their final published form. Below are some recent examples.
JOURNAL ARTICLES
Climate Change Increases Energy Demand and Cost in Texas
Weather, Climate, and Society
Climate change is driving large increases in electricity demand and costs in Texas’ ERCOT market. Compared to a 1950–1980 baseline climate, ERCOT electricity demand in 2023 was 1.9 ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Patients’ affinity for AI messages drops if they know the technology was used
A survey of patients showed a slight preference for AI messages over messages written by their clinician, but overall satisfaction was high for both communications