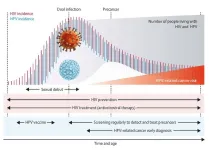
(Press-News.org) Public health advice on the safe consumption of glycerol-containing slush ice drinks, also known as slushees, may need revising, conclude researchers after carrying out a detailed review of the medical notes of 21 children who became acutely unwell shortly after drinking one of these products.
Their findings, published in the journal Archives of Disease in Childhood, show that in each case the child became acutely unwell with a cluster of symptoms soon after drinking a slush ice drink, which the researchers refer to as glycerol intoxication syndrome.
The clinical and biochemical features were similar in all of these children and included reduced consciousness, a sudden sharp drop in blood sugar (hypoglycaemia), and a build-up of acid in the blood (metabolic acidosis).
Such symptoms, when they occur together, can indicate poisoning or inherited metabolic disorders, prompting further investigations.
Brightly coloured slush ice drinks are designed to appeal to children, note the researchers. While the ingredients vary, most of those available in the UK and Ireland are ‘no added sugar’ or ‘sugar free’ products and contain glycerol (E422, also known as glycerin), they add.
Glycerol stops the ice from fully freezing, so maintaining the slush effect in the absence of a high sugar content, they explain.
With a view to informing public health policy and guidance for parents, the researchers scrutinised the medical notes of 21 children who had become acutely unwell after consuming a slush ice drink and had initially been diagnosed with hypoglycaemia after their arrival in emergency care.
Apart from one child referred in 2009, all the others were referred for further review between 2018 and 2024.
Diagnosis was informed by lab test confirmation of at least two of the following: hypoglycaemia; metabolic acidosis; glyceroluria (high levels of glycerol in the urine), and backed up by negative biochemical, enzyme, and/or genetic test results for underlying inherited metabolic disorders.
Information on sex was available for 18 of the children, just over half of whom (10; 56%) were male. Their average age was 3 and a half, but ranged from 2 to nearly 7.
How quickly they became ill was known for 15: in 14 (93%) this was within 60 minutes. Similarly, state of consciousness was known for 17, and in 16 this was significantly and suddenly reduced. One child had a seizure. Urgent neuroimaging was carried out in 4 (33%) out of 12 children.
Twenty children had documented hypoglycaemia (blood glucose 2.6 mmol/l or below); but in 13 (65%) this was even lower, indicating severe hypoglycaemia. Metabolic acidosis was present in 16 of the 17 children for whom this information was available.
Twelve of 16 children had low levels of potassium, and 8 out of 9 in whom this was measured had falsely high blood fat levels (pseudohypertriglycerideraemia). The researchers concluded that the children had had glycerol intoxication syndrome.
All the children recovered quickly after initial resuscitation and stabilisation of their blood glucose. They were discharged with advice to avoid slush ice drinks. Twenty did so and had no further episodes of hypoglycaemia.
But one drank another slush ice drink at the age of 7 and developed symptoms within an hour, rapidly progressing to vomiting and drowsiness. The parents gave the child a glucose drink, and called an ambulance. When the paramedics arrived, the child’s blood glucose was back to normal and symptoms were already resolving.
Most of the cases in the series presented for emergency care between 2018 and 2024. And the researchers suggest: “A cause of the recent apparent surge in cases may be the reduced sugar content of these drinks, secondary to two main factors: first, public health and parental concerns about high sugar ingestion, and second, the introduction of a ‘sugar tax’ on high sugar (>5%)-containing drinks in Ireland and the UK in 2018 and 2019, respectively.”
These drinks sold in countries where there’s no sugar tax, contain a much higher glucose content and often don’t contain any glycerol at all, they add.
Based on some of the cases in this series, the UK Food Standards Agency recommended that young children (4 and under) shouldn’t be given slush ice drinks containing glycerol, and that those aged 10 or younger should not have more than one.The Food Safety Authority of Ireland (FSAI) followed suit with similar guidance in 2024.
But the researchers believe that these recommendations may no longer be enough.
“There is poor transparency around slush ice drink glycerol concentration; estimating a safe dose is therefore not easy. It is also likely that speed and dose of ingestion, along with other aspects, such as whether the drink is consumed alongside a meal or during a fasting state, or consumed after high-intensity exercise, may be contributing factors,” they write.
“Food Standards Scotland and the FSAI suggested that 125 mg/kg of body weight per hour is the lowest dose that is associated with negative health effects. For a toddler this may equate to 50–220 ml of a slush ice drink. The standard size drink sold in the UK and Ireland is 500 ml,” they point out.
Given that these drinks don’t confer any nutritional or health benefits, “recommendations on their safe consumption therefore need to be weighted towards safety,” they suggest.
And they conclude: “To ensure safe population-level recommendations can be easily interpreted at the individual parental level, and given the variability across an age cohort of weight, we suggest that recommendations should be based on weight rather than age. Alternatively, the recommended age threshold may need to be higher (8 years), to ensure the dose per weight would not be exceeded, given normal population variation in weight.”
END
Public health advice on safety of glycerol-containing slush ice drinks likely needs revising
Detailed review of 21 cases of acutely ill children linked to these products prompts concerns
2025-03-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Water aerobics for more than 10 weeks can trim waist size and aid weight loss
2025-03-11
Water/aqua aerobics for 10 or more weeks at a time can trim waist size and aid weight loss, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published in the open access journal BMJ Open
This type of exercise is particularly effective in overweight/obese women and the over 45s, the analysis indicates.
Global estimates for 2022 indicate that more than 43% of adults worldwide were overweight, and that 504 million women and 374 million men were obese, note the researchers, adding that obesity contributes to an estimated 2.8 million deaths every year.
The buoyancy of water helps reduce joint injuries commonly associated with land based exercise ...
New study in the Lancet HIV highlights gaps in HPV-related cancer prevention for people living with HIV
2025-03-11
A new study published in The Lancet HIV reveals gaps in knowledge surrounding the prevention of HPV-related cancers in people living with HIV and outlines future research priorities. A literature review, conducted by a team of international experts underscores the need for further research and highlights existing disparities in healthcare for this vulnerable population.
HPV-related cancers are preventable, primarily through vaccination. However, a Professor of Epidemiology at the University of Tartu and one of the study’s authors Anneli Uusküla said that the study found a lack of evidence on the effectiveness of ...
Growth rates of broilers contribute to behavior differences, shed light on welfare impacts
2025-03-11
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. — As poultry companies weigh cost and efficiency with higher animal welfare standards, research comparing conventional and slow-growing broiler breeds showed that the slow-growing chickens displayed behaviors more closely associated with positive welfare.
Broilers — chickens specifically bred for meat production — are typically raised for six to eight weeks, while slow-growing broilers need up to 12 weeks to reach maturity.
Though gaining popularity in some European ...
Nature-inspired 3D-printing method shoots up faster than bamboo
2025-03-11
Charging forward at top speed, a garden snail slimes up 1 millimeter of pavement per second. By this logic, Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology researchers’ new 3D printing process speeds past existing methods — at a snail’s pace.
Researchers in Beckman’s Autonomous Materials Systems Group created “growth printing,” which mimics tree trunks’ outward expansion to print polymer parts quickly and efficiently without the molds and expensive equipment typically associated with 3D printing. Their work appears in the journal Advanced Materials.
“Humans ...
Scientists create a type of catalog, the ‘colocatome,’ of non-cancerous cells’ influence on cancer
2025-03-11
Even cells experience peer pressure.
Scientists have long studied the ins and outs of cancer cells to learn more about the disease, but they’re increasingly finding that noncancerous cells near the cancer cells exert a powerful influence over a tumor’s trajectory.
“Not all cells in a tumor are cancer cells — they’re not even always the most dominant cell type,” said Sylvia Plevritis, PhD, chair of Stanford Medicine’s department of biomedical data science. “There are many other cell types that support tumors.”
To better capture the whole picture of cells’ locations and interactions, Plevritis ...
MSU researchers use unique approaches to study plants in future conditions
2025-03-11
As major changes continue for our planet’s climate, scientists are concerned about how plants will grow and adapt.
Researchers in the MSU-DOE Plant Research Laboratory, or PRL, Sharkey lab are studying changes in plant metabolism that occur when plants are grown in high light, high CO2 (HLHC) conditions.
They found that under these conditions, plants photosynthesize more, which can lead to larger plants, and potentially larger crop yields. However, there are tradeoffs; scientists also found that plants lose carbon under these conditions, which they need to make food. This ...
More than marks: How wellbeing shapes academic success
2025-03-11
With Australia’s National Assessment Program (NAPLAN) beginning today, new research from the University of South Australia highlights a critical but often overlooked factor in student success – wellbeing.
In a world first* study of more than 215,000 students, UniSA researchers found that while standardised tests measure academic skills, different dimensions of wellbeing - emotional wellbeing, engagement, and learning readiness - can play a crucial role in performance.
Specifically, the study found that learning readiness - which includes foundational skills such as perseverance, confidence, and engagement ...
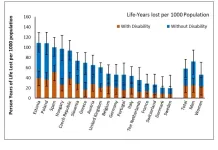
Study quantifies loss of disability-free years of life from COVID-19 pandemic
2025-03-11
Among 289 million adults in 18 European countries, more than 16 million years of life were lost from 2020 through 2022 due to the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a new study published March 11th in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine by Sara Ahmadi-Abhari of Imperial College London, UK, and colleagues.
The direct and indirect impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on both total and disability-free years of life lost are important for policy setting and resource allocation, but they have not been thoroughly investigated.
In the new study, researchers ...
Butterflies choose mates because they are more attractive, not just easier to see
2025-03-11
A simple neural change alters mating preferences in male butterflies, aiding rapid behavioral evolution, Nicholas VanKuren and Nathan Buerkle at the University of Chicago, US, and colleagues, report March 11th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology.
Heliconius are a group of tropical butterflies known for their wide variety of wing patterns and colors, which act as a warning to predators. Because wing coloration is crucial for their survival, males have evolved a preference for females with the same wing color. But the sensory and neurological mechanisms behind these preferences are poorly understood.
Researchers ...
SwRI receives $3 million NASA astrobiology grant to study microbial life in Alaska’s arctic sand dunes
2025-03-11
SAN ANTONIO — March 11, 2025 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) has received a three-year, $2,999,998 million grant from NASA to identify and characterize life and its biosignatures in frozen sand dunes in Alaska, under conditions similar to dune fields on early Mars and Saturn’s moon Titan. The Assessing Regional Reflectors of Astrobiology in Kobuk dunes for Interplanetary Science (ARRAKIS) project team, which includes researchers from Brigham Young University and the University of California—Davis, seek insight into ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] Public health advice on safety of glycerol-containing slush ice drinks likely needs revisingDetailed review of 21 cases of acutely ill children linked to these products prompts concerns