(Press-News.org) A simple neural change alters mating preferences in male butterflies, aiding rapid behavioral evolution, Nicholas VanKuren and Nathan Buerkle at the University of Chicago, US, and colleagues, report March 11th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology.
Heliconius are a group of tropical butterflies known for their wide variety of wing patterns and colors, which act as a warning to predators. Because wing coloration is crucial for their survival, males have evolved a preference for females with the same wing color. But the sensory and neurological mechanisms behind these preferences are poorly understood.
Researchers investigated the genetic and sensory mechanisms behind mate preferences in two subspecies of Heliconius cydno butterflies that have either yellow or white patches on their wings. They identified four genomic regions linked to both wing color and mate preference, including the ‘K locus’, which has also been associated with these traits in other Heliconius butterflies. Next, they investigated gene expression patterns in the retina, optic lobe and brain at different stages of development. They found seven genetic variants that were located in genomic regions associated with mate preference, and were also expressed at significantly different levels in yellow and white males, making them strong candidates for influencing mating preferences. To understand how males perceive different wing colors, they investigated the color sensitivity and activity of photoreceptors in the butterflies’ eyes. They found that green-sensitive photoreceptors inhibited the activity of most UV-sensitive photoreceptors in males which preferred yellow-winged females but comparatively few in other butterflies. This relatively simple modification of the peripheral nervous system could provide a physiological basis for altering the perception and attractiveness of the two wing colors.
The results show that the butterflies’ mate preferences result from differences in how sensory information is processed. This suggests that male Heliconius cydno butterflies find females with a matching wing color more attractive, not just easier to see. Inhibitory relationships between photoreceptors are easily evolvable, which may facilitate rapid behavioral evolution, the authors say.
The authors add, “Our work generated a striking picture of how a critical visual behavior - mate choice - is controlled, from variation in the connections between neurons in the eye down to genetic variation across the genome.”
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: https://plos.io/416TwUA
Citation: VanKuren NW, Buerkle NP, Lu W, Westerman EL, Im AK, Massardo D, et al. (2025) Genetic, developmental and neural changes underlying the evolution of butterfly mate preference. PLoS Biol 23(3): e3002989. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002989
Author countries: United States
Funding: see manuscript
END
Butterflies choose mates because they are more attractive, not just easier to see
Study links genetics, vision and neural processing to mating behavior in Heliconius butterflies
2025-03-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
SwRI receives $3 million NASA astrobiology grant to study microbial life in Alaska’s arctic sand dunes
2025-03-11
SAN ANTONIO — March 11, 2025 —Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) has received a three-year, $2,999,998 million grant from NASA to identify and characterize life and its biosignatures in frozen sand dunes in Alaska, under conditions similar to dune fields on early Mars and Saturn’s moon Titan. The Assessing Regional Reflectors of Astrobiology in Kobuk dunes for Interplanetary Science (ARRAKIS) project team, which includes researchers from Brigham Young University and the University of California—Davis, seek insight into ...
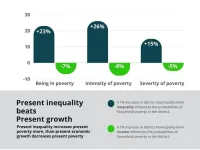
Inequality destroys the benefits of positive economic growth for the poor
2025-03-11
A unique analysis of district-level data reveals why inequality is so destructive to the home consumption welfare of people living below the poverty line, especially during times of significant economic decline, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. During negative economic growth, the welfare of the poor should be the main focus area.
Research from the University of Johannesburg shows how inequality can demolish most of the benefits of positive economic growth and social grants for people living in poverty, especially during economic downturns.
The study by Prof ...
HSS presents innovative research aimed at faster recovery after knee surgery at AAOS Annual Meeting
2025-03-11
At this year’s American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons (AAOS) annual meeting, investigators at Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) presented several significant studies, with three focused on new ways to help patients recover faster after total knee arthroplasty (TKA), also known as knee replacement surgery.
What follows are highlights from these studies:
Limiting Use of Tourniquets During Knee Replacement Surgery Improves Patient Outcomes
Tourniquets have traditionally been used during TKA to reduce blood loss and the need for transfusions. However, a new study of almost 18,000 patients from 2019 to 2023 found that prolonged tourniquet use was linked ...
Advancing catalysis: Novel porous thin-film approach developed at TIFR Hyderabad enhances reaction efficiency
2025-03-11
Catalytic function and its efficiency play a significant role in industrial reactions, and consistent reforms are made in the methodology to enhance the large-scale synthesis of drugs, polymers, and other desired products. Available catalysts can be homogeneous, which means that they possess the same phase as the reactants and products, making them difficult to separate from the reaction mixture. On the other hand, heterogeneous catalysts are a preferred choice for such reactions because of their ease of separation and reusability.
The past decade has seen the emergence of porous ...
Small, faint and 'unexpected in a lot of different ways': U-M astronomers make galactic discovery
2025-03-11
A discovery made by a team led by researchers at the University of Michigan tugs at the seams of some key cosmic lessons we thought we had learned from our own galaxy.
This new knowledge comes from the outskirts of Andromeda, the Milky Way's nearest major galactic neighbor, where astronomers have found the system's smallest and dimmest satellite galaxy to date.
This dwarf galaxy, named Andromeda XXXV and located roughly 3 million light-years away, is forcing astronomers to rethink how galaxies evolve in different cosmic environments and survive different epochs of the universe.
Although the discovery bears ...
Study finds that supportive workplace culture advances implementation of lifestyle medicine in health systems
2025-03-11
Workplace culture plays an integral role in the successful adoption of lifestyle medicine programming within health systems, according to a new study published in BMJ Open.
Researchers developed case studies of health systems with lifestyle medicine programming that had a diversity of size, location, payer model and patient population. More than 40 individuals from those health systems, including administrative leaders, physicians and other team members involved in lifestyle medicine programs, participated in the data collection.
The study found ...
USPSTF statement on screening for food insecurity
2025-03-11
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) concludes that the current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of screening for food insecurity on health outcomes in the primary care setting. According to survey data, 12.8% of households experienced food insecurity in 2022, with 7.7% of households experiencing low food security and 5.1% experiencing very low food security. Nearly one-third of households with incomes below the federal poverty threshold are food insecure. Food insecurity is one among a multitude of medical, psychological, and social conditions ...
‘Fishial’ recognition: Neural network identifies coral reef sounds
2025-03-11
WASHINGTON, March 11, 2025 – Coral reefs are some of the world’s most diverse ecosystems. Despite making up less than 1% of the world’s oceans, one quarter of all marine species spend some portion of their life on a reef. With so much life in one spot, researchers can struggle to gain a clear understanding of which species are present and in what numbers.
In JASA, published on behalf of the Acoustical Society of America by AIP Publishing, researchers from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution combined acoustic monitoring with a neural network to identify fish activity on coral reefs ...
Cardiovascular health and biomarkers of neurodegenerative disease in older adults
2025-03-11
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that promoting cardiovascular health in older adults may help alleviate the burden of neurodegenerative diseases, particularly among Black adults, who are known to experience a higher prevalence of cardiovascular disease.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Anisa Dhana, MD, MSc, email anisa_dhana@rush.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.0527)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Ethics in patient preferences for AI–drafted responses to electronic messages
2025-03-11
About The Study: In this survey study, participants expressed a mild preference for messages written by artificial intelligence (AI) but had a slightly decreased satisfaction when told AI was involved. Patient experience must be considered along with ethical implementation of AI. Although AI disclosure may slightly reduce satisfaction, disclosure should be maintained to uphold patient autonomy and empowerment.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Anand Chowdhury, MD, MMCi, email anand.chowdhury@duke.edu.
To access the embargoed study: ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
[Press-News.org] Butterflies choose mates because they are more attractive, not just easier to seeStudy links genetics, vision and neural processing to mating behavior in Heliconius butterflies