(Press-News.org) Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) concludes that the current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of screening for food insecurity on health outcomes in the primary care setting. According to survey data, 12.8% of households experienced food insecurity in 2022, with 7.7% of households experiencing low food security and 5.1% experiencing very low food security. Nearly one-third of households with incomes below the federal poverty threshold are food insecure. Food insecurity is one among a multitude of medical, psychological, and social conditions common among economically disadvantaged households. The USPSTF routinely makes recommendations about the effectiveness of preventive care services. This is a new USPSTF topic.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2025.0879)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, financial disclosures, funding and support, etc.
Note: More information about the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, its process, and its recommendations can be found on the newsroom page of its website.
# # #
Media advisory: To contact the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, email the Media Coordinator at Newsroom@USPSTF.net or call 301-951-9203. The full report and related articles are linked to this news release.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time and all USPSTF articles remain free indefinitely https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2025.0879?guestAccessKey=756929f4-9b8e-4200-a23e-8220ebdcee47&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=031125
END
USPSTF statement on screening for food insecurity
JAMA
2025-03-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
‘Fishial’ recognition: Neural network identifies coral reef sounds
2025-03-11
WASHINGTON, March 11, 2025 – Coral reefs are some of the world’s most diverse ecosystems. Despite making up less than 1% of the world’s oceans, one quarter of all marine species spend some portion of their life on a reef. With so much life in one spot, researchers can struggle to gain a clear understanding of which species are present and in what numbers.
In JASA, published on behalf of the Acoustical Society of America by AIP Publishing, researchers from Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution combined acoustic monitoring with a neural network to identify fish activity on coral reefs ...
Cardiovascular health and biomarkers of neurodegenerative disease in older adults
2025-03-11
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that promoting cardiovascular health in older adults may help alleviate the burden of neurodegenerative diseases, particularly among Black adults, who are known to experience a higher prevalence of cardiovascular disease.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Anisa Dhana, MD, MSc, email anisa_dhana@rush.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.0527)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Ethics in patient preferences for AI–drafted responses to electronic messages
2025-03-11
About The Study: In this survey study, participants expressed a mild preference for messages written by artificial intelligence (AI) but had a slightly decreased satisfaction when told AI was involved. Patient experience must be considered along with ethical implementation of AI. Although AI disclosure may slightly reduce satisfaction, disclosure should be maintained to uphold patient autonomy and empowerment.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Anand Chowdhury, MD, MMCi, email anand.chowdhury@duke.edu.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Patients’ affinity for AI messages drops if they know the technology was used
2025-03-11
DURHAM, N.C. – In a Duke Health-led survey, patients who were shown messages written either by artificial intelligence (AI) or human clinicians indicated a preference for responses drafted by AI over a human. That preference was diminished, though not erased, when told AI was involved.
The study, publishing March 11 in JAMA Network Open, showed high overall satisfaction with communications written both by AI and humans, despite their preference for AI. This suggests that letting patients know AI was used does not greatly reduce confidence in the message.
“Every health system is grappling with this issue of whether we disclose the use of AI and how,” ...
New ACS led study finds wildfires pose challenges to cancer care
2025-03-11
Due to the physical, psychological, and socioeconomic consequences of a cancer diagnosis and treatment, people with cancer are especially vulnerable during extreme weather events like hurricanes, tornadoes, and wildfires, which are becoming more common and damaging with climate change. A new national study led by American Cancer Society (ACS) and Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health researchers finds patients whose facility was impacted by a wildfire disaster during recovery from lung cancer surgery had longer length of stay (LOS) than similar patients treated at the same facility, but at times when no disaster occurred. The findings are out today in the Journal ...
Scientists discover new heavy-metal molecule ‘berkelocene’
2025-03-11
A research team led by the Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) has discovered “berkelocene,” the first organometallic molecule to be characterized containing the heavy element berkelium.
Organometallic molecules, which consist of a metal ion surrounded by a carbon-based framework, are relatively common for early actinide elements like uranium (atomic number 92), but they are scarcely known for later actinides like berkelium (atomic number 97).
“This is the first time that evidence for the formation of a chemical bond between berkelium and carbon has been obtained. The discovery provides ...
Repeated esophagogastroduodenoscopy and colonoscopy in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal bleeding
2025-03-11
Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is a common and potentially life-threatening condition that requires prompt and accurate diagnosis. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) and colonoscopy are the primary diagnostic modalities, but initial examinations may sometimes fail to identify the bleeding source. In such cases, repeated endoscopic evaluations can improve detection rates. This review explores the role of repeat EGD and colonoscopy in diagnosing GI bleeding, highlighting the conditions under which they are most beneficial and the challenges associated with their use.
Incidence and Causes of Gastrointestinal ...
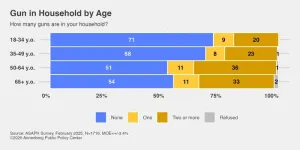
Over 1 in 3 adults in households with guns do not store all in locked locations
2025-03-11
PHILADELPHIA – Since 2017, firearm-related injuries in the United States have been the most common cause of death from injury among children through young adults, ages 1 to 24, surpassing motor vehicle accidents, according to a 2022 study. Access to firearms in one’s home increases the risk of suicide and accidental death.
But over a third of Americans with guns in their homes say they do not store all of them in a locked location (37%), according to the latest health survey from the Annenberg Public Policy Center (APPC) of the University of Pennsylvania. ...
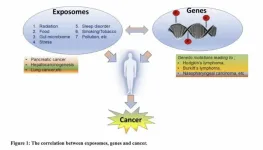
How environmental exposures affect genes and increase cancer risk
2025-03-11
“Environmental exposures may cause genetic damage, lead to mutations in key genes, and/or block the DNA repair mechanisms increasing the risk of cancer.”
BUFFALO, NY – March 11, 2025 – A new editorial was published in Oncotarget, Volume 16, on March 10, 2025, titled “EXPOSOMES and GENES: The duo influencing CANCER initiation and progression.”
In this editorial, Drs. Uzma Saqib, Katherine E. Ricks, Alexander G. Obukhov, and Krishnan Hajela from Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya (DAVV) in Indore, India, discuss how environmental factors, known as exposomes, interact with genes to influence cancer risk. The authors highlight how pollution, diet, ...
Rising CO2 levels: Impacts on crop nutrition and global food supplies
2025-03-11
A recent study published in Engineering delves into the complex impacts of elevated CO2 levels on food security, plant growth, and crop quality. As the global atmospheric CO2 concentration continues to rise, understanding these effects is crucial for ensuring future food supplies.
On one hand, elevated CO2 can have some positive effects on plants. For C3 plants, it can stimulate photosynthesis, leading to increased dry matter yield and grain production. In legumes, it enhances N2 fixation, which is beneficial for reducing reliance on chemical fertilizers. Additionally, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
[Press-News.org] USPSTF statement on screening for food insecurityJAMA