(Press-News.org) Prescriptions for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in England have risen 18% year on year since the pandemic. This is higher than previously reported, and masks wide regional variations in prescribing rates, finds research published in the open access journal BMJ Mental Health.
The trends likely reflect growing public and professional awareness of the condition, driven in part by social media, as well as the potential impact of COVID-19, suggest the researchers. But the regional variations point to inequalities in access to care, they add.
ADHD is common in children, with a global prevalence of around 7%, note the researchers, while its prevalence in symptomatic adults is also on the rise, with a reported rate of nearly 7%.
Five drugs are licensed for its treatment in the UK: three stimulants (methylphenidate, dexamfetamine, lisdexamfetamine); and two non-stimulants (atomoxetine, guanfacine). And in the absence or lack of availability of alternative treatment options, such as psychological or behavioural therapy, these drugs have a key role in ADHD management, say the researchers.
Several studies have reported an increase in ADHD prescriptions in England since the COVID-19 pandemic, but most of these studies were based on the old NHS structure—before the introduction of 42 integrated care systems—and/or focused on specific groups or types of drug.
And little is currently known about the potential influence of other factors, such as social deprivation, inequalities, and mental health needs, they add.
To explore this further, they mined the English Prescribing Dataset from April 2019 to March 2024, looking at prescription trends for the 5 currently licensed ADHD drugs at national, regional, and integrated care board (ICB) levels.
The findings showed that prescriptions increased significantly from around 25 items per 1000 people in 2019-20, before the advent of the pandemic to 41.55 items in 2023-24, with an average annual increase of 18% nationally—higher than previously reported.
Methylphenidate remained the most frequently prescribed drug (19 items/1000 people), but the highest increase was for lisdexamfetamine, prescriptions for which increased by 55% year on year, rising from 2.86 items/1000 people in 2019-20 to 8.68 items in 2023-24.
ADHD prescriptions rose in all 7 regions of England, but there were significant regional variations: London saw the highest annual increase of 28%; the Northeast and Yorkshire saw the lowest at 13%.
The second highest change in the annual prescription rate of almost 19.5% was in Southeast England.
Prescribing trends also varied widely at the ICB level. The NHS Birmingham and Solihull ICB witnessed the highest increase in prescriptions of almost 51.5%, but with considerable variation within the ICB itself. The smallest increase of just over 4.5% was in NHS Norfolk and Waveney ICB.
Further analysis showed significant statistical associations between socioeconomic factors and ADHD prescriptions, particularly ethnicity and deprivation, but also age and inequality.
Several factors may explain the substantial rise in prescription rates, say the researchers. “Increased public and professional awareness, partly driven by social media platforms like TikTok and Instagram, has likely encouraged more people to seek assessment, diagnosis and treatment,” they write.
And they caution: “There is a pressing need for research into effective methods for vetting and moderating ADHD-related information on social media platforms to ensure that awareness efforts do not inadvertently spread misinformation.”
The widespread disruption and increased psychological stress levels caused by the COVID-19 pandemic may also have driven up prescribing rates, they suggest.
“While our study has identified significant changes in prescription patterns during and after the pandemic, it is crucial to determine whether these trends represent a temporary shift or a more permanent change in ADHD prescriptions,” they emphasise.
And they conclude: “The significant rise in ADHD prescriptions across England highlights the urgent need for policies that address both regional and socioeconomic disparities in ADHD care access. Targeted efforts should be made to meet the needs of each region by identifying specific barriers to care and their root causes.”
END
Yearly 18% rise in ADHD prescriptions in England since COVID-19 pandemic
Figures reflect growing public and professional awareness and potential impact of COVID-19. But wide regional variations point to inequalities in access to care, say researchers
2025-03-11
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Public health advice on safety of glycerol-containing slush ice drinks likely needs revising
2025-03-11
Public health advice on the safe consumption of glycerol-containing slush ice drinks, also known as slushees, may need revising, conclude researchers after carrying out a detailed review of the medical notes of 21 children who became acutely unwell shortly after drinking one of these products.
Their findings, published in the journal Archives of Disease in Childhood, show that in each case the child became acutely unwell with a cluster of symptoms soon after drinking a slush ice drink, which the researchers refer to as glycerol intoxication ...
Water aerobics for more than 10 weeks can trim waist size and aid weight loss
2025-03-11
Water/aqua aerobics for 10 or more weeks at a time can trim waist size and aid weight loss, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published in the open access journal BMJ Open
This type of exercise is particularly effective in overweight/obese women and the over 45s, the analysis indicates.
Global estimates for 2022 indicate that more than 43% of adults worldwide were overweight, and that 504 million women and 374 million men were obese, note the researchers, adding that obesity contributes to an estimated 2.8 million deaths every year.
The buoyancy of water helps reduce joint injuries commonly associated with land based exercise ...
New study in the Lancet HIV highlights gaps in HPV-related cancer prevention for people living with HIV
2025-03-11
A new study published in The Lancet HIV reveals gaps in knowledge surrounding the prevention of HPV-related cancers in people living with HIV and outlines future research priorities. A literature review, conducted by a team of international experts underscores the need for further research and highlights existing disparities in healthcare for this vulnerable population.
HPV-related cancers are preventable, primarily through vaccination. However, a Professor of Epidemiology at the University of Tartu and one of the study’s authors Anneli Uusküla said that the study found a lack of evidence on the effectiveness of ...
Growth rates of broilers contribute to behavior differences, shed light on welfare impacts
2025-03-11
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. — As poultry companies weigh cost and efficiency with higher animal welfare standards, research comparing conventional and slow-growing broiler breeds showed that the slow-growing chickens displayed behaviors more closely associated with positive welfare.
Broilers — chickens specifically bred for meat production — are typically raised for six to eight weeks, while slow-growing broilers need up to 12 weeks to reach maturity.
Though gaining popularity in some European ...
Nature-inspired 3D-printing method shoots up faster than bamboo
2025-03-11
Charging forward at top speed, a garden snail slimes up 1 millimeter of pavement per second. By this logic, Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology researchers’ new 3D printing process speeds past existing methods — at a snail’s pace.
Researchers in Beckman’s Autonomous Materials Systems Group created “growth printing,” which mimics tree trunks’ outward expansion to print polymer parts quickly and efficiently without the molds and expensive equipment typically associated with 3D printing. Their work appears in the journal Advanced Materials.
“Humans ...
Scientists create a type of catalog, the ‘colocatome,’ of non-cancerous cells’ influence on cancer
2025-03-11
Even cells experience peer pressure.
Scientists have long studied the ins and outs of cancer cells to learn more about the disease, but they’re increasingly finding that noncancerous cells near the cancer cells exert a powerful influence over a tumor’s trajectory.
“Not all cells in a tumor are cancer cells — they’re not even always the most dominant cell type,” said Sylvia Plevritis, PhD, chair of Stanford Medicine’s department of biomedical data science. “There are many other cell types that support tumors.”
To better capture the whole picture of cells’ locations and interactions, Plevritis ...
MSU researchers use unique approaches to study plants in future conditions
2025-03-11
As major changes continue for our planet’s climate, scientists are concerned about how plants will grow and adapt.
Researchers in the MSU-DOE Plant Research Laboratory, or PRL, Sharkey lab are studying changes in plant metabolism that occur when plants are grown in high light, high CO2 (HLHC) conditions.
They found that under these conditions, plants photosynthesize more, which can lead to larger plants, and potentially larger crop yields. However, there are tradeoffs; scientists also found that plants lose carbon under these conditions, which they need to make food. This ...
More than marks: How wellbeing shapes academic success
2025-03-11
With Australia’s National Assessment Program (NAPLAN) beginning today, new research from the University of South Australia highlights a critical but often overlooked factor in student success – wellbeing.
In a world first* study of more than 215,000 students, UniSA researchers found that while standardised tests measure academic skills, different dimensions of wellbeing - emotional wellbeing, engagement, and learning readiness - can play a crucial role in performance.
Specifically, the study found that learning readiness - which includes foundational skills such as perseverance, confidence, and engagement ...
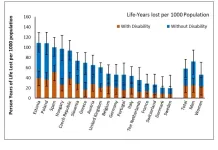
Study quantifies loss of disability-free years of life from COVID-19 pandemic
2025-03-11
Among 289 million adults in 18 European countries, more than 16 million years of life were lost from 2020 through 2022 due to the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a new study published March 11th in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine by Sara Ahmadi-Abhari of Imperial College London, UK, and colleagues.
The direct and indirect impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on both total and disability-free years of life lost are important for policy setting and resource allocation, but they have not been thoroughly investigated.
In the new study, researchers ...
Butterflies choose mates because they are more attractive, not just easier to see
2025-03-11
A simple neural change alters mating preferences in male butterflies, aiding rapid behavioral evolution, Nicholas VanKuren and Nathan Buerkle at the University of Chicago, US, and colleagues, report March 11th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology.
Heliconius are a group of tropical butterflies known for their wide variety of wing patterns and colors, which act as a warning to predators. Because wing coloration is crucial for their survival, males have evolved a preference for females with the same wing color. But the sensory and neurological mechanisms behind these preferences are poorly understood.
Researchers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
Air pollution from wildfires linked to higher rate of stroke
Tiny flows, big insights: microfluidics system boosts super-resolution microscopy
Pennington Biomedical researcher publishes editorial in leading American Heart Association journal
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
[Press-News.org] Yearly 18% rise in ADHD prescriptions in England since COVID-19 pandemicFigures reflect growing public and professional awareness and potential impact of COVID-19. But wide regional variations point to inequalities in access to care, say researchers