(Press-News.org) A lung function test used to help diagnose asthma works better in the morning, becoming less reliable throughout the day, Cambridge researchers have found.
Using real world data from 1,600 patients, available through a database created for speeding up research and innovation, the team also found that its reliability differs significantly in winter compared to autumn.
Asthma is a common lung condition that can cause wheezing and shortness of breath, occasionally severe. Around 6.5% of people over six years old in the UK are affected by the condition. Treatments include the use of inhalers or nebulisers to carry medication into the lungs.
The majority of asthma attacks occur at nighttime or early in the morning. Although this may in part be due to cooler nighttime air and exposure to dust mites and allergens, it also suggests that circadian rhythms – our ‘body clocks’ – likely play a role.
Researchers at the Victor Phillip Dahdaleh Heart and Lung Research Institute, a collaboration between the University of Cambridge and Royal Papworth Hospital NHS Foundation Trust (RPH), wanted to explore whether these circadian rhythms may also have an impact on our ability to diagnose asthma, using routinely performed clinical testing.
Typically, people with suspected asthma will be offered a spirometry test, which involves taking a deep breath in, then breathing out hard and fast for as long as possible into a tube to assess lung function. They will then be administered the drug salbutamol via an inhaler or nebuliser, and shortly afterwards retake the spirometry test.
Salbutamol works by opening up the airways, so a positive test result – that is, a difference in readings between the initial and follow-up spirometry tests – means that the airways must have been narrower or obstructed to begin with, suggesting that the patient could have asthma.
Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust (CUH) has recently set up the Electronic Patient Record Research and Innovation (ERIN) database so that researchers can access patient data in a secure environment to help in their research and speed up improvements in patient care.
Using this resource, the Cambridge team analysed data from 1,600 patients referred to CUH between 2016 and 2023, adjusted for factors such as age, sex, body mass index (BMI), smoking history, and the severity of the initial impairment in lung function.
In findings published today in Thorax, the researchers found that starting at 8.30am, with every hour that passed during the working day, the chances of a positive response to the test – in other words, the patient’s lungs responding to treatment, suggesting that they could have asthma – decreased by 8%.
Dr Ben Knox-Brown, Lead Research Respiratory Physiologist at RPH, said: “Given what we know about how the risk of an asthma attack changes between night and day, we expected to find a difference in how people responded to the lung function test, but even so, we were surprised by the size of the effect.
“This has potentially important implications. Doing the test in the morning would give a more reliable representation of a patient's response to the medication than doing it in the afternoon, which is important when confirming a diagnosis such as asthma.”
The researchers also discovered that individuals were 33% less likely to have a positive result if tested during autumn when compared to those tested during winter.
Dr Akhilesh Jha, a Medical Research Council Clinician Scientist at the University of Cambridge and Honorary Consultant in Respiratory Medicine at CUH, said that there may be a combination of factors behind this difference.
“Our bodies have natural rhythms – our body clocks,” Jha said. “Throughout the day, the levels of different hormones in our bodies go up and down and our immune systems perform differently, for example. Any of these factors might affect how people respond to the lung function test.
“The idea that the time of day, or the season of the year, affects our health and how we respond to treatments is something we’re seeing increasing evidence of. We know, for example, that people respond differently to vaccinations depending on whether they’re administered in the morning or afternoon. The findings of our study further support this idea and may need to be taken into account when interpreting the results of these commonly performed tests.”
Reference
Knox-Brown, B et al. The effect of time of day and seasonal variation on bronchodilator responsiveness: The SPIRO-TIMETRY study. Thorax; 12 March 2025; DOI: 10.1136/thorax-2024-222773
END
Routine asthma test more reliable in the morning and has seasonal effects, say doctors
2025-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Yearly 18% rise in ADHD prescriptions in England since COVID-19 pandemic
2025-03-11
Prescriptions for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in England have risen 18% year on year since the pandemic. This is higher than previously reported, and masks wide regional variations in prescribing rates, finds research published in the open access journal BMJ Mental Health.
The trends likely reflect growing public and professional awareness of the condition, driven in part by social media, as well as the potential impact of COVID-19, suggest the researchers. But the regional variations point to inequalities in access to care, they add.
ADHD is ...
Public health advice on safety of glycerol-containing slush ice drinks likely needs revising
2025-03-11
Public health advice on the safe consumption of glycerol-containing slush ice drinks, also known as slushees, may need revising, conclude researchers after carrying out a detailed review of the medical notes of 21 children who became acutely unwell shortly after drinking one of these products.
Their findings, published in the journal Archives of Disease in Childhood, show that in each case the child became acutely unwell with a cluster of symptoms soon after drinking a slush ice drink, which the researchers refer to as glycerol intoxication ...
Water aerobics for more than 10 weeks can trim waist size and aid weight loss
2025-03-11
Water/aqua aerobics for 10 or more weeks at a time can trim waist size and aid weight loss, finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence, published in the open access journal BMJ Open
This type of exercise is particularly effective in overweight/obese women and the over 45s, the analysis indicates.
Global estimates for 2022 indicate that more than 43% of adults worldwide were overweight, and that 504 million women and 374 million men were obese, note the researchers, adding that obesity contributes to an estimated 2.8 million deaths every year.
The buoyancy of water helps reduce joint injuries commonly associated with land based exercise ...
New study in the Lancet HIV highlights gaps in HPV-related cancer prevention for people living with HIV
2025-03-11
A new study published in The Lancet HIV reveals gaps in knowledge surrounding the prevention of HPV-related cancers in people living with HIV and outlines future research priorities. A literature review, conducted by a team of international experts underscores the need for further research and highlights existing disparities in healthcare for this vulnerable population.
HPV-related cancers are preventable, primarily through vaccination. However, a Professor of Epidemiology at the University of Tartu and one of the study’s authors Anneli Uusküla said that the study found a lack of evidence on the effectiveness of ...
Growth rates of broilers contribute to behavior differences, shed light on welfare impacts
2025-03-11
FAYETTEVILLE, Ark. — As poultry companies weigh cost and efficiency with higher animal welfare standards, research comparing conventional and slow-growing broiler breeds showed that the slow-growing chickens displayed behaviors more closely associated with positive welfare.
Broilers — chickens specifically bred for meat production — are typically raised for six to eight weeks, while slow-growing broilers need up to 12 weeks to reach maturity.
Though gaining popularity in some European ...
Nature-inspired 3D-printing method shoots up faster than bamboo
2025-03-11
Charging forward at top speed, a garden snail slimes up 1 millimeter of pavement per second. By this logic, Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology researchers’ new 3D printing process speeds past existing methods — at a snail’s pace.
Researchers in Beckman’s Autonomous Materials Systems Group created “growth printing,” which mimics tree trunks’ outward expansion to print polymer parts quickly and efficiently without the molds and expensive equipment typically associated with 3D printing. Their work appears in the journal Advanced Materials.
“Humans ...
Scientists create a type of catalog, the ‘colocatome,’ of non-cancerous cells’ influence on cancer
2025-03-11
Even cells experience peer pressure.
Scientists have long studied the ins and outs of cancer cells to learn more about the disease, but they’re increasingly finding that noncancerous cells near the cancer cells exert a powerful influence over a tumor’s trajectory.
“Not all cells in a tumor are cancer cells — they’re not even always the most dominant cell type,” said Sylvia Plevritis, PhD, chair of Stanford Medicine’s department of biomedical data science. “There are many other cell types that support tumors.”
To better capture the whole picture of cells’ locations and interactions, Plevritis ...
MSU researchers use unique approaches to study plants in future conditions
2025-03-11
As major changes continue for our planet’s climate, scientists are concerned about how plants will grow and adapt.
Researchers in the MSU-DOE Plant Research Laboratory, or PRL, Sharkey lab are studying changes in plant metabolism that occur when plants are grown in high light, high CO2 (HLHC) conditions.
They found that under these conditions, plants photosynthesize more, which can lead to larger plants, and potentially larger crop yields. However, there are tradeoffs; scientists also found that plants lose carbon under these conditions, which they need to make food. This ...
More than marks: How wellbeing shapes academic success
2025-03-11
With Australia’s National Assessment Program (NAPLAN) beginning today, new research from the University of South Australia highlights a critical but often overlooked factor in student success – wellbeing.
In a world first* study of more than 215,000 students, UniSA researchers found that while standardised tests measure academic skills, different dimensions of wellbeing - emotional wellbeing, engagement, and learning readiness - can play a crucial role in performance.
Specifically, the study found that learning readiness - which includes foundational skills such as perseverance, confidence, and engagement ...
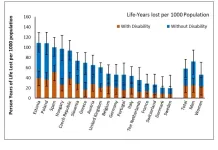
Study quantifies loss of disability-free years of life from COVID-19 pandemic
2025-03-11
Among 289 million adults in 18 European countries, more than 16 million years of life were lost from 2020 through 2022 due to the COVID-19 pandemic, according to a new study published March 11th in the open-access journal PLOS Medicine by Sara Ahmadi-Abhari of Imperial College London, UK, and colleagues.
The direct and indirect impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on both total and disability-free years of life lost are important for policy setting and resource allocation, but they have not been thoroughly investigated.
In the new study, researchers ...