(Press-News.org) A new study revealed significant differences in the appearance and behaviour of the two one-horned Asiatic rhinoceros species, challenging long-standing classifications and supporting a re-evaluation of their status.
The study, led by zoologist Francesco Nardelli and paleontologist Kurt Heißig, highlights how millions of years of evolutionary pressures have shaped the distinct adaptations of the Indian (Rhinoceros unicornis) and Sundaic (Rhinoceros sondaicus) rhinoceroses. The critically endangered Sundaic rhinoceros has a slender skull, a broader and lower back of the head, and a shorter nose and teeth suited for browsing leaves. In contrast, the Indian rhinoceros has a more robust skull and taller teeth adapted for grazing on grasses.
“Adaptations of large terrestrial mammals to various environments are linked to the diversity of food items they can consume, which is reflected in the variation of their dental and cranial morphologies,” the researchers write in their paper, published in the journal ZooKeys. “In rhinoceroses, these adaptations are identified in their teeth structure and head posture.”
The Sundaic rhinoceros, now confined to Java's Ujung Kulon peninsula, is a browsing species with uniquely polygonal-patterned skin and, unlike any other living rhinoceros, hornless females. In contrast, the Indian rhinoceros is a grazer of riverine grasslands in northern India and Nepal. With deep skin folds and a heavier build, the Indian rhinoceros is considerably larger than its Sundaic relative. It is superseded in size only by the elephant and the white rhinoceros, with males weighing more than 2,000 kg and females reaching 1,600 kg.
Fossil evidence confirms that these differences evolved independently over a long period of time. The authors maintain that they represent fundamental anatomical and ecological distinctions and reflect deep evolutionary adaptations.
The behaviour of the two species also differs significantly, with the Sundaic rhinoceros being solitary wanderers and Indian rhinoceros forming temporary crashes.
“Both species possess unique adaptations for survival, emphasising the importance of understanding their systematics for effective conservation,” the researchers write in their paper.
Based on these findings, the scientists propose a more precise scientific name for the Sundaic rhino: Eurhinoceros sondaicus. "Recognizing Eurhinoceros sondaicus as a distinct genus provides a more accurate reflection of its evolutionary history and ecological specialization," they assert. “This refined classification not only enhances our understanding of rhinoceros evolution but also provides a clearer framework for conservation planning, helping to tailor strategies for the protection of these critically endangered animals.”
Original Source:
Nardelli F, Heißig K (2025) A taxonomic review of the genus Rhinoceros with emphasis on the distinction of Eurhinoceros (Perissodactyla, Rhinocerotidae). ZooKeys 1230: 303-333. https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.1230.127858
END
A new name for one of the world's rarest rhinoceroses
2025-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Why do children use loopholes? New research explains the development of intentional misunderstandings in children
2025-03-12
Most people are familiar with loopholes. When your boss, landlord, partner, customer, or government asks you to do something you don’t want to do, and yet you can’t say “no,” you may resort to malicious compliance – doing what someone asked, but not actually what they meant. Most parents are probably familiar with such “little lawyer” behavior too: if a parent says, “Time to put the tablet down,” a child might physically put the tablet down on the table – and then keep playing on it. While such ...
How satisfied are you with your mattress? New research survey aims to find out
2025-03-12
Sleep quality is a crucial aspect of health, yet while adults spend around a third of their lives sleeping, there is surprisingly little research on mattresses. Mass General Brigham researchers developed and tested the Boston Mattress Satisfaction Questionnaire (BMSQ), a new tool to rigorously assess mattress satisfaction and characteristics.
They administered the BMSQ to a representative sample of over 1,000 adults in the United States, finding that the tool is internally consistent and viable for assessing mattress ...
Democracy first? Economic model begs to differ
2025-03-12
Recent studies on economic growth report that preventing the abuse of state power through democratic institutions is critical to a nation’s development. However, there has been little prior research on how societies transition in response to the two conflicting goals of limiting the state’s stranglehold on governance while improving its administrative capacity through citizens’ political participation.
Osaka Metropolitan University Associate Professor Ryosuke Okazawa of the Graduate School of Economics led a team that ...
Opening a new chapter in 3D microprinting with the dream material 'MXene'!
2025-03-12
The Smart 3D Printing Research Team at KERI, led by Dr. Seol Seung-kwon, has developed the world’s first technology for printing high-resolution 3D microstructures using 'MXene,' a material known as the dream material.
MXene, first discovered in the United States in 2011, is a two-dimensional nanomaterial composed of alternating metal and carbon layers. MXene possesses high electrical conductivity and electromagnetic shielding capabilities. Due to its easy combination with various metal chemicals, MXene has gained significant attention ...
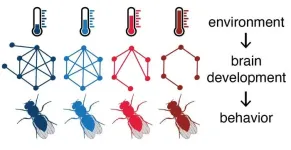
Temperature during development influences connectivity between neurons and behavior in fruit flies
2025-03-12
The rate of development of poikilothermic animals, such as insects, fish, and reptiles, is determined by environmental temperature. A research team at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) has recently demonstrated how temperature can affect brain development in fruit flies. "In the area of the brain we examined, neurons formed more synapses and connected to more synaptic partners at lower temperatures," stated Dr. Carlotta Martelli, head of the team at the Institute of Developmental Biology and Neurobiology of JGU. In their study, the scientists focused on the olfactory circuit of Drosophila melanogaster, because the sense of smell determines important behavioral patterns in ...
Are you just tired or are you menopause tired?
2025-03-12
CLEVELAND, Ohio (March 12, 2025)—Multiple menopause symptoms can make women feel fatigued. Hot flashes, sleep problems, pain, and depression are just a few. A new study suggests that heavy or prolonged menstrual bleeding may increase fatigue, which helps to explain why midlife women are two-to-four times more likely to experience debilitating forms of syndromic fatigue. Results of the study are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
Most women transitioning through ...
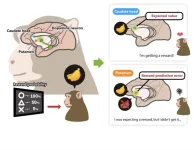
Fluorescent dope
2025-03-12
Kyoto, Japan -- We're all familiar with Pavlovian conditioning, in which a reward-anticipatory behavior follows a reward-predicting stimulus. Perhaps you experience it yourself when passing a café or restaurant and catching a whiff of something delectable.
Behind this mechanism is dopamine released within the striatum, the largest structure of the subcortical basal ganglia, which links motor movements and motivation. Yet it has remained unclear exactly what kind of dopamine signal is transmitted to the striatum to cause this behavior in primates.
In order to understand this dopamine signal, a team of researchers from Kyoto University ...
Meningococcal vaccine found to be safe and effective for infants in sub-Saharan Africa
2025-03-12
University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers helped conduct an important new global health study that found a vaccine that protects against five strains of meningitis prevalent in sub-Saharan Africa is safe and effective for use in young children beginning at 9 months of age. This study provided evidence that formed the basis for the World Health Organization’s (WHO) decision last year to recommend the pentavalent Men5CV meningitis vaccine for infants ages 9 months and older.
Results of the study were published today in the journal Lancet.
In January 2024, the WHO recommended that all countries in the African meningitis belt introduce Men5CV into their routine immunization ...
Integrating stopping smoking support into talking therapies helps more people quit – new study
2025-03-12
Research from the University of Bath, funded by Cancer Research UK, published on No Smoking Day 2025, shows that integrating smoking cessation support into NHS Talking Therapies for depression and anxiety increases quit rates. This is an important step in addressing the high rates of smoking in this population.
Led by Dr Gemma Taylor at the University of Bath, alongside researchers from several other institutions, the study published in Addiction also found that adding smoking support to mental health treatment didn’t disrupt therapy. Instead, it offered a practical way to tackle mental and physical health together.
About the Study
The trial was conducted across four NHS ...
Breast cancer death rates will rise in elderly EU patients but fall for all other ages
2025-03-12
Death rates from breast cancer will fall in 2025 in every age group in the EU and the UK apart from in EU patients aged 80 years and older. In these older patients, overall mortality rates from the disease are predicted to rise by nearly 10% in 2025.
However, in the UK, breast cancer death rates are expected to decrease by 7% in this age group, compared to rates observed between 2015-2019. In Spain, there is also a 4% decrease in patients aged 80 and over.
These findings are from a new study published in the leading cancer journal Annals of Oncology [1] today (Wednesday), ...