(Press-News.org) (Toronto, March 13, 2025) A new study published in JMIR Public Health and Surveillance by a team from Stanford Medicine investigates the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) to revolutionize citizen science and advance health equity. The study, titled “The Promise and Perils of Artificial Intelligence in Advancing Participatory Science and Health Equity in Public Health,” explores how AI technologies can empower communities to actively participate in scientific research and addresses critical ethical considerations.
This research, published by JMIR Publications, examines the potential of AI to significantly enhance citizen science by enabling more inclusive and impactful projects, ultimately aiming to advance health equity and public health outcomes.
Several promising AI applications are discussed in the study, including:
Conversational AI: Large language models can facilitate more accessible and engaging interactions between researchers and citizen scientists, breaking down communication barriers and enabling more inclusive participation.
Generative AI: Tools like text-to-image AI can assist in data visualization, making research findings more understandable and engaging for the public.
Predictive analytics: AI can analyze large datasets to identify trends and predict potential public health risks, empowering communities to proactively address emerging challenges.
The study also acknowledges the potential risks associated with using AI in citizen science, such as bias in AI algorithms, data privacy concerns, and the potential for AI to exacerbate existing inequalities. The researchers emphasize the importance of responsible AI development and implementation, including robust ethical frameworks and ongoing community engagement.
To help explain the research, one of the authors has provided a video discussion of the paper's key points.
###
About JMIR Publications:
JMIR Publications is a leading open access publisher of digital health research and a champion of open science. With a focus on author advocacy and research amplification, JMIR Publications partners with researchers to advance their careers and maximize the impact of their work. As a technology organization with publishing at its core, we provide innovative tools and resources that go beyond traditional publishing, supporting researchers at every step of the dissemination process. Our portfolio features a range of peer-reviewed journals, including the renowned Journal of Medical Internet Research.
To learn more about JMIR Publications, please visit jmirpublications.com or connect with us via Twitter, LinkedIn, YouTube, Facebook, and Instagram.
Head office: 130 Queens Quay East, Unit 1100, Toronto, ON, M5A 0P6 Canada
Media contact: communications@jmir.org
The content of this communication is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work, published by JMIR Publications, is properly cited.
END
Stanford Medicine research explores the promise and perils of AI in citizen science
Study investigates how AI can advance health equity through community-based research
2025-03-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New approaches to tackle coupled urban risks: a people-centric and complex systems perspective
2025-03-13
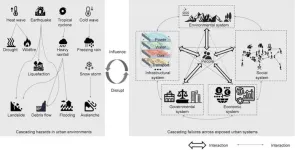
As urbanization surges and climate change intensifies, cities worldwide are facing an increasing number of coupled risks. A recent paper published in Engineering offers fresh insights into understanding and managing these risks.
The complexity of coupled risks in cities, which result from the compounded effects of interacting uncertainties across multiple interdependent objectives, is a major concern. A disruption in one urban subsystem can trigger a chain reaction, affecting other subsystems and leading to unforeseen consequences. For example, the extreme rainfall not only damaged infrastructure ...
OFC conference to showcase energy-efficient optical links that result in faster, low-power photonic chips
2025-03-13
Researchers have demonstrated an integrated optical link on a silicon wafer that exhibits high-speed data transmission with very low power consumption. The advance, which was possible because of new low-energy membrane photonic devices made from indium phosphide, could help improve the power efficiency of integrated photonic circuit boards and chip packages without compromising speed.
Tatsurou Hiraki from NTT Corporation in Japan will present this research at OFC, the premier global event for optical communications and networking, which will take place 30 March – 03 April 2025 at the Moscone Center ...
Ultra-low dose CT aids pneumonia diagnosis in immunocompromised patients
2025-03-13
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Denoised ultra-low dose CT can effectively diagnose pneumonia in immunocompromised patients using only 2% of the radiation dose of standard CT, according to a study published today in Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
“For patients with weakened immune systems, lung infections can be life threatening,” said lead study author Maximiliano Klug, M.D., a radiologist in the division of diagnostic imaging at the Sheba Medical Center in Ramat Gan, Israel. “CT scans are the gold standard for detecting pneumonia, but repeated ...
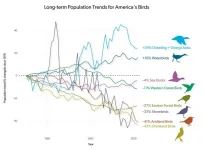
US bird populations continue alarming decline, new report finds
2025-03-13
ITHACA, NY.—The release of the 2025 U.S. State of the Birds report was announced today at the 90th annual North American Wildlife and Natural Resources Conference in Louisville, Kentucky. The report, produced by a coalition of leading science and conservation organizations, reveals continued widespread declines in American bird populations across all mainland and marine habitats, with 229 species requiring urgent conservation action. The report comes five years after the landmark 2019 study that documented the loss of 3 ...
RSV hospitalization risk among older adults linked to age and certain risk conditions
2025-03-13
Among older adults in Spain, hospitalisation rates from respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection increases progressively with age and is more likely among people with other health issues and who live in nursing homes, according to a study published in Eurosurveillance. The hospitalisation rate varied considerably with age and the presence of risk conditions, with important implications for possible targeted interventions.
This population-based cohort study analysed patient data for adults over the age of 60 years in seasons 2016/17 to 2019/20 obtained through electronic medical records ...
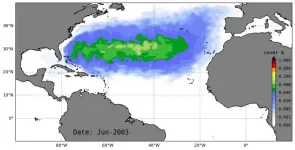
Co-authored USF study identifies ‘surprising’ cause of sargassum blooms in Caribbean
2025-03-13
TAMPA, Fla. (March 13, 2025) – The Great Atlantic Sargassum Belt has puzzled researchers since 2011. A recent study published in Nature Communications may have identified what drove a tipping point that established the phenomenon in the tropical Atlantic Ocean.
Using computer modeling, a team of international researchers demonstrated that sargassum blooms were brought to the tropics by strong ocean currents and wind and thrived in ideal growing conditions.
Specifically, two consecutive years of a strong negative North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO), a shift in atmospheric pressure over the Atlantic that changes circulation and wind patterns, pushed sargassum into the tropics starting ...
Statins, aspirin may impact muscle health in smokers
2025-03-13
Miami (March 13, 2025) – For current and former smokers, statins may reduce the amount of chest muscle loss, while aspirin may contribute to increased chest muscle loss, according to a new study. The study is published in the January 2025 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
Many people who are current or former smokers are prescribed statins to manage high cholesterol and aspirin to manage heart disease. Research has shown that current or former smokers experience increased skeletal muscle loss, especially in people ...
Retiring abroad puts older adults at risk for loneliness, study finds
2025-03-13
Many people dream of retiring to a warmer, less expensive country. But retirees who move abroad may be at greater risk of loneliness than those who stay in their home country, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“International retirement migration is increasingly popular in Europe and around the world. On social media you see all the people in Europe sunbathing in Spain, American retirees are moving to Mexico and Japanese retirees to Malaysia,” said study lead author Esma Betül Savaş, MSc, of the Netherlands Interdisciplinary Demographics Institute. “Although these retirement migrants generally ...
Insilico Medicine secures $110 million Series E financing to advance AI and robotics- driven drug discovery innovation
2025-03-13
Cambridge, MA, Mar 13 — Insilico Medicine(“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, announced today that it has successfully secured a $110 million Series E financing led by a private equity fund of Value Partners Group (HKG:0806), one of Asia’s largest independent asset management firms, with strong participation from industry- and technology-focused new investors, as well as continued support from global existing backers.
The funds raised in this round will be directed to advance Insilico's innovative drug pipeline ...
Researchers at Case Western Reserve University identify RNA molecule as possible driver of gastric cancer
2025-03-13
CLEVELAND—Researchers at Case Western Reserve University have discovered molecules that present the potential to drive the development of gastric cancer—among the world’s deadliest forms of the disease.
Gastric, or stomach cancer, remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths, according to the American Cancer Society, because it’s difficult to diagnose at an early stage and treatments often fail once the disease has spread.
But a team of researchers led by Kishore Guda, associate professor at the Digestive ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
[Press-News.org] Stanford Medicine research explores the promise and perils of AI in citizen scienceStudy investigates how AI can advance health equity through community-based research