(Press-News.org) CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Converting one type of cell to another — for example, a skin cell to a neuron — can be done through a process that requires the skin cell to be induced into a “pluripotent” stem cell, then differentiated into a neuron. Researchers at MIT have now devised a simplified process that bypasses the stem cell stage, converting a skin cell directly into a neuron.
Working with mouse cells, the researchers developed a conversion method that is highly efficient and can produce more than 10 neurons from a single skin cell. If replicated in human cells, this approach could enable the generation of large quantities of motor neurons, which could potentially be used to treat patients with spinal cord injuries or diseases that impair mobility.
“We were able to get to yields where we could ask questions about whether these cells can be viable candidates for the cell replacement therapies, which we hope they could be. That’s where these types of reprogramming technologies can take us,” says Katie Galloway, the W. M. Keck Career Development Professor in Biomedical Engineering and Chemical Engineering.
As a first step toward developing these cells as a therapy, the researchers showed that they could generate motor neurons and engraft them into the brains of mice, where they integrated with host tissue.
Galloway is the senior author of two papers describing the new method, which appear today in Cell Systems. MIT graduate student Nathan Wang is the lead author of both papers.
From skin to neurons
Nearly 20 years ago, scientists in Japan showed that by delivering four transcription factors to skin cells, they could coax them to become induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). Similar to embryonic stem cells, iPSCs can be differentiated into many other cell types. This technique works well, but it takes several weeks, and many of the cells don’t end up fully transitioning to mature cell types.
“Oftentimes, one of the challenges in reprogramming is that cells can get stuck in intermediate states,” Galloway says. “So, we’re using direct conversion, where instead of going through an iPSC intermediate, we’re going directly from a somatic cell to a motor neuron.”
Galloway’s research group and others have demonstrated this type of direct conversion before, but with very low yields — fewer than 1 percent. In Galloway’s previous work, she used a combination of six transcription factors plus two other proteins that stimulate cell proliferation. Each of those eight genes was delivered using a separate viral vector, making it difficult to ensure that each was expressed at the correct level in each cell.
In the first of the new Cell Systems papers, Galloway and her students reported a way to streamline the process so that skin cells can be converted to motor neurons using just three transcription factors, plus the two genes that drive cells into a highly proliferative state.
Using mouse cells, the researchers started with the original six transcription factors and experimented with dropping them out, one at a time, until they reached a combination of three — NGN2, ISL1, and LHX3 — that could successfully complete the conversion to neurons.
Once the number of genes was down to three, the researchers could use a single modified virus to deliver all three of them, allowing them to ensure that each cell expresses each gene at the correct levels.
Using a separate virus, the researchers also delivered genes encoding p53DD and a mutated version of HRAS. These genes drive the skin cells to divide many times before they start converting to neurons, allowing for a much higher yield of neurons, about 1,100 percent.
“If you were to express the transcription factors at really high levels in nonproliferative cells, the reprogramming rates would be really low, but hyperproliferative cells are more receptive. It’s like they’ve been potentiated for conversion, and then they become much more receptive to the levels of the transcription factors,” Galloway says.
The researchers also developed a slightly different combination of transcription factors that allowed them to perform the same direct conversion using human cells, but with a lower efficiency rate — between 10 and 30 percent, the researchers estimate. This process takes about five weeks, which is slightly faster than converting the cells to iPSCs first and then turning them into neurons.
Implanting cells
Once the researchers identified the optimal combination of genes to deliver, they began working on the best ways to deliver them, which was the focus of the second Cell Systems paper.
They tried out three different delivery viruses and found that a retrovirus achieved the most efficient rate of conversion. Reducing the density of cells grown in the dish also helped to improve the overall yield of motor neurons. This optimized process, which takes about two weeks in mouse cells, achieved a yield of more than 1,000 percent.
Working with colleagues at Boston University, the researchers then tested whether these motor neurons could be successfully engrafted into mice. They delivered the cells to a part of the brain known as the striatum, which is involved in motor control and other functions.
After two weeks, the researchers found that many of the neurons had survived and seemed to be forming connections with other brain cells. When grown in a dish, these cells showed measurable electrical activity and calcium signaling, suggesting the ability to communicate with other neurons. The researchers now hope to explore the possibility of implanting these neurons into the spinal cord.
The MIT team also hopes to increase the efficiency of this process for human cell conversion, which could allow for the generation of large quantities of neurons that could be used to treat spinal cord injuries or diseases that affect motor control, such as ALS. Clinical trials using neurons derived from iPSCs to treat ALS are now underway, but expanding the number of cells available for such treatments could make it easier to test and develop them for more widespread use in humans, Galloway says.
###
The research was funded by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences and the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Program.
END
MIT engineers turn skin cells directly into neurons for cell therapy
A new, highly efficient process for performing this conversion could make it easier to develop therapies for spinal cord injuries or diseases like ALS.
2025-03-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
High sugar-sweetened beverage intake and oral cavity cancer in smoking and nonsmoking women
2025-03-13
About The Study: High sugar-sweetened beverage intake was associated with a significantly increased risk of oral cavity cancer in women, regardless of smoking or drinking habits, yet with low baseline risk in this study. Additional studies are needed in larger cohorts, including males, to validate the impact of these findings.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Brittany Barber, MD, MSc, email bbarber1@uw.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamaoto.2024.5252)
Editor’s ...
Area socioeconomic status, vaccination access, and female HPV vaccination
2025-03-13
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study of area deprivation, vaccination access, and human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination status in Osaka City, Japan, higher socioeconomic status and higher medical facility access were associated with higher cumulative HPV vaccination uptake. These findings suggest that further strategies, including a socioecologic approach, are needed to increase HPV vaccination and reduce disparities in uptake.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding ...
Checking PSA levels too soon after prostate cancer surgery can lead to overtreatment
2025-03-13
After surgical removal of the prostate to treat prostate cancer, clinicians monitor Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) levels. Persistently elevated PSA levels indicate residual cancer and are linked to worse outcomes. But in a paper published in JAMA Oncology, Mass General Brigham researchers found that the current standard monitoring time of one-and-a-half to two months following surgery is too short to accurately identify recurrence and inform treatment decisions. Rather, PSA levels should be measured for at least three months to avoid overtreatment.
“Checking ...
CityUHK researchers develop an innovative bio-detection platform for cancer early screening and disease monitoring
2025-03-13
Cancer continues to be a leading cause of mortality worldwide, highlighting the urgent need to develop more advanced, efficient, and early detection methods. Addressing this critical need, City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) is leading a groundbreaking research project aimed at developing an innovative technology platform for early detection of cancer and personalised treatment. The project aims specifically to enhance the detection of circulating tumor cells (CTCs), paving the way for significant advancements in cancer diagnosis and care. This is one of the first batch of projects that has secured funding by the RAISe+ Scheme.
The RAISe+ Scheme (the Research, ...
English translation of harnessing data for improved productivity: managing the full life cycle of data licensed at the London Book Fair
2025-03-13
On March 11, 2025, at the China Collective Stand of the London Book Fair, Tsinghua University Press (TUP) and the University of Toronto Press (UTP) sign a licensing agreement for the English version of Harnessing Data for Improved Productivity: Managing the Full Life Cycle of Data. This collaboration is a big step forward in putting China’s data management innovations on the global map, showcasing the nation’s cutting-edge achievements through leading ...
COVID-19 discovery opens door to new treatments for chronic lung problems
2025-03-13
University of Virginia School of Medicine scientists have discovered how severe COVID-19 can destroy immune cells’ ability to repair the lungs, helping explain the lingering effects of long COVID. The findings suggest a new treatment approach for long COVID as well as other conditions, both short-term and chronic, caused by respiratory infections such as the flu.
Led by UVA’s Jie Sun, PhD, the researchers found that severe viral infections including COVID-19 and the flu can gravely damage a key organelle inside immune cells called macrophages. Macrophages direct lung repair after tissue damage, but their ability to do so is crippled ...
Stanford Medicine research explores the promise and perils of AI in citizen science
2025-03-13
(Toronto, March 13, 2025) A new study published in JMIR Public Health and Surveillance by a team from Stanford Medicine investigates the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) to revolutionize citizen science and advance health equity. The study, titled “The Promise and Perils of Artificial Intelligence in Advancing Participatory Science and Health Equity in Public Health,” explores how AI technologies can empower communities to actively participate in scientific research and addresses critical ethical considerations.
This research, published by JMIR Publications, examines the potential of AI to significantly enhance citizen science by enabling more inclusive ...
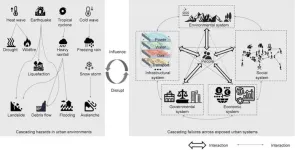
New approaches to tackle coupled urban risks: a people-centric and complex systems perspective
2025-03-13
As urbanization surges and climate change intensifies, cities worldwide are facing an increasing number of coupled risks. A recent paper published in Engineering offers fresh insights into understanding and managing these risks.
The complexity of coupled risks in cities, which result from the compounded effects of interacting uncertainties across multiple interdependent objectives, is a major concern. A disruption in one urban subsystem can trigger a chain reaction, affecting other subsystems and leading to unforeseen consequences. For example, the extreme rainfall not only damaged infrastructure ...
OFC conference to showcase energy-efficient optical links that result in faster, low-power photonic chips
2025-03-13
Researchers have demonstrated an integrated optical link on a silicon wafer that exhibits high-speed data transmission with very low power consumption. The advance, which was possible because of new low-energy membrane photonic devices made from indium phosphide, could help improve the power efficiency of integrated photonic circuit boards and chip packages without compromising speed.
Tatsurou Hiraki from NTT Corporation in Japan will present this research at OFC, the premier global event for optical communications and networking, which will take place 30 March – 03 April 2025 at the Moscone Center ...
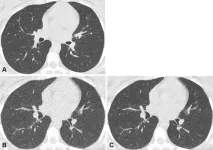
Ultra-low dose CT aids pneumonia diagnosis in immunocompromised patients
2025-03-13
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Denoised ultra-low dose CT can effectively diagnose pneumonia in immunocompromised patients using only 2% of the radiation dose of standard CT, according to a study published today in Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
“For patients with weakened immune systems, lung infections can be life threatening,” said lead study author Maximiliano Klug, M.D., a radiologist in the division of diagnostic imaging at the Sheba Medical Center in Ramat Gan, Israel. “CT scans are the gold standard for detecting pneumonia, but repeated ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] MIT engineers turn skin cells directly into neurons for cell therapyA new, highly efficient process for performing this conversion could make it easier to develop therapies for spinal cord injuries or diseases like ALS.