(Press-News.org)
University of Virginia School of Medicine scientists have discovered how severe COVID-19 can destroy immune cells’ ability to repair the lungs, helping explain the lingering effects of long COVID. The findings suggest a new treatment approach for long COVID as well as other conditions, both short-term and chronic, caused by respiratory infections such as the flu.
Led by UVA’s Jie Sun, PhD, the researchers found that severe viral infections including COVID-19 and the flu can gravely damage a key organelle inside immune cells called macrophages. Macrophages direct lung repair after tissue damage, but their ability to do so is crippled by the loss of the critical organelles, called peroxisomes, Sun and his team found.
Promisingly, the UVA scientists found that they could enhance the damaged organelles’ ability to function – and improve the immune system’s ability to heal lung damage – using a drug that has already been approved by the federal Food and Drug Administration.
“COVID-19 can leave the lungs unable to heal properly by damaging these tiny structures inside our cells. Our discovery is important because it not only explains why some people continue to have breathing problems long after their initial illness but also points us toward a potential treatment to help them recover by targeting a tiny organelle inside critical immune cells,” said Sun, of UVA’s Carter Center for Immunology Research and UVA’s Division of Infectious Diseases and International Health. “A tiny organelle can have big roles! I hope our work could lead to new peroxisome-centric therapies that can help people suffering from long COVID.”
Understanding Long COVID
Peroxisomes are often overlooked and under studied, the researchers note. The organelles are tiny structures known to play vital roles in breaking down toxins and fats within cells. But UVA’s new research suggests that they are also critical to resolving inflammation after severe viral lung infections. As such, they could represent an important avenue for treating acute and chronic conditions that follow those infections.
Sun and his collaborators found that severe COVID infections “drastically” alter peroxisomes inside macrophages, they report in a new scientific paper. This dramatic “remodeling” inhibited peroxisome development and caused them to degrade, robbing them of their ability to function properly. The result was stubborn inflammation and lung scarring. The scientists found persistent peroxisome impairment in both lab mice and human patients after severe COVID-19 infections.
They were able to reverse that impairment in early testing, however, using sodium phenylbutyrate, a drug already approved by the FDA to treat patients with high levels of ammonia in their blood. More research is needed before the drug could be deployed for treating long COVID, but the scientists say their findings warrant additional study.
Further, the discovery of the peroxisomes’ role in controlling inflammation and in repairing alveola (air sacs) in the lungs suggests that targeting them could be useful for treating stubborn post-infection problems caused by influenza and other respiratory viruses, Sun says.
“We are collaborating with scientists and physicians at UVA and other institutions to understand the exact function of this understudied organelle in long COVID and other chronic lung diseases such as interstitial lung disease [ILD],” he said. “Ultimately, we want to develop peroxisome-targeting therapies to give patients the chance to breathe more easily again and get back to their normal lives.”
Findings Published
The researchers have published their findings in the journal Science. The research team consisted of Xiaoqin Wei, Wei Qian, Harish Narasimhan, Ting Chan, Xue Liu, Mohd Arish, Samuel Young, Chaofan Li, In Su Cheon, Jane Qing Yu, Gislane de Almeida Santos, Xiao-Yu Zhao, Eric V. Yeatts, Olivia J. Spear, Megan Yi, Tanyalak Parimon, Yinshan Fang, Young S Hahn, Timothy N.J. Bullock, Lindsay A. Somerville, Mark H. Kaplan, Anne I. Sperling, Yun Michael Shim, Robert Vassallo, Peter Chen, Sarah E. Ewald, Anja C. Roden, Jianwen Que, Dianhua Jiang and Sun.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health, grants AI147394, AG069264, AI112844, HL170961, AI176171, AI154598, R01HL132287, R01HL167202, R01HL132177, F31HL170746, T32AI007496, R01HL155759, R01HL159953, R01HL172990, P01-HL108793, HL159675, HL152293, AI163753 and R01DK122737.
UVA has filed a patent application on the concept of targeting peroxisomes for treating acute and chronic conditions after viral injuries.
To keep up with the latest medical research news from UVA, subscribe to the Making of Medicine blog at http://makingofmedicine.virginia.edu.
END
(Toronto, March 13, 2025) A new study published in JMIR Public Health and Surveillance by a team from Stanford Medicine investigates the potential of artificial intelligence (AI) to revolutionize citizen science and advance health equity. The study, titled “The Promise and Perils of Artificial Intelligence in Advancing Participatory Science and Health Equity in Public Health,” explores how AI technologies can empower communities to actively participate in scientific research and addresses critical ethical considerations.
This research, published by JMIR Publications, examines the potential of AI to significantly enhance citizen science by enabling more inclusive ...
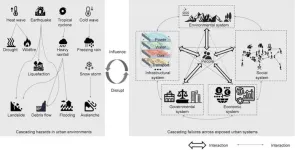
As urbanization surges and climate change intensifies, cities worldwide are facing an increasing number of coupled risks. A recent paper published in Engineering offers fresh insights into understanding and managing these risks.
The complexity of coupled risks in cities, which result from the compounded effects of interacting uncertainties across multiple interdependent objectives, is a major concern. A disruption in one urban subsystem can trigger a chain reaction, affecting other subsystems and leading to unforeseen consequences. For example, the extreme rainfall not only damaged infrastructure ...
Researchers have demonstrated an integrated optical link on a silicon wafer that exhibits high-speed data transmission with very low power consumption. The advance, which was possible because of new low-energy membrane photonic devices made from indium phosphide, could help improve the power efficiency of integrated photonic circuit boards and chip packages without compromising speed.
Tatsurou Hiraki from NTT Corporation in Japan will present this research at OFC, the premier global event for optical communications and networking, which will take place 30 March – 03 April 2025 at the Moscone Center ...
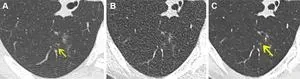
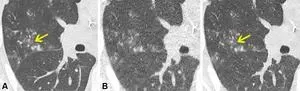
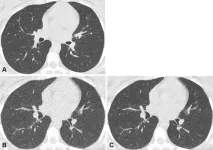
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Denoised ultra-low dose CT can effectively diagnose pneumonia in immunocompromised patients using only 2% of the radiation dose of standard CT, according to a study published today in Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
“For patients with weakened immune systems, lung infections can be life threatening,” said lead study author Maximiliano Klug, M.D., a radiologist in the division of diagnostic imaging at the Sheba Medical Center in Ramat Gan, Israel. “CT scans are the gold standard for detecting pneumonia, but repeated ...
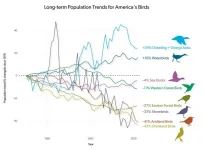
ITHACA, NY.—The release of the 2025 U.S. State of the Birds report was announced today at the 90th annual North American Wildlife and Natural Resources Conference in Louisville, Kentucky. The report, produced by a coalition of leading science and conservation organizations, reveals continued widespread declines in American bird populations across all mainland and marine habitats, with 229 species requiring urgent conservation action. The report comes five years after the landmark 2019 study that documented the loss of 3 ...
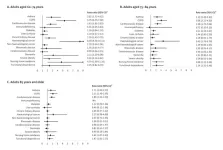
Among older adults in Spain, hospitalisation rates from respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection increases progressively with age and is more likely among people with other health issues and who live in nursing homes, according to a study published in Eurosurveillance. The hospitalisation rate varied considerably with age and the presence of risk conditions, with important implications for possible targeted interventions.
This population-based cohort study analysed patient data for adults over the age of 60 years in seasons 2016/17 to 2019/20 obtained through electronic medical records ...
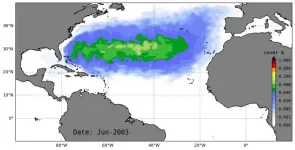
TAMPA, Fla. (March 13, 2025) – The Great Atlantic Sargassum Belt has puzzled researchers since 2011. A recent study published in Nature Communications may have identified what drove a tipping point that established the phenomenon in the tropical Atlantic Ocean.
Using computer modeling, a team of international researchers demonstrated that sargassum blooms were brought to the tropics by strong ocean currents and wind and thrived in ideal growing conditions.
Specifically, two consecutive years of a strong negative North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO), a shift in atmospheric pressure over the Atlantic that changes circulation and wind patterns, pushed sargassum into the tropics starting ...
Miami (March 13, 2025) – For current and former smokers, statins may reduce the amount of chest muscle loss, while aspirin may contribute to increased chest muscle loss, according to a new study. The study is published in the January 2025 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
Many people who are current or former smokers are prescribed statins to manage high cholesterol and aspirin to manage heart disease. Research has shown that current or former smokers experience increased skeletal muscle loss, especially in people ...
Many people dream of retiring to a warmer, less expensive country. But retirees who move abroad may be at greater risk of loneliness than those who stay in their home country, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“International retirement migration is increasingly popular in Europe and around the world. On social media you see all the people in Europe sunbathing in Spain, American retirees are moving to Mexico and Japanese retirees to Malaysia,” said study lead author Esma Betül Savaş, MSc, of the Netherlands Interdisciplinary Demographics Institute. “Although these retirement migrants generally ...
Cambridge, MA, Mar 13 — Insilico Medicine(“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, announced today that it has successfully secured a $110 million Series E financing led by a private equity fund of Value Partners Group (HKG:0806), one of Asia’s largest independent asset management firms, with strong participation from industry- and technology-focused new investors, as well as continued support from global existing backers.
The funds raised in this round will be directed to advance Insilico's innovative drug pipeline ...