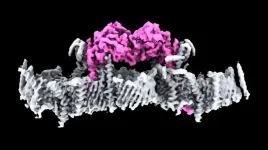
(Press-News.org) The early mammals that lived alongside the dinosaurs upwards of 150 million years ago (mya) were likely covered in dark and dusky greyish-brown fur, according to a quantitative reconstruction of Mesozoic mammal coloration, hinting at their shrouded and nocturnal nature. The findings, drawn from a comparative analysis of fossilized melanosomes, provide insights into the ecology and evolutionary history of early mammals. From communication to camouflage, animal coloration plays an important role in numerous behavioral ecological functions. While some animals, like birds, exhibit a striking and vivid array of plumage, mammal furs are generally limited to muted tones due to their reliance on the single pigment melanin. Although lacking in palette, mammals have evolved diverse and distinctive coat patterns. However, due to the scarcity of data on the pigmentation of extinct mammals, the evolutionary history of pelage coloration remains poorly understood. Recent studies have shown that melanosomes – the organelles responsible for pigmentation – can be preserved in fossilized specimens. Similar techniques have successfully reconstructed dinosaur coloration but have not been widely applied to fossil mammals, despite well-preserved fur specimens. Using scanning electron microscopy and precise spectrophotometric data, Ruoshuang Li and colleagues analyzed melanosomes from 116 living mammals to create a predictive model for reconstructing pelage color based on melanosome morphology. Li et al. then applied the model to fossilized melanosomes of 6 Mesozoic mammaliaforms – including a newly described euharamiyidan species from the Late Jurassic (~158.5 mya). The authors discovered that these early mammals’ fur was predominantly and uniformly darkly colored, without any patterns like the stripes and spots that adorn many modern mammals. This suggests that, despite evolutionary divergence in their phylogeny and ecology, early mammals’ melanin color system remained largely unchanged. This stands in stark contrast to the varied melanosome structures found in feathered dinosaurs, early birds, and pterosaurs, indicating a distinct evolutionary pattern for mammalian coloration. According to the authors, the dark, uniformly dull fur found in these species – typical of modern nocturnal mammals like moles, mice, rats, and nocturnal bats – supports previous hypotheses that early mammals were also largely nocturnal and colored for camouflage. Additionally, the high melanin content in their fur could have been beneficial for thermoregulation and providing mechanical strength for protection. Following the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event, mammals rapidly diversified into niches previously occupied by dinosaurs, leading to more diverse melanosome structures and new pelage color strategies better suited to a wider variety of environments.
END
Mesozoic mammals had uniform dark fur
Summary author: Walter Beckwith
2025-03-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Wartime destruction of Kakhovka Dam in Ukraine has long-term environmental consequences
2025-03-13
The deliberate destruction of the Kakhovka Dam in Ukraine during the Russo-Ukrainian war unleashed a hidden environmental crisis, destroying ecosystems and releasing polluted sediments into downstream water systems, according to a new study. The findings provide critical new insights into the prolonged ecological risks of strategic dam destruction during warfare and the effects that may persist for years beyond war. “Our work highlights the far-reaching environmental consequences of the [Kakhovka Dam] destruction and raises concerns not only about the use of water as a weapon, but also about ...
NIH’s flat 15% funding policy is misguided and damaging
2025-03-13
The U.S. National Institutes of Health’s recent decision to impose a 15% cap on facilities and administrative (F&A) cost reimbursements threatens to undermine the quality and sustainability of university research by slashing indirect funding by $4 billion. In a Policy Forum, Jeongwon Choi and colleagues argue that this policy is fundamentally flawed, as it disregards the essential role of indirect costs, such as infrastructure, utilities, and administrative support, in enabling scientific research. The current system, governed by rigorous federal oversight and audits, ensures that F&A reimbursements are fair and necessary, varying across institutions based on actual costs. NIH’s ...
AI reveals new insights into the flow of Antarctic ice
2025-03-13
As the planet warms, Antarctica’s ice sheet is melting and contributing to sea-level rise around the globe. Antarctica holds enough frozen water to raise global sea levels by 190 feet, so precisely predicting how it will move and melt now and in the future is vital for protecting coastal areas. But most climate models struggle to accurately simulate the movement of Antarctic ice due to sparse data and the complexity of interactions between the ocean, atmosphere, and frozen surface.
In a paper published March 13 in Science, researchers at Stanford University used machine learning to analyze high-resolution ...
Scientists solve decades-long Parkinson’s mystery
2025-03-13
WEHI researchers have made a huge leap forward in the fight against Parkinson’s disease, solving a decades-long mystery that paves the way for development of new drugs to treat the condition.
First discovered over 20 years ago, PINK1 is a protein directly linked to Parkinson’s disease – the fastest growing neurodegenerative condition in the world. Until now, no one had seen what human PINK1 looks like, how PINK1 attaches to the surface of damaged mitochondria, or how it is switched on.
In ...
Spinning, twisted light could power next-generation electronics
2025-03-13
Researchers have advanced a decades-old challenge in the field of organic semiconductors, opening new possibilities for the future of electronics.
The researchers, led by the University of Cambridge and the Eindhoven University of Technology, have created an organic semiconductor that forces electrons to move in a spiral pattern, which could improve the efficiency of OLED displays in television and smartphone screens, or power next-generation computing technologies such as spintronics and quantum computing.
The semiconductor they developed emits circularly polarised ...
A planetary boundary for geological resources: Limits of regional water availability
2025-03-13
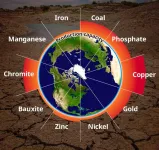
Geological resources such as critical metals and minerals, essential for the diffusion of technologies such as renewable energy and energy storage towards a decarbonized society, are indispensable for supporting modern life in the form of various products and services. Their demand is expected to increase in the coming years owing to global population as well as economic growth. Thus far, scientists and policymakers have primarily discussed geological resource availability from the viewpoint of reserves and resources in the ecosphere and technosphere. However, resources such as ...
Astronomy’s dirty window to space
2025-03-13
When we observe distant celestial objects, there is a possible catch: Is that star I am observing really as reddish as it appears? Or does the star merely look reddish, since its light has had to travel through a cloud of cosmic dust to reach our telescope? For accurate observations, astronomers need to know the amount of dust between them and their distant targets. Not only does dust make objects appear reddish (“reddening”), it also makes them appear fainter than they really are (“extinction”). It’s like we are looking out into space through a dirty ...
New study reveals young, active patients who have total knee replacements are unlikely to need revision surgery in their lifetime
2025-03-13
A 40-year study by Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) researchers has found that active young adults who underwent total knee replacement were unlikely to require knee replacement revision in their lifetime, according to a new study shared today in a podium presentation at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2025 Annual Meeting.1
“As an increasing number of younger adults in their 40s and 50s consider total knee replacement, many wonder how long knee implants last before requiring a revision procedure,” ...
Thinking outside the box: Uncovering a novel approach to brainwave monitoring
2025-03-13
ROCHESTER, Minnesota — Mayo Clinic researchers have found a new way to more precisely detect and monitor brain cell activity during deep brain stimulation, a common treatment for movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease and tremor. This precision may help doctors adjust electrode placement and stimulation in real time, providing better, more personalized care for patients receiving the surgical procedure. The study is published in the Journal of Neurophysiology.
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) involves implanting electrodes in the brain that emit electrical pulses to alleviate symptoms. The electrodes remain inside the brain connected to a battery implanted near ...
Combination immunotherapy before surgery may increase survival in people with head and neck cancer
2025-03-13
CHAPEL HILL, North Carolina—Researchers conducting a clinical trial of immunotherapy drugs for people with head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCCs) found that patients responded better to a combination of two immunotherapies than patients who received just one immunotherapy drug.
The scientists also analyzed immune cells in each person’s tumor after one month of immunotherapy to see which type of immune cells were activated to fight their cancer, suggesting that some of the cells and targets they identified could help individualize treatment benefit.
The findings appeared March 13, 2025 in Cancer Cell.
HNSCCs occur in the oral cavity, pharynx, hypopharynx, larynx, nasal ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
[Press-News.org] Mesozoic mammals had uniform dark furSummary author: Walter Beckwith