(Press-News.org) The Nano Materials Research Division at the Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS), led by Dr. Tae-Hoon Kim and Dr. Jung-Goo Lee, has successfully developed a groundbreaking grain boundary diffusion process that enables the fabrication of high-performance permanent magnets without the use of expensive heavy rare earth elements. This pioneering technology, marks the world’s first achievement in this field.
Permanent magnets are key components in various high-value-added products, including electric vehicle (EV) motors and robots. However, conventional permanent magnet manufacturing processes have been heavily dependent on heavy rare earth elements, which are exclusively produced by China, leading to high resource dependency and production costs. To overcome these limitations, the research team successfully developed a high-end, high-performance permanent magnet without the use of expensive heavy rare earth elements. The core of this breakthrough technology lies in its two-step grain boundary diffusion process.
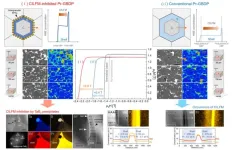
The grain boundary diffusion process is a key technology designed to enhance the performance of permanent magnets. In this process, the heavy rare-earth materials is coated to the surface of the magnet, followed by high-temperature heat treatment. During the heat-treatment, the heavy rare-earths diffuse into the magnet’s interior along the grain boundaries, improving the coercivity—the ability of the magnet to retain its magnetization.
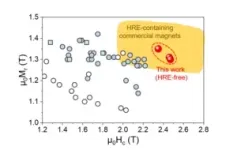
The two-step grain boundary diffusion process developed by the research team involves first thermally infiltrating a new high-melting-point metal-containing material into the magnet at high temperatures, followed by room-temperature cooling. In the second step, a low-cost light rare earth (Praseodymium, Pr)-containing material is re-infiltrated into the magnets at high-temperature. A key innovation of this technology is its ability to suppress abnormal grain coarsening, an unique phenomenon occurred during the grain boundary diffusion process. Such undesirable grain growth degrades the diffusion efficiency and magnetic performance. The research team successfully controlled this issue, which had been a major limiting factor in conventional GBDP, thereby enhancing diffusion efficiency. As a result, the diffusion material is rapidly infiltrated into the magnet, significantly improving coercivity. This advancement enables the magnet to achieve performance grades of 45SH to 40UH, equivalent to commercial magnets that contain heavy rare earth elements (HREs), despite using only light rare earth elements.
If this technology is commercialized, it is expected to reduce manufacturing costs while enhancing performance in high-value industries that require high-efficiency motors, such as electric vehicles (EVs), drones, and flying cars.
Dr. Tae-Hoon Kim, the principal investigator of the study, stated,“Currently, the use of expensive heavy rare earth elements in magnets for electric vehicle motors and high-end home appliances is inevitable. However, due to the concentration of heavy rare earth resources in specific regions and their high costs, researchers worldwide have been striving for years to develop technologies that can reduce or replace heavy rare earths in magnets—yet progress has remained stagnant.”He further explained, “By introducing a novel concept, this technology demonstrates the potential to break free from heavy rare earth dependency in high-performance magnet manufacturing. Moreover, it presents a new direction for research on grain boundary diffusion processes, a core technique in the permanent magnet industry.”Additionally, he emphasized, “If commercialized, this technology will mark the first instance of South Korea securing a dominant position in the most critical aspect of permanent magnet technology.”
This research was conducted with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) under the Nano and Materials Technology Development Program. The findings were published online on December 24 in the internationally renowned journal Acta Materialia (First Author: Seolmi Lee, Student Researcher).
###
About Korea Institute of Materials Science(KIMS)
KIMS is a non-profit government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT of the Republic of Korea. As the only institute specializing in comprehensive materials technologies in Korea, KIMS has contributed to Korean industry by carrying out a wide range of activities related to materials science including R&D, inspection, testing&evaluation, and technology support.
END
Breaking free from dependence on rare resources! A domestic high-performance permanent magnet emerges!
KIMS successfully developed a high-performance permanent magnet without expensive heavy rare earth elements
2025-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Symptoms of long-COVID can last up to two years after infection with COVID-19
2025-03-14
23% of people infected with SARS-CoV-2 between 2021 and 2023 developed long-COVID, and in more than half of them the symptoms persisted for two years. These are the main conclusions of a study conducted by ISGlobal, a centre supported by the ”la Caixa” Foundation, and in collaboration with the Germans Trias i Pujol Research Institute (IGTP), as part of the European END-VOC project. The risk of developing long-COVID depends on several factors, according to the results published in BMC Medicine.
After overcoming an initial ...
Violence is forcing women in Northern Ireland into homelessness, finds new report
2025-03-14
Violence is trapping women across Northern Ireland in cycles of trauma and homelessness, with some facing further abuse in temporary accommodation, despite moving there to find a place of safety.
The research from Heriot-Watt University and University of Edinburgh was commissioned by the Community Foundation for Northern Ireland and funded by the Oak Foundation. It is based on in-depth interviews with women with lived experience of violence over five areas of Northern Ireland.
The areas include Belfast and Derry, one smaller urban area in County Down, and two more rural areas of County Antrim and County Fermanagh. The report also covers findings from focus groups with frontline workers ...
Latin American intensivists denounce economic and cultural inequities in the global scientific publishing system
2025-03-13
Researchers from Brazilian, Argentine, and Uruguayan institutions analyze the barriers that low- and middle-income countries face in disseminating research on intensive care medicine, particularly in the treatment of critically ill patients. Published this month in The Lancet, the study highlights how historical and economic biases perpetuate inequalities and suggests changes to make the scientific publishing system more inclusive and representative of the global community.
Low- and middle-income countries are home to 85% of the world's population and bear a disproportionate burden of critical illnesses. ...
Older adults might be more resistant to bird flu infections than children, Penn research finds
2025-03-13
PHILADELPHIA— Prior exposures to specific types of seasonal influenza viruses promote cross-reactive immunity against the H5N1 avian influenza virus, according to new research from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Older adults who were exposed to seasonal flu viruses that circulated prior to 1968 were found to be more likely to have antibodies that bind to the H5N1 avian flu virus. The findings, published today in Nature Medicine¸ suggest that younger adults and children would benefit more from H5N1 vaccines, even those not tailored specifically to the current strain circulating in birds and ...
Dramatic increase in research funding needed to counter productivity slowdown in farming
2025-03-13
ITHACA, N.Y. – Climate change and flagging investment in research and development has U.S. agriculture facing its first productivity slowdown in decades. A new study estimates the public sector investment needed to reverse course.
In the paper, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers model both the dampening effects of climate change on U.S. agriculture and the accelerating effects of publicly funded research and development (R&D) – and use the estimates to quantify the investment in research required to maintain agricultural productivity through 2050.
They find that a 5% to 8% per year growth in research investment ...
How chemistry and force etch mysterious spiral patterns on solid surfaces
2025-03-13
Key takeaways
Curiosity about a mistake that left tiny dots on a germanium wafer with evaporated metal films led to the discovery of beautiful spiral patterns etched on the surface of the semiconductor by a chemical reaction.
Further experiments showed that the patterns arise from chemical reactions that are coupled to mechanical forces through the deformation of a catalyzing agent.
The new system is the first major advance in experimental methods to study chemical pattern formation since the 1950s. Studying these complex systems will help scientists understand other natural processes, from crack formation in materials to how stress ...
Unraveling the mysteries of polycystic kidney disease
2025-03-13
OKLAHOMA CITY – Polycystic kidney disease (PKD), a family of genetic disorders that causes clusters of cysts to form on the kidney, is among the most common genetic disorders, affecting some 500,000 people in the United States. Roughly one in every 1,000 people will develop some form of cystic kidney disease during their lifetime, and nearly 40,000 Oklahomans have a chronic kidney disease, according to the Oklahoma Health Care Authority.
For many patients, dialysis – a time-consuming and costly procedure – is one of few treatment options. A 2021 study ...
Mother’s high-fat diet can cause liver stress in fetus, study shows
2025-03-13
OKLAHOMA CITY – When mothers eat a diet high in fat and sugars, their unborn babies can develop liver stress that continues into early life. A new study published in the journal Liver International sheds light on changes to the fetus’s bile acid, which affects how liver disease develops and progresses.
Bile acids typically help with digestion and absorb dietary fats in the small intestine, but when they reach excessive levels, they become toxic and can damage the liver. While the mother can detoxify the acids, the fetus lacks that ability. Bile acids may re-circulate to the mother for detoxification, but if they don’t, they build ...
Weighing in on a Mars water debate
2025-03-13
More than 3 billion years ago, Mars intermittently had liquid water on its surface. After the planet lost much of its atmosphere, however, surface water could no longer persist. The fate of Mars’ water—whether it was buried as ice, confined in deep aquifers, incorporated into minerals or dissipated into space—remains an area of ongoing research, one of particular interest to LASP Senior Research Scientist Bruce Jakosky, former principal investigator of the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (MAVEN) mission.
Last week, in a letter to the editor ...
Researchers ‘seq’ and find a way to make pig retinal cells to advance eye treatments
2025-03-13
MADISON — Inside the human eye, the retina is made up of several types of cells, including the light-sensing photoreceptors that initiate the cascade of events that lead to vision. Damage to the photoreceptors, either through degenerative disease or injury, leads to permanent vision impairment or blindness.
David Gamm, director of UW–Madison’s McPherson Eye Research Institute and professor of ophthalmology and visual sciences, says that stem cell replacement therapy using lab-grown photoreceptors ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
[Press-News.org] Breaking free from dependence on rare resources! A domestic high-performance permanent magnet emerges!KIMS successfully developed a high-performance permanent magnet without expensive heavy rare earth elements